Search results (31 results)
-
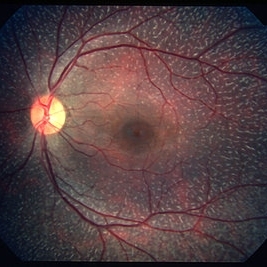 Fundus Albipunctatus
Fundus Albipunctatus
Mar 29 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
Fundus albipunctatus (one of the stationary night blindness syndromes with multiple white dots in the periphery and normal optic disc and vessels).
Condition/keywords: fundus albipunctatus
-
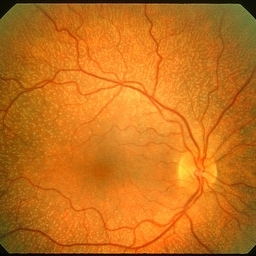 Fundus Albipunctatus
Fundus Albipunctatus
Mar 29 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
Typical fundus albipunctatus a kind of stationary night blindness; notice the normal disc and vessels #1.
Condition/keywords: fundus albipunctatus
-
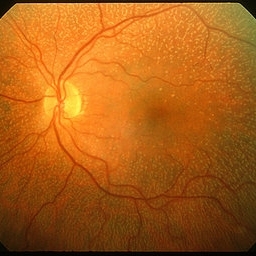 Fundus Albipunctatus
Fundus Albipunctatus
Mar 29 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
Typical fundus albipunctatus a kind of stationary night blindness ; notice the normal disc and vessels #2.
Condition/keywords: fundus albipunctatus
-
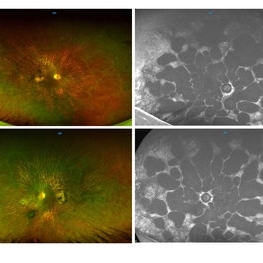 Gyrate Atrophy
Gyrate Atrophy
Oct 31 2018 by Dhaivat Shah
50-year-old male came in with complaint of daytime vision loss for a year and nighttime vision loss for more than 20 years, gradually increasing day by day. Fundus showed paving-stone like areas of atrophy of the RPE involving the macula which coalesces to form a characteristic scalloped border at the junction of normal and abnormal RPE. Gyrate atrophy is an autosomal recessive dystrophy caused by tenfold elevations of plasma ornithine, which is toxic to the RPE and choroid. Patients with gyrate atrophy have hyperpigmented fundi, with lobular loss of the RPE and choroid, normally sparing the fovea. The finding of generalized hyperpigmentation of the remaining RPE helps to clinically distinguish gyrate atrophy from choroideremia. Affected patients usually develop night blindness during the first decade of life and experience progressive loss of visual field and visual acuity later in the disease course. Early diagnosis is crucial because treatment in form of Arginine free diet and oral pyridoxine helps in slowing the progression of disease.
Imaging device: Optos
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), gyrate atrophy
-
 Fundus Albipunctata
Fundus Albipunctata
Dec 27 2016 by Elad Moisseiev, MD
A 53-year-old female patient with high myopia and complaints of stationary night blindness since childhood. Fundus: myopic fundus with yellow dots in the posterior pole. Genetics: Homozygous mutations in RDH5 gene - c.160C>T (p.R54X), confirming the diagnosis of fundus albipunctata.
Photographer: Galit Yair-Pur
Condition/keywords: fundus albipunctatus
-
 Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Apr 16 2022 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
Oguchi's disease showing the Mizo Nakamura phenomenon in wide field Fundus photo
Photographer: Mr Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB)
-
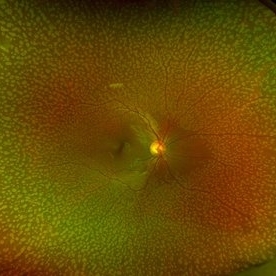 Benign Familial Fleck Retina
Benign Familial Fleck Retina
Feb 2 2023 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
12 year boy first born of consanguineous marriage, came for routine eye check up with BCVA 20/40 OU. He has no night blindness. His OCT showed thickening of the RPE with dome like elevations involving the ellipsoid layer. Dark adapted ERG showed normal 'b' wavesPhotopic ERG showed reduced 'a' and b waves.
