Search results (38 results)
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left AF
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left AF
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both right and left eyes have symmetrical ring of mottled hypo/hyper AF around the fovea and disc. The HyperAF areas correspond to RPE deposits on OCT as well as areas of blockage on FA, and drusenoid deposits seen on fundus photos 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
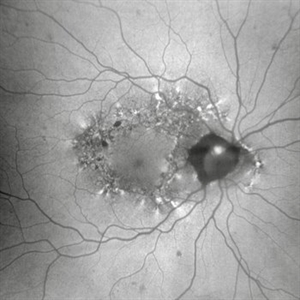 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right AF
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right AF
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both right and left eyes have symmetrical ring of mottled hypo/hyper AF around the fovea and disc. The HyperAF areas correspond to RPE deposits on OCT as well as areas of blockage on FA, and drusenoid deposits seen on fundus photos. Disc drusen in right eye present as HyperAF spot 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left FP
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left FP
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both the right and left Eye have fairly symmetrical, extrafoveal drusenoid-like flecks and focal and faint areas of RPE hyperplasia (in addition to mild NPDR and PPA) 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right FP
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right FP
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both the right and left Eye have fairly symmetrical, extrafoveal drusenoid-like flecks and focal and faint areas of RPE hyperplasia (in addition to mild NPDR and PPA) 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - OCT OD
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - OCT OD
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
OCT shows mild RPE deposit inferiorly (corresponds to area of FA blockage and HyperAF) and a focal area of iRORA with loss of EZ more superiorly (possibly due to regression of RPE deposit). No choroidal thickening (like in pachychoroid pigment epitheliopathy or cscr) 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Zeiss Cirrus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - OCT OS
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - OCT OS
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Magnified section of radial scan through the left eye showing a focal nodular RPE deposit that corresponds to a focal drusenoid deposit in temporal macula, that HypoFLs and HyperAFs. Choroid not significantly thickened or thinned, and the nodular thickening may be just above a large outer choroid vessel?) 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had both diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Zeiss Cirrus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right FA (4 min)
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Right FA (4 min)
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both eyes had similar FA findings. There was no dark choroid or signs of leakage. Granular staining around the fovea and disc were present, and the HypoAF areas corresponded to the drusenoid deposits that showed HyperAF. Mild MAs present due to NPDR 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had boith diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left FA (7 min)
MIDD (Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness) - Left FA (7 min)
Nov 30 2024 by John S. King, MD
Both eyes had similar FA findings. There was no dark choroid or signs of leakage. Granular staining around the fovea and disc were present, and the HypoAF areas corresponded to the drusenoid deposits that showed HyperAF. Mild MAs present due to NPDR 57 yo WF referred for AMD vs Pattern Dystrophy that was diagnosed 10 years ago. Reported some slow progressive vision loss in both eyes for distance and near. Denies nyctalopia or hemeralopia. Background medical history includes HTN, CVD, and DM. No family history of eye problems. Denied pentosan use. Anterior segment showed moderate cataracts (OD>OS). Posterior segment exam showed macular changes and mild NPDR. The macular appearance showed a symmetrical, paramacular ring of fleck-like drusenoid material with some faint focal areas of RPE hyperplasia. Fundus Photos, AF, OCT were performed as well as a gene test. Further questioning showed revealed that her mother and maternal grandmother had boith diabetes mellitus and sensorineural hearing loss. The patient developed diabetes in her teens, and some high frequency hearing loss in her early twenties. She had not had a previous genetic test or diagnosis of MIDD. Gene testing is pending for the mitochondrial component. Invitae's retinal panel, which does not include mitochondrial disorders, only showed a variant of uncertain significance, HMCN1. I discussed this case with Dr. Freund, and it is similar to a the case report : Inoue M, Kiss S, Freund KB. MACULAR PIGMENT RINGS AS THE PRESENTING FINDING OF MITOCHONDRIAL MYOPATHY, ENCEPHALOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS, AND STROKELIKE EPISODES. Retin Cases Brief Rep. 2015 Fall;9(4):260-4. doi: 10.1097/ICB.0000000000000182. PMID: 26200388.
