Search results (0 results)
-
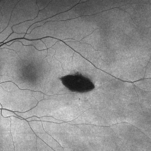 Torpedo Maculopathy
Torpedo Maculopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Optos fundus autofluorescence photograph of a 35-year-old asymptomatic female with no ocular or medical history with stable and chronic appearing torpedo-shaped macula lesion in the left eye.
Photographer: Peter Sotirakos, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Autoflurescence Imaging
Condition/keywords: autofluorescence imaging, genetics, macula, maculopathy, Optos, torpedo maculopathy
-
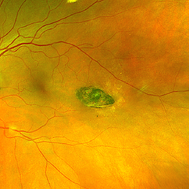 Torpedo Maculopathy
Torpedo Maculopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Optos color fundus photograph of a 35-year-old asymptomatic female with no ocular or medical history with stable and chronic appearing torpedo-shaped macula lesion in the left eye.
Photographer: Peter Sotirakos, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Imaging
Condition/keywords: macula, Optos, torpedo maculopathy
-
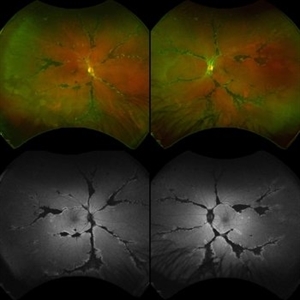 Pigmented Paravenous Retinochoroidal Atrophy (PPRCA)
Pigmented Paravenous Retinochoroidal Atrophy (PPRCA)
Jun 30 2025 by Maria Letícia Costa Holanda
Fundoscopy of a 42-year-old asymptomatic man with pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy. Pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy (PPRCA) is a rare disorder of unknown etiology. The disease is characterized by pigment accumulation along the distribution of retinal veins. The findings are usually incidental with minimal effect on vision.
Photographer: Guilherme da Cruz Reis, CLINOS Eye Hospital - Feira de Santana (BA),Brazil
Condition/keywords: pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy (PPCRA)
-
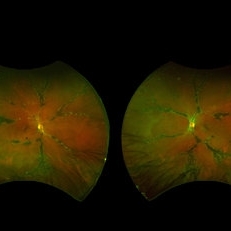 Pigmented Paravenous Chorioretinal Atrophy (PPCRA)
Pigmented Paravenous Chorioretinal Atrophy (PPCRA)
Jun 27 2025 by Maria Letícia Costa Holanda
Fundoscopy of a 42-year-old asymptomatic man with pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy. Pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy (PPRCA) is a rare disorder of unknown etiology. The disease is characterized by pigment accumulation along the distribution of retinal veins. The findings are usually incidental with minimal effect on vision.
Photographer: Guilherme da Cruz Reis, CLINOS Eye Hospital - Feira de Santana (BA),Brazil
Condition/keywords: pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy (PPCRA)
-
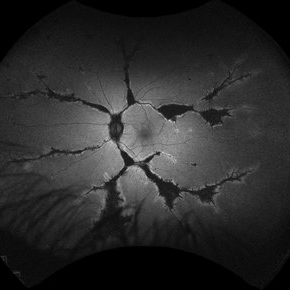 Pigmented Paravenous Retinochoroidal Atrophy (PPRCA)
Pigmented Paravenous Retinochoroidal Atrophy (PPRCA)
Jun 27 2025 by Maria Letícia Costa Holanda
Fundoscopy of a 42-year-old asymptomatic man with pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy. Pigmented paravenous retinochoroidal atrophy (PPRCA) is a rare disorder of unknown etiology. The disease is characterized by pigment accumulation along the distribution of retinal veins. The findings are usually incidental with minimal effect on vision.
Photographer: Guilherme da Cruz Reis, CLINOS Eye Hospital - Feira de Santana (BA),Brazil
Condition/keywords: pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy (PPCRA)
-
 Prepapillary Vascular Loop
Prepapillary Vascular Loop
Jan 20 2021 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Prepapillary congenital vascular loop in an asymptomatic patient.
Photographer: Lisa Breeding, Saint Louis University
Condition/keywords: vascular loop, venous loop
-
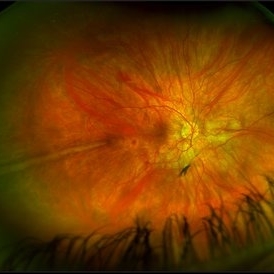 Prominent Long Ciliary Nerve
Prominent Long Ciliary Nerve
Jan 25 2022 by Kachelle Brown
Ultra-wide field photograph of a 48-year-old female with a prominent long ciliary nerve. Patient presented asymptomatic, and was referred for a macula on retinal detachment. Patient was diagnosed with high myopia and a posterior vitreous detachment, and the physician discussed increased risk of floaters, myopic degeneration and retinal detachment associated with high myopia. -24.00 prior to cataract surgery OU per patient.
