-
 Slide 5-1
Slide 5-1
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
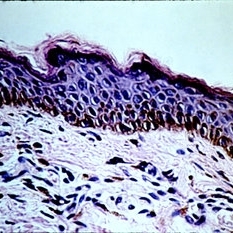
Normal lid skin from a darkly pigmented individual.
Condition/keywords: normal eye
-
 Slide 5-2
Slide 5-2
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
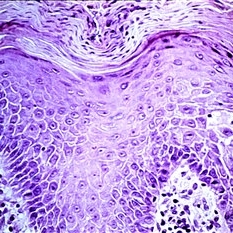
The thickened epidermis shows acanthosis (prickle cell proliferation) and parakeratosis (retention of nuclei in desquamating surface-layer cells).
Condition/keywords: acanthosis, epidermis, Keratosis pilaris (KP), prickle cell proliferation
-
 Slide 5-3
Slide 5-3
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
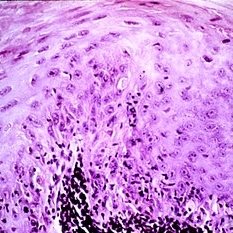
Loss of orderly maturation of epidermal cells (dysplasia). The red blood cell-like ellipse in the center of the epithelium is a cell which has keratinized out of place (dyskeratosis).
Condition/keywords: dyskeratosis, dysplasia, epidermal cells, epithelium
-
 Slide 5-4
Slide 5-4
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
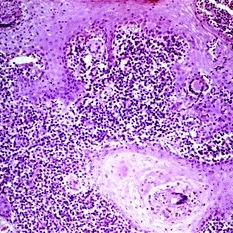
Marked downward proliferation of acanthotic epithelium (pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia) at the edge of a fungal ulcer.
Condition/keywords: acanthosis, fungal ulcer
-
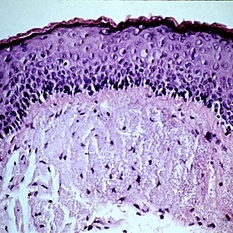 Slide 5-5
Slide 5-5
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Thick layer of basophilic (bluish) glassy fibers in the subepithelial tissue represents elastosis.
Condition/keywords: basophilic, elastosis, subepithelial tissue
-
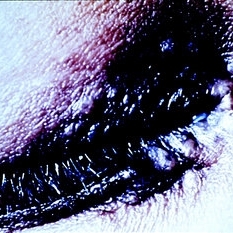 Slide 5-6
Slide 5-6
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Papula lid lesions of sarcoid. (Courtesy of Donald Morris, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: eye lid, sarcoid
-
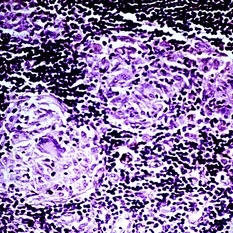 Slide 5-7
Slide 5-7
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Discrete pink clumps of epithelioid cells in sarcoid. Note the giant cell in one clump.
Condition/keywords: epithelioid cells, giant cell, sarcoid
-
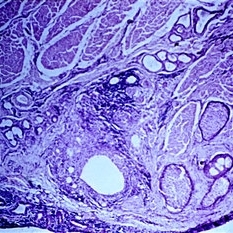 Slide 5-8
Slide 5-8
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Small chalazion in situ in the lid. Lipogranulomatous reaction around large and small clear spaces (pools of dissolved fat) from a single obstructed meibomian lobule.
Condition/keywords: chalazion, lipogranulomatous reaction, meibomian lobule, situ
-
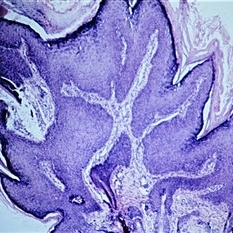 Slide 5-9
Slide 5-9
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Verruca vulgaris of the lid showing acanthotic downgrowths of epithelium incurving toward the center.
