Search results (24 results)
-
cRORA
Aug 5 2020 by Dhaivat Shah
A 54-year-old healthy male presented to us with a decreased vision in right eye since past 8 years. The patient gave a history of bleed in right eye before 8 years for which some intravitreal injection was given; post which there no major visual improvement. No details or documentation was available regarding the same. His BCVA in the right eye was 5/60. Fundus examination revealed a sharply demarcated hypopigmented patch over the macula with mild posterior excavation suggestive of macular scar. OCT image shows foveal thinning with loss of Retinal pigment epithelium and outer retinal layers (RORA). There are 2 types of RORAs, complete and incomplete. Complete RORA and incomplete RORA are entities defined by various imaging modalities describing atrophy of the retinal pigment epithelial and the outer retinal layers. OCT imaging defines incomplete RORA (iRORA) as a region of signal hyper transmission into the choroid and a corresponding zone of attenuation ordisruption of the RPE (<250um) and evidence of overlying photoreceptor degeneration (<250um). There should not be any RPE tear associated with it. OCT imaging describes complete RORA (cRORA) based on 4 inclusion criteria. These include, area of hypertransmission of more than 250um, zone of attenuation or disruption of the RPE of more than 250um in diameter, evidence of overlying photoreceptor degeneration and absence of scrolled RPE or other signs of an RPE tear. Other modalities used to define these include fundus autoflourescence(FAF), near infrared reflectance(NIR) and color fundus photograph(CFP). On CFP, it shows a sharply demarcated hypopigmented of >250um size with better visibility of choroidal vessels. FAF shows a hypo autoflourescent patch with sharply demarcated borders of size >250um, the colour of which is similar to that of the optic nerve head or retinal blood vessels excluding any pigmentation or artefact. On NIR, it shows a hyperreflective area with sharply demarcated borders of >250um size excluding any artefact. RORA can be seen in conditions like geographical atrophy in ARMD, central areolar choroidal dystrophy, atrophy secondary to anti-VEGF treatment. References: 1. Sadda SR, Guymer R, Holz FG, et al. Consensus Definition for Atrophy Associated with Age-Related Macular Degeneration on OCT: Classification of Atrophy Report 3 [published correction appears in Ophthalmology. 2019 Jan;126(1):177]. Ophthalmology. 2018;125(4):537-548. 2. Guymer RH, Rosenfeld PJ, Curcio CA, et al. Incomplete Retinal Pigment Epithelial and Outer Retinal Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Classification of Atrophy Meeting Report 4. Ophthalmology. 2020;127(3):394-409. 3. Eng VA, Rayess N, Nguyen HV, Leng T. Complete RPE and outer retinal atrophy in patients receiving anti-VEGF treatment for neovascular age-related macular degeneration. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232353.
Photographer: Miss Anjum Zafar Khan
Imaging device: Choithram Netralaya
Condition/keywords: macular scar, outer retina, retinal pigment epithelium
-
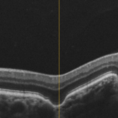 Focal Choroidal Excavation
Focal Choroidal Excavation
Jan 6 2019 by Aristofanes Canamary jr
A 51-year-old female who reported low visual acuity on AO, worse in the OE. Fundoscopy of OE is observed color and brightness alteration in macular region. Focal concave-shaped chorioretinal anomaly in the foveal region and other two anomaly peripapilary and temporal to the fovea with a hyporreflective subretinal space distinguishing from each other.