Photographer: Kachelle Brown
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: fundus photograph, high myopia, long ciliary nerve, optos, right eye, ultra-widefield image
-
 Choroidal Melanoma with Extraocular Extension
Choroidal Melanoma with Extraocular Extension
May 18 2020 by McGill University Health Centre
Choroidal melanoma is often asymptomatic and diagnosis is incidental. The tumors may grow beneath the retina, or may break through the Bruch membrane and disrupt the retina. Tumors breaking through the Bruch membrane and disrupting the retina have a characteristic “mushroom” shape. This enucleation specimen demonstrates a section of a choroidal melanoma showing an intraocular tumor with an extraocular extension (arrow).
Condition/keywords: extraocular extension
-
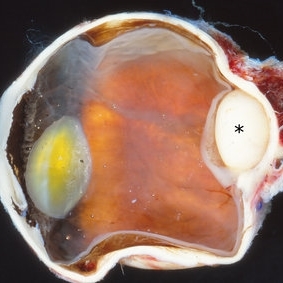 Choroidal Tumor
Choroidal Tumor
May 18 2020 by McGill University Health Centre
Choroidal melanoma is often asymptomatic and diagnosis is incidental. The tumors may grow beneath the retina, or may break through the Bruch membrane and disrupt the retina. Tumors breaking through the Bruch membrane and disrupting the retina have a characteristic “mushroom” shape. The enucleation specimen in (A) shows a whitish, nodular choroidal tumor at the posterior pole (*). Note the retinal detachment overlying the tumor.
Condition/keywords: choroidal tumor
-
DDI Toxicity 2
Mar 5 2015 by Andrew M Hendrick, MD
Fundus photograph of an asymptomatic 54-year-old male with a history of HIV and chronic DDI use.
Photographer: Matt Raeber, Emory University
Condition/keywords: drug toxicity
-
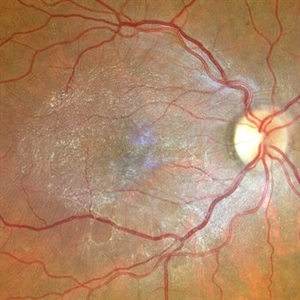 Epiretinal Membrane
Epiretinal Membrane
Sep 6 2021 by Ricardo Leitão Guerra
65-year-old woman with an asymptomatic ERM (BCVA=20/20).
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: epiretinal membrane (ERM)
-
 Fibrotic granuloma vs. Pseudoduplication of the Optic Disc
Fibrotic granuloma vs. Pseudoduplication of the Optic Disc
Nov 29 2023 by Virginia Gebhart
74 year-old female with presumed fibrotic granuloma. Previously diagnosed as pseudoduplication of the optic disc by general ophthalmologist. OCT showed elevation in the RPE, more consistent with granuloma. Pt has been aware for many years, asymptomatic. Will observe.
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart
Imaging device: Topcon 50DX
Condition/keywords: fibrotic scar, granuloma, Pseudoduplication of optic disc
-
 Horse Shoe Tear
Horse Shoe Tear
Sep 16 2017 by Purva Patwari
Asymptomatic horse shoe tear found on preoperative cataract assessment of a 54-year-old male patient. Laser barrage was done and he underwent Phacoemulsification surgery a month later.
Photographer: Dr Purva Patwari,Patwari Retina Center,Ahmedabad,India
Imaging device: Zeiss Visucam 500
-
 Hosreshoe Tears on Posterior Pole
Hosreshoe Tears on Posterior Pole
Mar 22 2025 by Deepak Bhojwani, MS
A fundus image of an asymptomatic 64 year old male with large horseshoe shaped breaks in inferonasal quadrant on posterior pole, an unusual location for retinal breaks.