Photographer: Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: Benign familial fleck retina
-
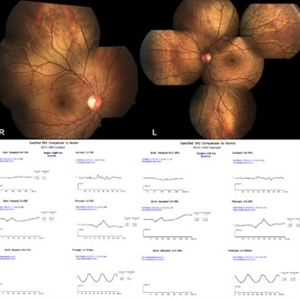 CSNB - Oguchi's Disease
CSNB - Oguchi's Disease
Feb 9 2021 by Dinesh Rungta, MBBS, DNB
• Golden tapetal reflex suggestive of CSNB - Oguchi disease. • MFERG – shows grossly reduced scotopic responses with normal photopic responses in both eyes
Photographer: Dr Shivam Madan , Giridhar Eye Institute, Kerala, India
Imaging device: CARL ZEISS FF450 FUNDUS CAMERA
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB), multifocal ERG (MFERG), Oguchi's disease
-
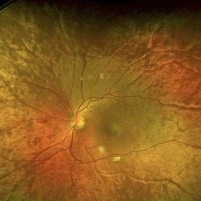 Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Apr 16 2022 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
Oguchi's disease showing the Mizo Nakamura phenomenon in wide field Fundus image
Photographer: Mr Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB)
-
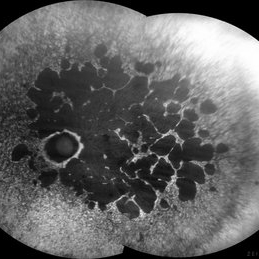 Rod Cone dystrophy
Rod Cone dystrophy
Nov 29 2022 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Fundus autofluorescence of the left eye in a 58 yo male with rod cone dystrophy. He presented with night blindness and peripheral vision loss since youth and recent decrease in central vision for the past 10 years. Notice multiple coin shaped hypoautofluorescent pacthes within central 20 degrees which are coalescing centrally. (fundus photo uploaded separately) He has one pathogenic variants of both CEP290 and PRPH2 genes.
Photographer: Sean Kelso, Saint Louis University
Condition/keywords: hereditary retinal degeneration, hereditary retinal dystrophy, rod cone dystrophy
-
 Fundus Albipunctatus
Fundus Albipunctatus
Apr 27 2021 by Priya Rasipuram Chandrasekaran, MBBS, DO, DNB, FRCS
This is the fundus photo montage of a 23-year-old male demonstrating whitish-yellow spots all over the fundus sparing the fovea at the level of retinal pigment epithelium. This belongs to the group of congenital stationary night blindness with flecks in the retina.
Condition/keywords: fleck retinopathy
-
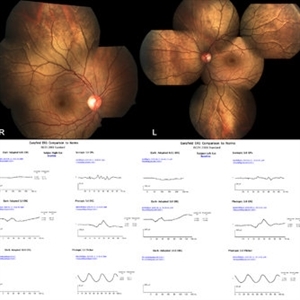 Oguchi's Disease
Oguchi's Disease
Feb 5 2021 by Dinesh Rungta, MBBS, DNB
• Montage image of a 19-year-old male with history of night blindness since childhood showing Bilateral Golden Tapetal Reflex suggestive of CSNB - Oguchi disease. • MFERG – shows grossly reduced scotopic responses with normal photopic responses in both eyes.
Photographer: Dr Shivam Madan, Giridhar Eye Institute, Kerala, India
Imaging device: CARL ZEISS FUNDUS CAMERA
Condition/keywords: multifocal ERG (MFERG), Oguchi's disease
-
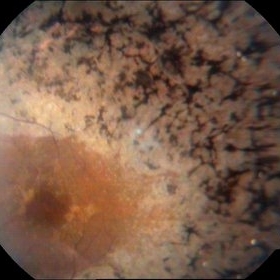 Macular Dystrophy
Macular Dystrophy
Sep 20 2014 by Mehul A Shah
A 28-year-old female presented with complaint of exotropia and night blindness, on examination she was found to have this picture.
