-
 By J. Sebag, MD, FACS, FRCOphth, FARVO
By J. Sebag, MD, FACS, FRCOphth, FARVO
VMR Institute for Vitreous Macula Retina - Uploaded on Sep 1, 2020.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on Sep 1, 2020.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Vitreous
- Condition/keywords
- hyalocytes
- Description
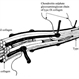
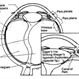
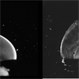
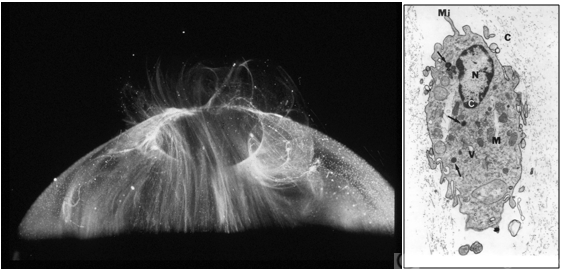
- LEFT: Dark-field slit microscopy was performed on this fresh, unfixed, post-mortem human eye that had undergone dissection to peel off the sclera, choroid, and retina. The posterior pole is imaged in this image with vitreous extruding out the prepapillary hole in the posterior vitreous cortex (small, to right) and the premacular dehiscence (larger, to left). Bright light scattering is seen from punctate structures with the posterior vitreous cortex, corresponding to hyalocytes distributed in a monolayer. RIGHT: Transmission electron microscopy of human hyalocyte in situ demonstrates embedding of the hyalocyte within the dense collagen matrix of the posterior vitreous cortex. Mi = microvilli; black C = collagen of posterior vitreous cortex; N = lobulated nucleus typical of mononuclear phagocytes; white C = dense marginal chromatin in nucleus; M = mitochondria; V = vacuoles; arrows = dense granule (original magnification = 11,670) [From Sebag J: The Vitreous - Structure, Function, and Pathobiology. Springer-Verlag, New York, 1989; right 48, left pg. 50 (images © Springer Nature, reprinted with permission); right image courtesy of J. L. Craft and D. M. Albert, MD, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA]

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.