Search results (201 results)
-
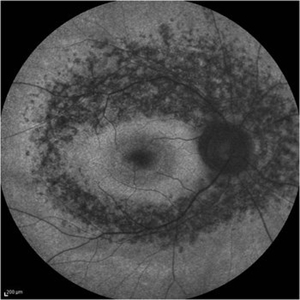 Retinitis Pigmentosa - Fundus Autofluorescence
Retinitis Pigmentosa - Fundus Autofluorescence
Sep 20 2014 by Rameez N Hussain, MD
Fundus autofluorescence of retinitis pigmentosa showing hyperautofluorescent rings or foveal hyperautofluorescence.
Photographer: Dr.Rameez N Hussain, MD, Central Imaging Center, Vitreo Retinal Services, Giridhar Eye Institute, Cochin, India
Imaging device: Heidelberg Blue Peak Autofluorescence imaging.
Condition/keywords: bone spicule, cystoid macular edema (CME), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), retinitis pigmentosa
-
Retinal Angiomatous Proliferation in Age-Related Macular Degeneration with Subretinal Neovascularization
Sep 24 2012 by James B. Soque, CRA, OCT-C, COA, FOPS
75-year-old white male with classic SRN with RAP. Lesion OD is active, and patient is receiving anti-VEGF treatment. Mid phase FA, 50 Deg, Mag 2x.
Photographer: James Soque, CRA, COA, Island Retina, Shirley, NY, USA
Imaging device: Topcon TRC 50 DX, OIS 5.0 MP Color, FA Camera, OIS Software
Condition/keywords: age-related macular degeneration (AMD), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), leakage, retinal angiomatous proliferation (RAP), subretinal neovascularization (SRNV)
-
 Stargardts Disease in FAF
Stargardts Disease in FAF
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a scanning laser ophthalmoscopic FAF image of a patient with Stargardts Disease captured with a Heidelberg Spectralis imaging unit. Note, besides the obvious hyper-autofluorescent areas centrally, the much smaller, and in greater number, pinpoints of hyper-autofluorescence extending from the vascular arcades into the mid-periphery.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke Universtiy Hospital
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), Stargardt disease
-
 Macular Hole, Autofluorescence
Macular Hole, Autofluorescence
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of a macular hole captured using a Heidelberg Spectralis.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Cneter Labs, Duke Universty Hospital
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), macular hole
-
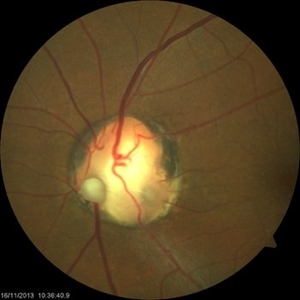 Optic Nerve Coloboma With 2 Pits, Nasal and Temporal Color
Optic Nerve Coloboma With 2 Pits, Nasal and Temporal Color
Nov 21 2013 by Alexandre Durao Alves Pereira, MD
Fundus photograph, color, red free, blue lite and FAF of a optic nerve coloboma with 2 pits, one nasal and other temporal.
Photographer: Alexandre Pereira
Imaging device: Visucam 300
Condition/keywords: color photo, optic nerve coloboma
-
Angioid Streaks & CNV (Fig 1)
Aug 25 2012 by Hamid Ahmadieh, MD
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of a 53-year-old woman with a juxtafoveal CNV secondary to angioid streaks.
Photographer: Hamid Ahmadieh, Ophthalmic Research Center, Labbafinejad Medical Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: angioid streaks, choroidal neovascularization (CNV), fundus autofluorescence (FAF)
-
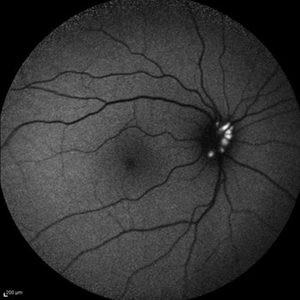 Optic Disc Drusen
Optic Disc Drusen
Jul 10 2013 by Hamid Ahmadieh, MD
Fundus autofluorescence image of the right eye of a 24-year-old woman with optic disc drusen and VA 20/20.