Photographer: Grace Melton and Carley Gunn
Imaging device: Clarus
Condition/keywords: Macular Dystrophy, Maternally Inherited Diabetes and Deafness, MIDD, Mitochondrial Disorder
-
 End Point of Macular Telangiectasia (Mac Tel) Type 2
End Point of Macular Telangiectasia (Mac Tel) Type 2
Oct 31 2024 by JULIAN VILLARREAL, MD
60 year old female with an end-stage proliferative macular telangiectasia type 2 with right-angle retinal vessels, manifested as blunted arterioles and venules that connect the superficial and deeper retinal plexus, chorioretinal anastomosis with a fibrovascular scar and a typical retinal pigment hyperplasia , fellow eye showed a focal discontinuity in the ellipsoid zone with a loss of the outer and a disorganization of the inner retinal layers, not involving the foveal center and a non exudative neovascularization
Photographer: Julián Villarreal MD
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: Mac Tel type 2, macular telangiectasia type 2
-
 Macular Telangiectasia Type 2
Macular Telangiectasia Type 2
Mar 29 2024 by Lucy V Cobbs, M.D.
Fundus autofluorescence photograph of both eyes of a patient with MacTel type 2. Fundus autofluorescence can aid in early diagnosis of disease, showing development of foveal hyperautofluorescence corresponding to deterioration of macular pigment and possible damage to Muller cells. As the disease progresses, RPE hyperplasia may develop and manifests as hypoautofluorescent regions.
Condition/keywords: Mac Tel type 2, retina
-
 Benign Uveal Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Benign Uveal Lymphoid Hyperplasia
Jan 24 2024 by Michell Goyal
Fundus photograph of woman with benign uveal lymphoid hyperplasia. The patient had no symptoms and tested 20/20 vision.
Condition/keywords: benign uveal lymphoid hyperplasia, lymphoid hyperplasia, Uveal Lymphoma
-
 Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
May 24 2023 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Montage fundus photograph of the left eye with end stage Sympathetic Ophthalmia, demonstrating optic nerve pallor, severe arterial attenuation, extensive chorioretinal atrophy (sclera is exposed in most areas), and peripheral RPE hyperplasia. Patient is a 50 yo Asian female with history of multiple vitrectomies due to retinal detachment and loss of vision who developed Sympathetic Ophthalmia in the other eye. This picture is 20 years after the disease process started, with end stage picture and HM vision.
Photographer: Sean Kelso, Saint louis university
Condition/keywords: sympathetic ophthalmia
-
 PEHCR (Peripheral Exudative Hemorrhagic Chorioretinopathy)
PEHCR (Peripheral Exudative Hemorrhagic Chorioretinopathy)
May 12 2023 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Ultrawide fundus photograph of the left eye demonstrating extensive peripheral hemorrhagic exudative detachment in a 79 yo Caucasian female with prior history of non-exudative AMD. Recent diagnosis of Acute myeloid leukemia with low platelet count which might have contributed to the above presentatuon. Please note the temporal subretinal hemorrhage as well as RPE atrophy and hyperplasia in the macula.