Photographer: DR DEEPAK BHOJWANI
Condition/keywords: horseshoe tear, posterior pole break, retinal break
-
 Idiopathic Peripapillary CNV
Idiopathic Peripapillary CNV
Jan 4 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
13 year old female with inactive CNV. Increased pigment 360 at 1 year follow up. No inflammation or SRF, pt remains asymptomatic
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: choroidal neovascularization (CNV), peripapillary choroidal neovascularization (PPCNVM)
-
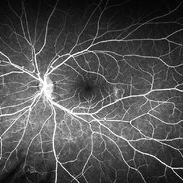 Idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms and neuroretinitis
Idiopathic retinal vasculitis, aneurysms and neuroretinitis
Apr 24 2022 by Aniruddha K Agarwal, MD
Ultra-wide field fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) of the left eye from an asymptomatic, healthy 33-year-old woman who was referred to the retina clinic from a refractive surgery unit due to the presence of vascular anomalies and hard exudates in both eyes. FFA revealed the characteristic sacular aneurysms at the bifurcation of retinal arterioles in the posterior pole, together with microvascular anomalies and capillary closure peripherally.
Photographer: Julio J GONZALEZ-LOPEZ, MD, PhD, FEBO and Teresa GONZALEZ-LOMAS, RN
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: IRVAN Syndrome, IUSG, neuroretinitis, retinal vasculitis, uveitis
-
 Indocyanine Green (ICG) of Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma (CCH)
Indocyanine Green (ICG) of Circumscribed Choroidal Hemangioma (CCH)
Feb 6 2025 by Jack B Margines, MD, MHCI
Peripheral patchy hyperfluorescence is seen on this early image of ICG-A on a 53-year-old asymptomatic with an extramacular circumscribed choroidal hemangioma.
Photographer: W Ryan Miliam, CRA, OCT-C, University of California, Irvine Gavin Herbert Eye Institute
Imaging device: Optos
Condition/keywords: choroidal hemangioma, indocyanine green (ICG) angiography
-
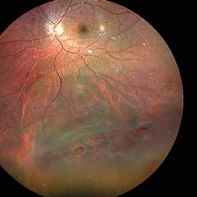 Inferior retinal detachment with lattice and holes
Inferior retinal detachment with lattice and holes
May 31 2023 by Aditya S Kelkar, MS, FRCS, FASRS,FRCOphth
Importance of dilated retina check up before Lasik surgery can't be better demonstrated...patient totally asymptomatic came for Lasik opinion and has inferior retinal detachment with lattice and holes, sparing the macula
Photographer: Dr. Sahil Wagh , National Institute of Opthalmology, Pune , India
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 500
Condition/keywords: inferior retinal detachment
-
Isolated Retinal Capillary Hemangioblastoma
Mar 11 2022 by Bryon R McKay, MD, PhD, FRCSC, DRCPSC - Retina
Optos widefield fundus photograph and IVFA of a 23-year-old female with asymptomatic isolated retinal capillary hemangioblastoma without exudation. IVFA demonstrates some mild late leakage. The tumor measures 1.5mm and was effectively ablated with laser photocoagulation.
Imaging device: Optos
Condition/keywords: retina capillary hemangioblastoma
-
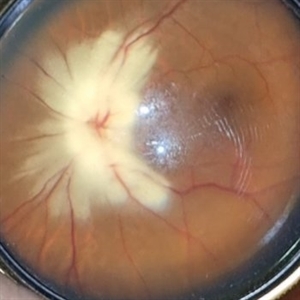 Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Apr 18 2025 by DR Rohit Gupta
The **myelinated nerve fibers of the optic disc** (also known as **medullated nerve fibers**) are retinal nerve fibers that retain their myelin sheath as they pass through the optic nerve head. Normally, retinal nerve fibers are unmyelinated to allow for light transparency, but in some cases, myelination extends anteriorly into the retina, appearing as a striking white, feathery patch on the optic disc or peripapillary retina. ### **Key Features:** 1. **Appearance:** - Dense, white, striated patches with feathery edges. - Typically located at the superior or inferior pole of the optic disc. - May obscure retinal vessels underneath. 2. **Clinical Significance:** - Usually **benign** and asymptomatic. - **Congenital** (present at birth or early childhood). - Rarely associated with **visual field defects** (e.g., scotomas corresponding to the area of myelination). - Occasionally linked with **high myopia** or **amblyopia** if extensive. 3. **Pathophysiology:** - Failure of oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells to stop myelination at the lamina cribrosa. - Normally, myelination stops at the optic nerve head, but in this condition, it extends into the retina. 4. **Diagnosis:** - **Fundoscopy:** Classic white, feathery appearance. - **Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT):** Shows thickened retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). - **Visual Field Testing:** May detect defects if large. 5. **Differential Diagnosis:** - Optic disc edema - Cotton wool spots - Retinoblastoma (rarely, but must be ruled out in children) 6. **Management:** - No treatment required if asymptomatic. - Monitor for amblyopia in children. - Rare cases with significant visual impairment may need further evaluation. ### **Fun Fact:** Myelinated nerve fibers are seen in **~0.5-1%** of the population and are usually an incidental finding.