Photographer: Solmaz Shahmohammadi, Negah Eye Center, Tehran
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), optic disc drusen
-
 Hypertensive Choroidopathy - Right Eye
Hypertensive Choroidopathy - Right Eye
Dec 21 2016 by Maciej Czepita
Fundus photograph and SD-OCT scan as well as fundus autofluorescence image (FAF) of the right eye of a 70-year-old woman with hypertensive choroidopathy. In the fundus image numerous Elschnig's spots are visible. Note the Hollenhorst plaque in the superior temporal artery. In the SD-OCT scan (green line on the fundus image) the RPE layer is uneven. Numerous hypo and hyperautofluorescent patches can be seen in the fundus autofluorescence image.
Photographer: Maciej Czepita, M.D., Ph.D., Pomeranian Medical University, Szczecin, Poland
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis HRA+OCT
Condition/keywords: hypertensive choroidopathy
-
Stargardts Disease in Fundus Autofluorescence
Sep 12 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Fundus autofluorescence of a patient with Stargardts disease. Note the central area of hypo-autofluorescence indicating atrophy surrounded by smaller areas of hyper-autofluorescence. Note also the much smaller, and in greater number, pinpoints of hyper-autofluorescence extending from the vascular arcades into the mid-periphery.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), Stargardt disease
-
 Tamoxifen Retinopathy- FAF
Tamoxifen Retinopathy- FAF
Aug 30 2012 by Young Hee Yoon, MD, PhD
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of an 58-year-old woman with a bilateral tamoxifen maculopathy. She had taken tamoxifen for 24 months due to breast cancer. In spite of discontinuation 2 years ago, her macula remained unchanged. Her best-corrected visual acuity was 20/50 in the right and 20/100 in the left.
Photographer: Soo Hyun Cho, Asan Medical Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg HRA II
Condition/keywords: drug toxicity, toxic maculopathy
-
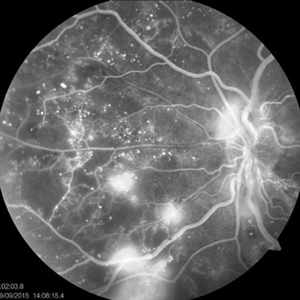 FFA - PDR
FFA - PDR
Mar 30 2018 by Lanin Chen
Fundus fluorescein angiography photo of the left eye of a 62-year-old woman with history of Type 2 diabetes mellitus since 20 years showing proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: Lanin Chen
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
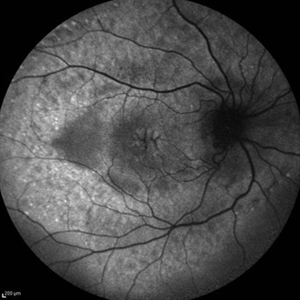 Cystoid Macular Edema (CME)
Cystoid Macular Edema (CME)
Sep 11 2012 by Hamid Ahmadieh, MD
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of the right eye a 17-year-old boy with chronic intermediate uveitis showing CME.
Photographer: Hamid Ahmadieh, MD, Ophthalmic Research Center, Labbafinejad Medical Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: cystoid macular edema (CME), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), intermediate uveitis
-
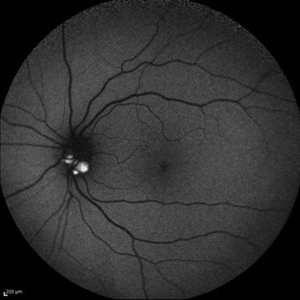 Optic Disc Drusen
Optic Disc Drusen
Jul 10 2013 by Hamid Ahmadieh, MD
Fundus autofluorescence image of the left eye of a 24-year-old woman with optic disc drusen and VA 20/20.
Photographer: Solmaz Shahmohammad, Negah Eye Center, Tehran
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), optic disc drusen
-
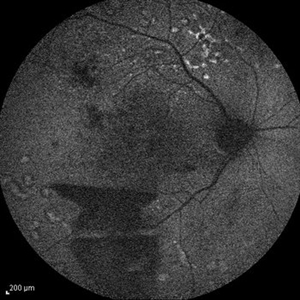 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Sep 15 2012 by Hamid Ahmadieh, MD
Fundus autofluorescence image of a 30-year-old woman with the history of scatter laser photocoagulation and a preretinal hemorrhage due to active PDR .