Photographer: Rocio Bentivegna, MD, Saint Louis University; Jessica Maddox, COA, Saint Louis University
Condition/keywords: peripheral exudative hemorrhagic chorioretinopathy (PEHCR)
-
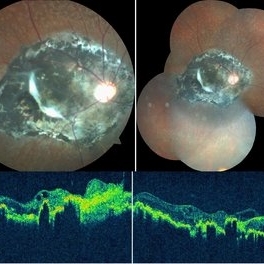 Chorioretinitis Sclopetaria
Chorioretinitis Sclopetaria
May 4 2021 by Priya Rasipuram Chandrasekaran, MBBS, DO, DNB, FRCS
This fundus photo and montage shows pigmentary changes with fibroglial proliferation of the disc and macula in a 36-year-old male following injury with an iron chain. This is usually following a high velocity non-penetrating missile or blast injury categorized as coup injury and can be both direct or indirect. The layers affected are the highly inelastic Bruch’s membrane with choriocapillaris and retinal pigment epithelium in contrast to the highly elastic retina and sclera. The high impact injury causes full thickness defect in the retina, Bruch’s membrane and choroid leading to retraction of the retina and choroid, leaving the intact bare sclera behind. Pathology included defects in the Bruch’s membrane and choroid, and extensive photoreceptor loss with hyperplasia of retinal pigment epithelium. Over the weeks, loose fibrous tissue gets replaced by dense connective tissue leading to scarring between retina and choroid as seen in our patient. The background shows fundus albipunctatus.
Condition/keywords: chorioretinitis sclopetaria
-
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
Feb 2 2021 by Niloofar Piri, MD
43-year-old female with large oval chorioretinal scar in posterior pole with heavy RPE hyperplasia and history of hydrocephalus s/p VP shunt since birth. Findings are consistent with congenital toxoplasmosis.
Condition/keywords: congenital toxoplasmosis
-
 Relentless Placoid Chorioretinitis
Relentless Placoid Chorioretinitis
Jan 22 2021 by Renata Garcia Franco, Md
20-year-old male with reduction of vision in both eyes, scotoma and metamorphopsia. Widespread multiple chorioretinal lesions with RPE hyperplasia, which appear from posterior pole to peripheral retina and inactive choroidal neovascular membrane.
Photographer: Fatima Hernandez, Instituto de la Retina del Bajio SC
Imaging device: Zeiss
Condition/keywords: chorioretinitis
-
 Relentless Placoid Chorioretinitis
Relentless Placoid Chorioretinitis
Jan 22 2021 by Renata Garcia Franco, Md
20-year-old male with reduction of vision in both eyes, scotoma and metamorphopsia. Widespread multiple chorioretinal lesions with RPE hyperplasia, which appear from posterior pole to peripheral retina.
Photographer: Fatima Hernandez, Instituto de la Retina del Bajio SC
Imaging device: Zeiss
Condition/keywords: chorioretinitis
-
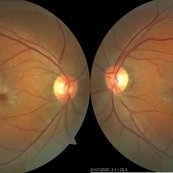 Idiopathic Parafoveal Telengiectasia - Type 2
Idiopathic Parafoveal Telengiectasia - Type 2
Nov 27 2020 by Priya Rasipuram Chandrasekaran, MBBS, DO, DNB, FRCS
This is the fundus photo of a 61-year-old male presenting with bilateral gradual loss of vision since 6 months. Bilateral fundus photo shows parafoveal greying with early crystals and retinal pigment hyperplasia around a dilated venule suggestive of type 2 idiopathic parafoveal telangiectasia.
Condition/keywords: parafoveal telangiectasia
-
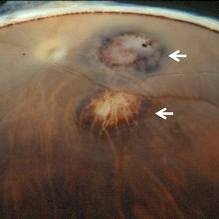 Toxoplasmic Chorioretinitis
Toxoplasmic Chorioretinitis
May 18 2020 by McGill University Health Centre
Toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is caused by parasitic infection from Toxoplasma gondii. Two forms are recognized: congenital and acquired. Congenital toxoplasmic chorioretinitis occurs because the infection is transplacental: T. gondii is among infections that cause TORCH syndrome. Acquired toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is produced by parasite ingestion, usually from raw or undercooked food. After parasitemia, the parasite directly invades the photoreceptors in the retina. In this enucleation specimen, chronic and subacute lesions coexist. In the active lesion located in the macula (arrow), the retina is necrotic, and reactive RPE cell hyperplasia surrounds the lesion. The chronic lesion (arrowhead) demonstrates atrophy of the retina and RPE in the center; in the periphery, RPE proliferation is present.