Photographer: Aristófanes Canamary Jr, UPO ophthalmology, Sao Paulo
Condition/keywords: excavation, optical coherence tomography (OCT), pachychoroid
-
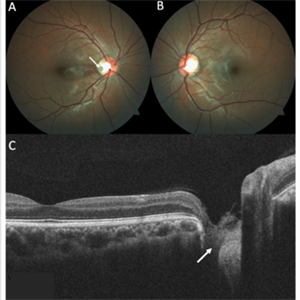 Optic Disc Pit
Optic Disc Pit
Nov 8 2021 by Michael Grinton
Optic disc pits are rare congenital abnormalities of the optic nerve head. Colour fundus image of an asymptomatic 18-year old male shows an optic disc pit in the right eye (A, white arrow); a small, grey, oval shaped excavation in the temporal segment of the optic disc. These pits are usually unilateral (B shows normal colour fundus of left eye) and asymptomatic. Imaging with optical coherence tomography (C) shows the optic disc pit in cross section (white arrow) and normal macular structure. In some patients with the condition, fluid can accumulate underneath the macular (serous macular detachment).
Condition/keywords: Optic disc pit, Optic nerve pit, Optic pit
-
 Focal Choroidal Excavation- An OCT Diagnosis
Focal Choroidal Excavation- An OCT Diagnosis
May 2 2017 by Deepak Bhojwani, MS
Right eye raster OCT image of a 46-year-old high myope (-8Dsph) showing conforming variety of foveal choroidal excacation.
Photographer: Dr Deepak Bhojwani
Condition/keywords: choroidal defect, excavation
-
Optic Disc Coloboma
Jul 24 2019 by Haider Ali
16-year-old boy with horizontal nystagmus and decreased vision in both eyes.
Photographer: Dr Haider Ali Chaudhry, Madinah Teaching Hospital, Faisalabad
Condition/keywords: coloboma, coloboma of optic disc, coloboma of the optic nerve, excavation, Morning Glory Syndrome
-
 Candida Endophthalmitis
Candida Endophthalmitis
Jan 26 2020 by Marlon García Roa, MD
Female, 30-years-old with <<< V Pregnancy Currently with 18 weeks gestation. Pathological personal history 1 month prior hospitalization for complicated acute appendicitis + pyelonephritis + severe thrombocytopenia (autoimmune treated with corticosteroids) with septic shock, appendectomy was performed, due to torpid evolution, intensive care unit with placement of central venous catheter treated with intravenous antibiotics is performed, CT scan is performed of thorax, abdomen and pelvis in search of aggregate pathology; finding multiple renal lithiasis that conditions hydronephrosis and reactivation of pyelonephritis, so he continued with antibiotic therapy and underwent endoscopic lithotomy, due to febrile persistence and with a positive blood culture result for candida Albicans, intravenous antifungals (anidulafungin) were started for 1 week, with improvement satisfactory for what was decided his discharge. During hospitalization it was required to transfuse 2 globular packages and platelet plasmapheresis as well as replacement of calcium, phosphorus and potassium. It refers to approximately 3 weeks of visual loss of the left eye associated with myodisopsia. visual acuity 20/100 Vitritis +, with floating vitreous abscess on the posterior pole, round papilla, slightly erased edges, excavation 0.3, macula without foveolar luster, conserved vein artery relationship, with vessels with multiple mineralization areas and superior peripheral lesion of ¼ diameter of papilla as ball of snow applied to retina.
Photographer: MARLON GARCIA ROA, INSTITUTO DE RETINA DEL BAJIO (INDEREB), QUERETARO, MEXICO
Condition/keywords: candida endophthalmitis
-
 Choroidal Excavation
Choroidal Excavation
Jun 3 2019 by Nelson Chamma Capelanes, MD
SD-OCT of a 32-year-old woman showing a subfoveal choroidal excavation associated with chronic central serous chorioretinopathy.
Photographer: NELSON CHAMMA CAPELANES, PROMACULA, BRAZIL
Imaging device: HEIDELBERG SPECTRALIS
Condition/keywords: central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR), choroidal excavation, pachychoroid
-
Optic Disc Coloboma
Jul 24 2019 by Haider Ali
16-year-old boy with horizontal nystagmus and decreased vision in both eyes.