Condition/keywords: acanthosis, epithelium, verruca vulgaris
-
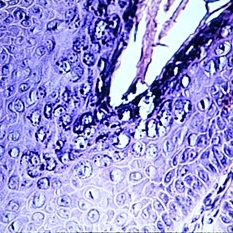 Slide 5-10
Slide 5-10
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Vacuolated epidermal cells containing basophilic intranuclear viral inclusions.
Condition/keywords: basophilic, epidermal cells
-
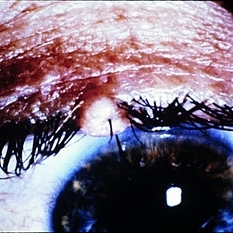 Slide 5-11
Slide 5-11
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Molluscum contagiosum nodule on lid margin.
Condition/keywords: eye lid, molluscum contagiosum nodule
-
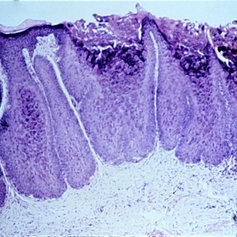 Slide 5-12
Slide 5-12
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Thick, acanthotic lobules of epithelial cells with large, red cytoplasmic inclusions in the inner cells.
Condition/keywords: acanthosis, cytoplasmic inclusions, inner cells
-
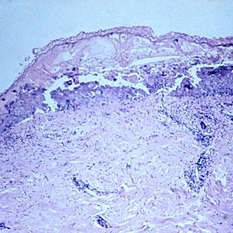 Slide 5-13
Slide 5-13
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Intraepidermal bulla in herpes zoster of the skin.
Condition/keywords: intraepidermal bulla
-
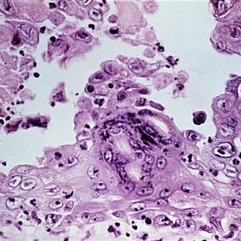 Slide 5-14
Slide 5-14
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Fusion of infected epidermal cells form giant cells in the base of a lesion. Note the many intranuclear red inclusion bodies.
Condition/keywords: epidermal cells, giant cell, intranuclear red inclusion bodies
-
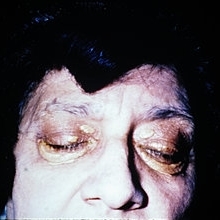 Slide 5-15
Slide 5-15
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Symmetrical plaques of xanthelasma.
Condition/keywords: xanthelasma
-
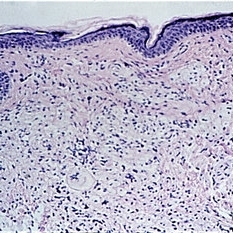 Slide 5-16
Slide 5-16
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Symmetrical plaques of xanthelasma.
Condition/keywords: symmetrical, xanthelasma
-
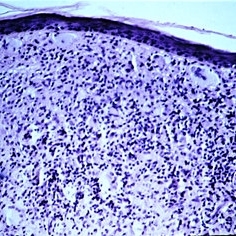 Slide 5-17
Slide 5-17
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Bland, foamy macrophage accumulation in the dermis from xanthelasma. Note the single Touton giant cell below the center.
Condition/keywords: epidermis, giant cell, macrophage accumulation
-
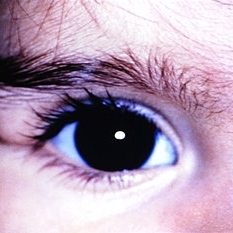 Slide 5-18
Slide 5-18
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Dermoid cyst of the left upper lid in an 11-month-old female (Courtesy of John Hoepner, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: cyst, eye lid
-
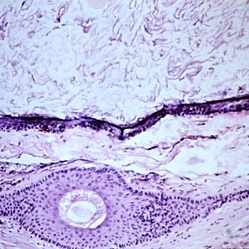 Slide 5-19
Slide 5-19
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Keratinizing epithelium lining a dermoid cyst in the center, with keratin contents and a single large hair above. The connective tissue wall has a large hair follicle in it.