Photographer: Drashti Netralaya,Dahod
Imaging device: Zeiss ff450
Condition/keywords: macular dystrophy
-
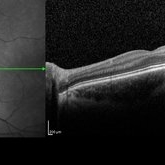 CSNB-OCT-OS
CSNB-OCT-OS
Aug 23 2021 by Jennifer Carstens
OCT/infrared image showing myopic fundus with normal retinal structure in patient with CACNA1F associated X-linked CSNB (OS).
Photographer: Jing Zhang, Ophthalmic Photographer
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB), infrared image, optical coherence tomography (OCT)
-
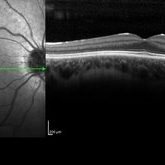 CSNB-OCT-OD
CSNB-OCT-OD
Aug 23 2021 by Jennifer Carstens
OCT/infrared image showing myopic fundus with normal retinal structure in patient with CACNA1F associated X-linked CSNB (OD).
Photographer: Jing Zhang, Ophthalmic Photographer
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB), infrared image, optical coherence tomography (OCT)
-
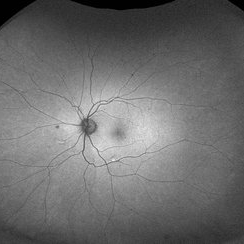 Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Apr 16 2022 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
Oguchi's disease showing the Mizo Nakamura phenomenon with autofluorescence image showing normal Fundus
Photographer: Mr Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB)
-
 Rod Cone dystrophy
Rod Cone dystrophy
Nov 29 2022 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Fundus photograph of the left eye in a 58 yo male with rod cone dystrophy. He presented with night blindness and peripheral vision loss since youth and recent decrease in central vision for the past 10 years. Notice waxy pallor of the nerve, severe arterial narrowing and chorioretinal atrophy mainly around the arcades as well as posterior pole along with RPE hyperplastic changes and atrophy. RPE atrophy in midperiphery has coin shaped appearance. FAF has characteristic appearance (uploaded separately) He has one pathogenic variants of both CEP290 and PRPH2 genes.
Photographer: Sean Kelso, Saint Louis University
Condition/keywords: hereditary retinal deg, hereditary retinal dystrophy, Rod cone dystrophy
-
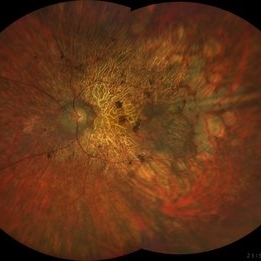
 Retinitis Pigmentosa #1
Retinitis Pigmentosa #1
Jul 22 2021 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Montage wide field fundus photograph of a 55-year-old male who presented with late onset night blindness and peripheral vision loss for one year. His central vision is preserved at 20/25. Fundus photograph demonstrates waxy pallor of the optic nerve, arterial narrowing, and peripheral RPE atrophy outside the arcades with bony spicules.
Photographer: Niloofar Piri, MD
Condition/keywords: retinitis pigmentosa
-
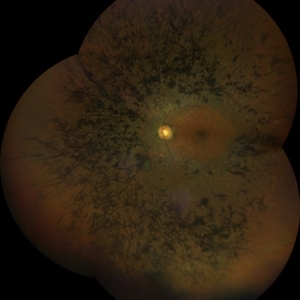 Retinitis Pigmentosa #2
Retinitis Pigmentosa #2
Jul 22 2021 by Niloofar Piri, MD
Montage wide field fundus photograph of the left eye of the same patient. 55-year-old male presented with late onset night blindness and peripheral vision loss for one year. Central vision is preserved at 20/25. ERG demonstrated extinguished rod function, and minimally diminished cone function. Waxy pallor of the optic nerve, arterial narrowing, and peripheral bony spicules are the classic triad of RP which are demonstrated in the photograph.