Photographer: Dr Haider Ali Chaudhry, Madinah Teaching Hospital, Faisalabad
Condition/keywords: coloboma, coloboma of optic disc, coloboma of the optic nerve, excavation, Morning Glory Syndrome
-
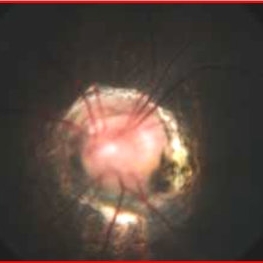 Morning Glory Syndrome
Morning Glory Syndrome
Apr 14 2018 by Dhaivat Shah
7-year-old male patient presented to our OPD when the mother noticed that the child is not able to see clearly through the left eye. BCVA OD 6/6 OS 6/60. OU anterior segment normal. Fundus OD was normal, OS showed an enlarged, funnel-shaped excavation that incorporated the optic disc. The disc itself was enlarged, pink in color and had a surrounding area of peripapillary chorioretinal pigmentary changes which was sparing the fovea. MRI orbit/brain came out to be normal. OS diagnosed to be Morning glory syndrome. The child was prescribed full-time glasses to correct the anisometropia and occlusion/patching of the right(normal) eye 2 hours per day and guarded visual prognosis was explained.
Photographer: Miss Marina Parvin
Condition/keywords: Morning Glory Syndrome
-
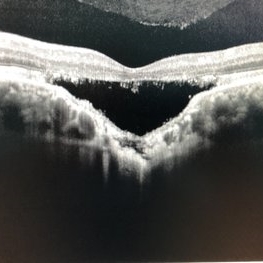 Choroidal Excavation
Choroidal Excavation
Jun 2 2019 by Nelson Chamma Capelanes, MD
SD-OCT of a 32-year-old woman showing a subfoveal choroidal excavation associated with chronic central serous chorioretinopathy.
Photographer: Nelson Chamma Capelanes, Promacula, Brazil
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis SD-OCT
Condition/keywords: choroidal excavation, chronic central serous chorioretinopathy (CSCR), pachychoroid
-
Focal Choroidal Excavation
Sep 14 2017 by Theodore Leng, MD, MS, FASRS
Focal choroidal excavation.
Condition/keywords: excavation
-
Optic Disc Coloboma
Jul 24 2019 by Haider Ali
16-year-old boy with horizontal nystagmus and decreased vision in both eyes.
Photographer: Dr Haider Ali Chaudhry, Madinah Teaching Hospital, Faisalabad
Condition/keywords: coloboma, coloboma of optic disc, coloboma of the optic nerve, excavation, Morning Glory Syndrome
-
 Slide 9-68
Slide 9-68
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Meridional complex with an enclosed ora bay. A peripheral retinal excavation is present posterior to the enclosed ora bay (arrow).
Condition/keywords: excavation, meridional complex, ora bay
-
Optic Disc Coloboma
Jul 24 2019 by Haider Ali
16-year-old boy with horizontal nystagmus and decreased vision in both eyes.
Photographer: Dr Haider Ali Chaudhry, Madinah Teaching Hospital, Faisalabad
Condition/keywords: coloboma, coloboma of optic disc, coloboma of the optic nerve, excavation, Morning Glory Syndrome
-
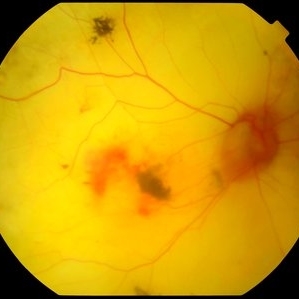 Atrophic Pigment Epithelium
Atrophic Pigment Epithelium
Jul 19 2019 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
Patient 16-years-old, visual acuity with light perception. In retinal evaluation presented total atrophy retinal pigment epithelium and total papilla excavation. Mobilization of pigments and presence of macular hemorrhage.