Condition/keywords: toxoplasmosis chorioretinitis
-
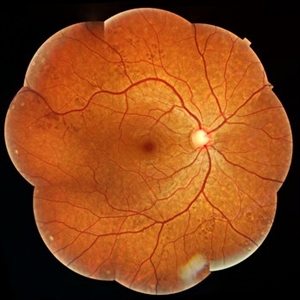 Congenital Hypertrophy of Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Congenital Hypertrophy of Retinal Pigment Epithelium
Sep 7 2019 by Hashim Ali Khan, OD, FAAO
Color fundus montage of a 22-year-old man with congenital hypertrophy of retinal pigment epithelium.
Condition/keywords: bear tracks, congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), RPE hyperplasia
-
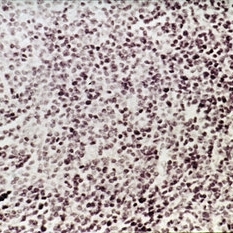 Slide 6-57
Slide 6-57
Mar 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Benign reactive lymphoid hyperplasia, showing monotonous infiltrate of mature lymphocytes with occasional mitotic figure (H&E x252).
Condition/keywords: hyperplasia, lymphocytes
-
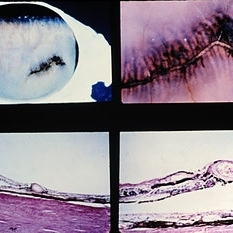 Slide 8-11
Slide 8-11
Mar 4 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Radial perivascular lattice degeneration. The lesion is located at or posterior to the equator and is associated with a major vessel. As with a typical lattice there is discontinuity of the internal limiting membrane, a loss of inner retinal layers, an overlying vitreous degeneration, vitreoretinal adhesion at the margin, sclerosis of vessels, and retinal pigment epithelial hypertrophy, hyperplasia, and migration into the retina. (E.P. No. 31493)
Condition/keywords: hyperplasia, lattice degeneration, lesion, retinal pigment epithelium, vitreoretinal adhesion, vitreoretinal degeneration
-
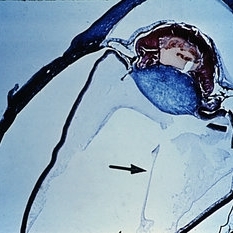 Slide 8-4
Slide 8-4
Mar 4 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Persistence and hyperplasia of the primary vitreous (PHPV). The dense fibrovascular tissue molds the posterior surface of the lens and has drawn the ciliary processes and peripheral retina toward the center of the mass. A section of the hyaloid artery is present in the vitreous cavity (arrow). (A.F.l.P. No. 744398)
Condition/keywords: ciliary, fibrovascular tissue, hyaloid artery, persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous (PHPV)
-
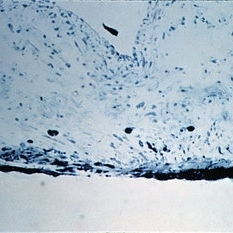 Slide 12-23
Slide 12-23
Feb 27 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Pigmentary glaucoma. Necrosis of the iris pigment epithelium, macrophages filled with pigment in the iris stroma, and atrophy and hyperplasia of the iris dilator muscle are present (H&E x101).
Condition/keywords: glaucoma, hyperplasia, retinal necrosis
-
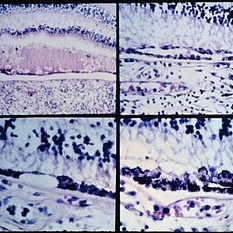 Slide 9-103
Slide 9-103
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Acute leukemia with focal areas of RPE defects (lower left), and areas of double-row (upper right) and nodular (lower right) RPE hyperplasia.
Condition/keywords: acute leukemia, retinal pigment epithelium

 Loading…
Loading…