Photographer: Hamid Ahmadieh, MD, Ophthalmic Research Center, Labbafinejad Medical Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences
Imaging device: Heidelberg HRA
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), preretinal hemorrhage
-
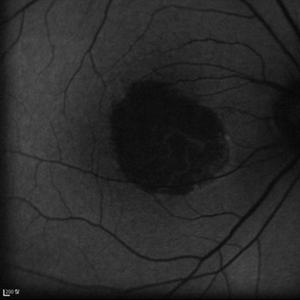 Geographic atrophy
Geographic atrophy
Aug 29 2012 by Young Hee Yoon, MD, PhD
FAF image of an 78-year-old woman. Her best-corrected visual acuity was counting fingers at 30cm.
Photographer: Kyoung Woon Kim, Asan Medical Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg
Condition/keywords: dry age-related macular degeneration (dry AMD), geographic atrophy
-
 RIP 2 FAF
RIP 2 FAF
Oct 7 2015 by Roberto Gallego-Pinazo, MD, PhD, DiSSO
Multicolor and autofluorescence sequence of a retinal pigment epithelium tear following intravitreal anti-VEGF injection.
Photographer: Rosa Dolz-Marco, University and Polytechnic Hospital La Fe, Valencia, Spain
Condition/keywords: age-related macular degeneration (AMD), autofluorescence imaging, choroidal neovascularization (CNV), multicolor, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) tear
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Tamoxifen Retinopathy- FAF
Tamoxifen Retinopathy- FAF
Aug 30 2012 by Young Hee Yoon, MD, PhD
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of an 58-year-old woman with a bilateral tamoxifen maculopathy. She had taken tamoxifen for 24 months due to breast cancer. In spite of discontinuation 2 years ago, her macula remained unchanged. Her best-corrected visual acuity was 20/50 in the right and 20/100 in the left.
Photographer: Kyoung Woon Kim, Asan Medical Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg
Condition/keywords: drug toxicity, toxic maculopathy
-
Central Areolar Choroidal Dystrophy
Jun 27 2013 by Jason S. Calhoun
Patient wanted second opinion for atrophic macular degeneration. VA is 20/400, right eye and 20/100, left eye. Patient has very poor vision and is also hearing impaired. Fundiscopic exam reveals very atrophy in the macula. FAF shows a central hole to the choroid with no neovascularization present.
Photographer: Jason S. Calhoun, Mayo Clinic Jacksonville, Florida
Imaging device: TOPCON TRC 50-EX
Condition/keywords: central areolar choroidal dystrophy (CACD)
-
cRORA
Aug 5 2020 by Dhaivat Shah
A 54-year-old healthy male presented to us with a decreased vision in right eye since past 8 years. The patient gave a history of bleed in right eye before 8 years for which some intravitreal injection was given; post which there no major visual improvement. No details or documentation was available regarding the same. His BCVA in the right eye was 5/60. Fundus examination revealed a sharply demarcated hypopigmented patch over the macula with mild posterior excavation suggestive of macular scar. OCT image shows foveal thinning with loss of Retinal pigment epithelium and outer retinal layers (RORA). There are 2 types of RORAs, complete and incomplete. Complete RORA and incomplete RORA are entities defined by various imaging modalities describing atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelial and the outer retinal layers. OCT imaging defines incomplete RORA (iRORA) as a region of signal hyper transmission into the choroid and a corresponding zone of attenuation ordisruption of the RPE (<250um) and evidence of overlying photoreceptor degeneration (<250um). There should not be any RPE tear associated with it. OCT imaging describes complete RORA (cRORA) based on 4 inclusion criteria. These include, area of hypertransmission of more than 250um, zone of attenuation or disruption of the RPE of more than 250um in diameter, evidence of overlying photoreceptor degeneration and absence of scrolled RPE or other signs of an RPE tear. Other modalities used to define these include fundus autoflourescence(FAF), near infrared reflectance(NIR) and color fundus photograph(CFP). On CFP, it shows a sharply demarcated hypopigmented of >250um size with better visibility of choroidal vessels. FAF shows a hypo autoflourescent patch with sharply demarcated borders of size >250um, the colour of which is similar to that of the optic nerve head or retinal blood vessels excluding any pigmentation or artefact. On NIR, it shows a hyperreflective area with sharply demarcated borders of >250um size excluding any artefact. RORA can be seen in conditions like geographical atrophy in ARMD, central areolar choroidal dystrophy, atrophy secondary to anti-VEGF treatment. References: 1. Sadda SR, Guymer R, Holz FG, et al. Consensus Definition for Atrophy Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration on OCT: Classification of Atrophy Report 3 [published correction appears in Ophthalmology. 2019 Jan;126(1):177]. Ophthalmology. 2018;125(4):537-548. 2. Guymer RH, Rosenfeld PJ, Curcio CA, et al. Incomplete Retinal Pigment Epithelial and Outer Retinal Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Classification of Atrophy Meeting Report 4. Ophthalmology. 2020;127(3):394-409. 3. Eng VA, Rayess N, Nguyen HV, Leng T. Complete RPE and outer retinal atrophy in patients receiving anti-VEGF treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232353.