Photographer: JEFFERSON R SOUSA - Study Center and Ophthalmological Research Dr. Andre M V Gomes, Institute Dr. Suel Abujamra São Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: Topcon TRC-50 DX, Imaginet 4.0, angle de 35 graus. Flash 12w-s
Condition/keywords: atrophic pigment epithelium
-
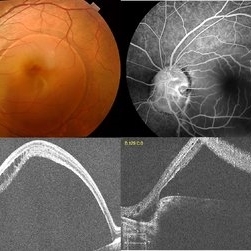 Optic Disc Pit with Coloboma (Hybrid Anomaly)
Optic Disc Pit with Coloboma (Hybrid Anomaly)
Jun 10 2021 by Janani Sreenivasan
Optic disc pit is a rare anomaly of the optic nerve head that can be associated with maculopathy leading to progressive visual deterioration. It belongs to the spectrum of congenital cavitary anomalies of the optic disc which encompasses extrapapillary cavitation, optic disc coloboma, and morning glory. Very rarely, optic disc pits are seen in combination with optic disc colobomas. Histopathologically, disc pit is defined as herniation of dysplastic retinal tissue into an excavation, rich in collagen, which can stretch into the subarachnoid space via a defect in the lamina cribrosa. Interestingly, this structural abnormality leading to a non-physiological communication between the intraocular and extraocular spaces is a common feature among all the congenital cavitary disc anomalies. Optic disc pit maculopathy is characterized by intraretinal and subretinal fluid at the area of macula. The origin of the retinal fluid remains unclear. Possible sources include the vitreous cavity, the subarachnoid space and the orbital space surrounding the dura. It has been estimated that approximately 25% to 75% of patients will develop serous detachment and/or retinoschisis of the central macula at some stage of their life. On fundus examination, ODPs typically appear as single grayish, round or oval depressions at the optic disc. Most commonly, they are detected at the inferotemporal segment of the disc, but may also be observed elsewhere, including the central area.The coexisting macular detachment can be related to lamellar or full-thickness macular holes, cystoid changes, retinal pigment epithelium atrophy and eventually to irreversible loss of vision,especially in longstanding cases. Herewith, we present a 32-years-old male patient presenting with an unusual combination of optic disc pit with maculopathy and optic disc coloboma (hybrid anomaly) in the same eye with corrected visual acuity of 3/60.
Photographer: Dr Janani Sreenivasan
Imaging device: Zeiss Cirrus HD-OCT
Condition/keywords: coloboma of optic disc, hybrid anomaly, macular detachment, optic disc, optic disc pit
-
 Slide 11-34
Slide 11-34
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Glaucoma cup ( x16). Histopathology shows a posterior bowing of the lamina cribrosa, an excavation of disk margins, a loss of nerve fiber layers, and optic atrophy. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 6596.)
Condition/keywords: glaucoma, lamina cribrosa
-
 Morning glory optic disc anomaly with retinal detachment
Morning glory optic disc anomaly with retinal detachment
Sep 13 2022 by Min Kim, MD, PhD, MBA, FASRS
Fundus examination of this 5 year-old male shows large funneled optic nerve with conical excavation of the dysplastic optic disc. 360° macula-involving retinal detachment was observed. The best corrected visual acuity of the right eye was counting fingers 10cm.
Photographer: Min Kim, M.D.-Ph.D.-M.B.A. Gangnam Severance Hospital Yonsei University College of Medicine, Department of Ophthalmology
Imaging device: Optos Silverstone P200TxE
Condition/keywords: Morning Glory Anomaly, Morning Glory Syndrome
-
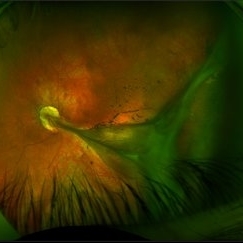 Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy
Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy
Aug 18 2021 by Samuel Dada
Ultra-widefield optos image of a 40-year with Familial Exudative Vitreoretinopathy, affecting his left eye. Patient born at 38 weeks. No NICU time. Has had genetic testing to determine cause of blindness. Physician suspects FEVR and will carry out further testing. Patient uses a 200x or 600x magnifying lens to view and focus on objects at a distance. Patient's vision on initial visit was 20/70.
