-
 By McGill University Health Centre
By McGill University Health Centre
The MUHC-McGill University
Co-author(s): Sabrina Bergeron, P. Zoroquiain, E. Esposito, S. Corredor Casas, P. Logan, A. N. Odashiro, Miguel N. Burnier, Paulina García de Alba Graue, McGill University Health Center-McGill University Ocular Pathology & Translational Research Laboratory - Uploaded on May 18, 2020.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on May 19, 2020.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Toxoplasmosis
- Condition/keywords
- toxoplasmosis chorioretinitis
- Description
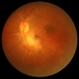
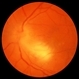
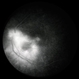
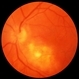
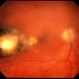
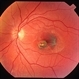
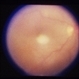
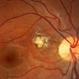
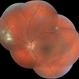
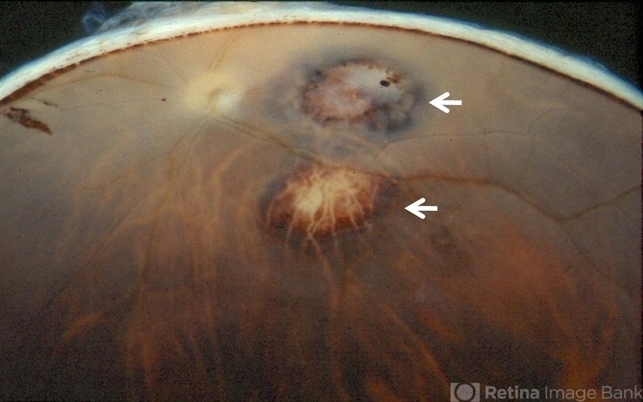
- Toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is caused by parasitic infection from Toxoplasma gondii. Two forms are recognized: congenital and acquired. Congenital toxoplasmic chorioretinitis occurs because the infection is transplacental: T. gondii is among infections that cause TORCH syndrome. Acquired toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is produced by parasite ingestion, usually from raw or undercooked food. After parasitemia, the parasite directly invades the photoreceptors in the retina. In this enucleation specimen, chronic and subacute lesions coexist. In the active lesion located in the macula (arrow), the retina is necrotic, and reactive RPE cell hyperplasia surrounds the lesion. The chronic lesion (arrowhead) demonstrates atrophy of the retina and RPE in the center; in the periphery, RPE proliferation is present.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.