Photographer: Niloofar Piri, MD
Condition/keywords: retinitis pigmentosa
-
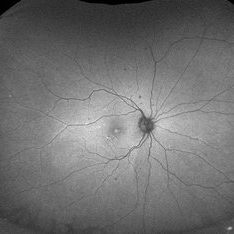 Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Mizuo Nakamura phenomenon
Apr 16 2022 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
Oguchi's disease showing the Mizo Nakamura phenomenon with autofluorescence image showing normal Fundus
Photographer: Mr Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB)
-
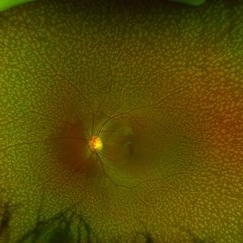 Benign familial Fleck Retina-left eye
Benign familial Fleck Retina-left eye
Feb 2 2023 by Hemanth Murthy, MBBS, MD, FASRS
12 year boy first born of consanguineous marriage, came for routine eye check up with BCVA 20/40 OU. He has no night blindness. His OCT showed thickening of the RPE with dome like elevations involving the ellipsoid layer. Dark adapted ERG showed normal 'b' wavesPhotopic ERG showed reduced 'a' and b waves.
Photographer: Veda Vyas
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: Benign familial Fleck Retina
-
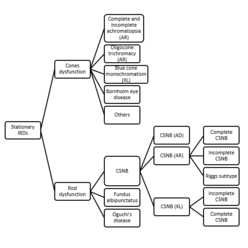 Figure 1: Classification of stationary inherited retinal disease
Figure 1: Classification of stationary inherited retinal disease
Dec 15 2023 by Joshua Friedman
Abbreviations: AD, autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive; CSNB, congenital stationary night blindness; IRD, inherited retinal disease; XL, X-linked.
Condition/keywords: stationary IRD
-
CSNB-ERG-crop
Aug 17 2021 by Christine Kay, MD
This is a full-field ERG of a patient with X-linked incomplete congenital stationary night blindness with proven mutation in CACNA1F, showing a "negative B wave" pattern.
Photographer: Christine Kay, MD
Condition/keywords: X-linked CSNB
-
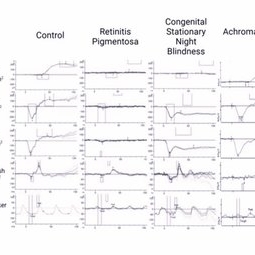 Representative Full Field Electroretinography Responses
Representative Full Field Electroretinography Responses
May 13 2024 by Gabrielle Hallai
The left most column are control full field ERG responses from an individual with no known retinal pathology. In the second column is an example from a patient with autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. This is an example of an intermediate case where rod function is extinguished but some cone function remains. In more advanced cases, full field ERG responses are typically extinguished to both scotopic and photopic stimuli. The third column is an example of congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB). While full field ERG responses can vary greatly depending on the specific subtype, this example of “complete CSNB” demonstrates extinguished rod pathway responses with the classic electronegative response for the scotopic 3.0 and 10.0 responses, consistent with bipolar cell dysfunction. Photopic cone responses are largely normal in this instance, but ”incomplete CSNB” can cause reduced photopic responses. In the final column, an example of full field ERG responses from a patient with achromatopsia. In achromatopsia, cone function is extinguished early in life, while rod pathway function is largely normal. ERG testing was completed using the Diagnosys ColorDome.
Photographer: Gabrielle Hallai, PhD, Cleveland Clinic Cole Eye Institute
Imaging device: Diagnosys ColorDome
Condition/keywords: achromatopsia, congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB), electroretinography, full field ERG, retinitis pigmentosa
-
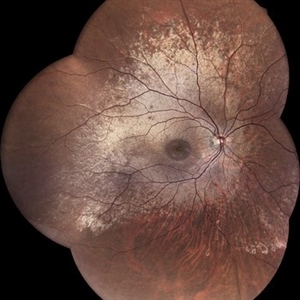 Oguchi's Disease with Mizuo-Nakamura Phenomenon
Oguchi's Disease with Mizuo-Nakamura Phenomenon
Feb 2 2025 by Malek Yassine, MD
Widefield retinography of a case of newly diagnosed Oguchi Disease with silver-gold metallic sheen within the posterior pole.
Photographer: Dr. Malek Yassine
Condition/keywords: congenital stationary night blindness (CSNB), Mizuo Nakamura Phenomenon, Oguchi's disease

 Loading…
Loading…