Photographer: Samuel Dada
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: dysplastic excavation, familial exudative vitreoretinopathy (FEVR), fundus photograph, left eye, Optos, pseudocolor, ultra-wide field imaging
-
 Morning Glory Disc Anomaly
Morning Glory Disc Anomaly
Feb 12 2024 by NIDHI PANWAR, MD FNB FICO
Fundus photograph of 43 year old male, hypertensive on medication, came for routine check up, and has been diagnosed to have poor vision left eye since childhood, denies any history of trauma. Vision left eye 6/18, Anterior segment normal, Fundus left eye shows excavated ,funnel-shaped optic nerve head, with central tuft of glial tissue obscuring the cup . The retinal vessels were seen emanating from the edge of disc in radial manner. In addition, the sectoral nasal retina shows localized area of hyperpigmented bony spicules like lesions. However, no history of nyctalopia or any other neurological disorder could be obtained.
Photographer: Nidhi Panwar, NMC Royal hospital, Sharjah , UAE
Imaging device: OPTOMAP
Condition/keywords: Morning Glory Anomaly, optic disc excavation
-
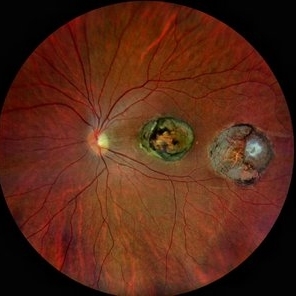 Macular Colobomata
Macular Colobomata
Jun 21 2022 by Sukanya Mondal, MBBS, MS, FICO, MRCSEd
Left eye fundus photograph of a 19-year-old girl, having low vision in the same eye since birth, showing well demarcated macular excavation and underlying scleral baring with hyper and hypopigmentated areas.
Photographer: Dr Sukanya Mondal, National Institute of Ophthalmology, Pune. India
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 500
Condition/keywords: macular coloboma
-
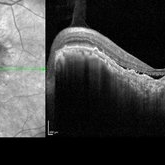 Focal choroidal excavation with Choroidal neovascular membrane
Focal choroidal excavation with Choroidal neovascular membrane
Nov 10 2022 by T. P . VIGNESH, MBBS,MS
SD-OCT of a 65 old woman revealing focal choroidal excavation with Choroidal neovascular membrane .
Photographer: Priyanka
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: Focal choroidal excavation
-
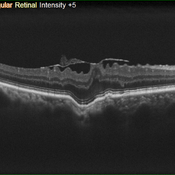 Focal Choroidal Excavation and Epiretinal Membrane
Focal Choroidal Excavation and Epiretinal Membrane
Jun 27 2019 by Andre Beckenkamp
56 y.o. male complaining of blurred vision.
Photographer: Andre Beckenkamp
Imaging device: Nidek RS 3000
Condition/keywords: choroidal excavation, epiretinal membrane (ERM)
-
 Multimodal Imaging in CHRPE
Multimodal Imaging in CHRPE
Mar 6 2025 by Gerardo - Montante Montelongo, MD
Fundus photograph of an 83-year-old male with a history of Diabetes, smoking, cataract surgery on the right eye in 2022, and open-angle glaucoma. Asymptomatic. Indirect ophthalmoscopy revealed 80% excavation, peripapillary atrophy, and a hyperpigmented perifoveal lesion with 35% atrophy, 10% drusen, and 5.1 mm diameter, corresponding to a CHRPE. At multimodal imaging, FFA shows hypoautofluorescence of the lesion, OCT shows preservation of internal retinal layers, atrophy of external retinal layer, with an RPE disruption, and posterior shadowing. USG shows a flat hyperechoic lesion 5.1 mm in diameter and 1.32 mm in thickness, solid and with high internal reflectance.
Photographer: Gerardo Montante-Montelongo, MD, Mexican Institute of Ophthalmology
Imaging device: Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), multimodal imaging

 Loading…
Loading…