Photographer: Miss Anjum Zafar Khan
Imaging device: Choithram Netralaya
Condition/keywords: macular scar, outer retina, retinal pigment epithelium
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: Case 1 - Image 2 of 7
Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy: Case 1 - Image 2 of 7
Oct 4 2012 by Gregg T. Kokame, MD, MMM, FASRS
Bluepeak Autofluorescence image of a 57-year-old woman with treatment-naive polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy. Series of images provides an comparative view of the same condition while utilizing a variet of different imaging procedures.
Photographer: Andrew Yuen, Retina Consultants of Hawaii
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: autofluorescence imaging, fundus autofluorescence (FAF), polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV)
-
 Geographic Atrophy
Geographic Atrophy
Mar 27 2013 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a combined FAF/SD-OCT in EDI mode of a patient with geographic atrophy and foveal sparing.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS. Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Eye Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: enhanced depth imaging, foveal sparing, fundus autofluorescence (FAF), geographic atrophy, optical coherence tomography (OCT)
-
Fundus autofluorescence of geographic atrophy
Apr 30 2015 by Mitzy E Torres Soriano, MD
Fundus autofluorescence of geographic atrophy (AMD).
Photographer: Mitzy E. Torres Soriano, MD; Centro medico Cagua-Estado Aragua. Venezuela
Imaging device: TOPCON
Condition/keywords: dry age-related macular degeneration (dry AMD), fundus autofluorescence (FAF), geographic atrophy
-
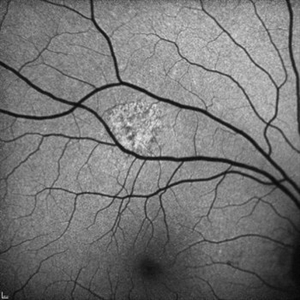 Unilateral Acute Idiopathic Maculopathy - Fundus Autofluorescence
Unilateral Acute Idiopathic Maculopathy - Fundus Autofluorescence
Sep 9 2012 by Robin Ray, MD
FAF of UAIM lesion
Photographer: Kidron Robertson, Georgia Eye Institute of the Southeast, Savannah, GA
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal inflammations, Coxsackie, unilateral acute idiopathic maculopathy
-
Measles Retinopathy
Jun 29 2013 by Jason S. Calhoun
52-year-old female wanted second opinion on retinal eval. Patient had PK and PDT in the left eye. VA was 20/30, right eye was count fingers. Pinhole was NI, both eyes. Patient's mother had measles. Notice pigment changes in both the color and FAF photo.
Photographer: Jason S. Calhoun, Mayo Clinic Jacksonville, Florida
Imaging device: TOPCON TRC 50-EX
Condition/keywords: measles retinopathy
-
Autofluorescence of Choroidal Melanoma
Oct 22 2017 by Daniel Rojas Abatte
Female patient, 53-years-old, diagnosis of choroidal melanoma, already operated in 2009 with brachytherapy.
Photographer: Daniel Rojas
Imaging device: Topcon TRC 50 DX
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF)

 Loading…
Loading…