Photographer: Dr Rohit gupta
Imaging device: Samsung S21
Condition/keywords: Medulated Nerve fibre, Medullated Nerve fibres, myelinated nerve fibers, Myelinated Nerve Fibres, optic disc drusen
-
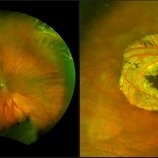 Operculated Hole and CHRPE
Operculated Hole and CHRPE
Jan 16 2018 by Carolyn Daley
58-year-old woman with an operculated hole and CHRPE in the right eye. Patient is asymptomatic so no treatment was recommended at this time.
Photographer: Carolyn Daley
Imaging device: Optos ultra wide field image
Condition/keywords: congenital hypertrophy of the retinal pigment epithelium (CHRPE), operculated retinal hole, Optos, ultra-wide field imaging
-
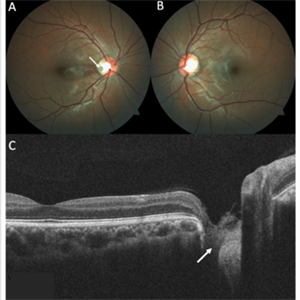 Optic Disc Pit
Optic Disc Pit
Nov 8 2021 by Michael Grinton
Optic disc pits are rare congenital abnormalities of the optic nerve head. Colour fundus image of an asymptomatic 18-year old male shows an optic disc pit in the right eye (A, white arrow); a small, grey, oval shaped excavation in the temporal segment of the optic disc. These pits are usually unilateral (B shows normal colour fundus of left eye) and asymptomatic. Imaging with optical coherence tomography (C) shows the optic disc pit in cross section (white arrow) and normal macular structure. In some patients with the condition, fluid can accumulate underneath the macular (serous macular detachment).
Condition/keywords: Optic disc pit, Optic nerve pit, Optic pit
-
 Optic Nerve Head Drusen
Optic Nerve Head Drusen
Feb 12 2015 by Timothy S Fuller, MD
Fundus autofluorescence image of a 34-year-old woman with striking, asymptomatic optic nerve head drusen.
Photographer: Nice Hesse, Texas Retina Associates
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: drusen of optic disc
-
 Optic Nerve Pit
Optic Nerve Pit
Feb 21 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
65 year old female with optic nerve pit. Asymptomatic, continued observation.
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart
Imaging device: Topcon TRC 50DX
Condition/keywords: congenital optic nerve pit, Optic nerve pit
-
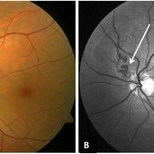 Peri-papillary Vascular Loop
Peri-papillary Vascular Loop
Jun 2 2020 by Dhaivat Shah
Peri-papillary vascular loops (PVL) are rare congenital vascular malformations, which are usually detected as accidental finding during routine fundus examination. They can often be confused with tributary vein occlusion or racemose hemangioma. Although benign and asymptomatic, they can be rarely associated with vitreous hemorrhage and arterial occlusion. We herein present a case of a 60-year-old hypertensive male, who was diagnosed elsewhere to have a tributary vein occlusion and was referred to us. FFA was advised to rule out neovascularization, surrounding capillary non perfusion and mass lesion (hemangioma). On FFA, the arterial loop showed a slightly delayed filling (3-5 seconds) as compared to the other arterial vessels and the original vessel appeared to be a branch arising from central retinal artery. The choroidal filling was delayed in the area supplied by the loop. A cilioretinal artery was also noted. The patient was diagnosed to have a Peri-papillary vascular arterial loop (PVL), likely to be congenital in origin. The patient was reassured and was advised yearly follow up. These loops are usually accidental findings discovered during routine fundus examination. Since these vessels are looped and tortuous, they exhibit a slower and laminar blood flow, which make them more prone for arterial occlusions. The vitreous in this area tends to be adherently attached, so during PVD induction, it is likely to cause a tear and hemorrhage leading to vitreous hemorrhage. Until and unless there is a break, this hemorrhage tends to resolve on its own and does not warrant treatment. If there is an evident break, it can be dealt with laser barrage.
Photographer: Choithram Netralaya
Condition/keywords: congenital prepapillary vascular loop

 Loading…
Loading…