Condition/keywords: cyst, epithelium
-
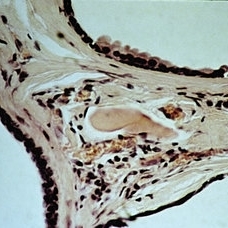 Slide 5-20
Slide 5-20
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Edge of three cystic cavities in a multilocular Moll cyst. The upper wall has a small area of "decapitate secretion" on the surface of the lining cells.
Condition/keywords: cyst, cystic cavities, decapitate secretion, multilocular
-
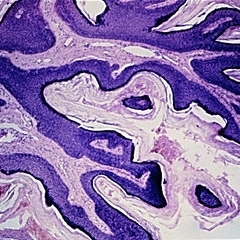 Slide 5-21
Slide 5-21
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Hyperkeratotic squamous papilloma consisting of thin, keratin-covered fronds with dermal cores.
Condition/keywords: dermal cores, papilloma
-
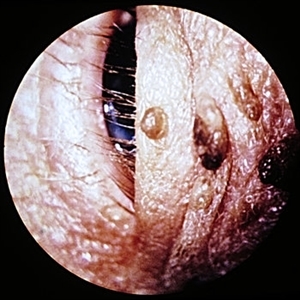 Slide 5-22
Slide 5-22
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Seborrheic keratoses with notable pigmentation. (Courtesy of Anthony Dark, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: Keratosis pilaris (KP)
-
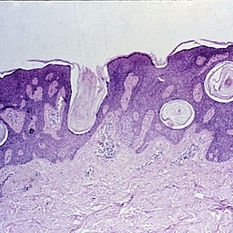 Slide 5-23
Slide 5-23
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Basal cell proliferation and keratin cysts of a typical seborrheic keratosis.
Condition/keywords: basal cell, cyst, Keratosis pilaris (KP)
-
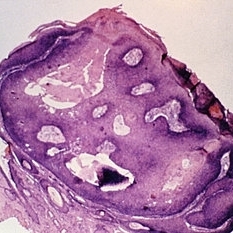 Slide 5-24
Slide 5-24
Feb 20 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Inverted follicular keratosis with thick, acanthotic, folded epithelium and keratin cysts.
Condition/keywords: acanthosis, cyst, epithelium
-
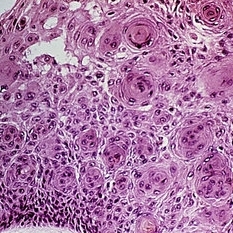 Slide 5-25
Slide 5-25
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Center of epidermis has three "squamous eddies" of whorled squamous cells.
Condition/keywords: epidermis, squamous cells, squamous eddies
-
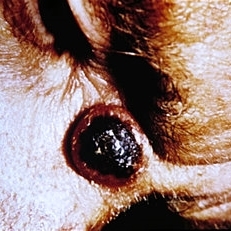 Slide 5-26
Slide 5-26
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Keratoacanthoma of the lid. (Courtesy of Anthony Dark, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: keratoacanthoma, lids
-
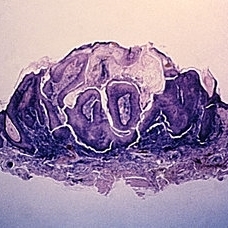 Slide 5-27
Slide 5-27
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Cup-shaped keratoacanthoma with central keratin plug.
Condition/keywords: keratin plug, keratoacanthoma
-
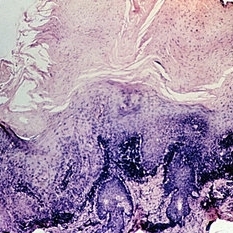 Slide 5-28
Slide 5-28
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Senile keratosis has marked hyperkeratinization with columns of para keratosis and dermal infiltrate.
Condition/keywords: dermal infiltrate, hyperkeratinization, senile keratosis
-
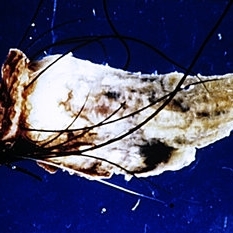 Slide 5-29
Slide 5-29
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
A cutaneous horn arising from an inverted follicular keratosis.
Condition/keywords: cutaneous horn, inverted follicular keratosis
-
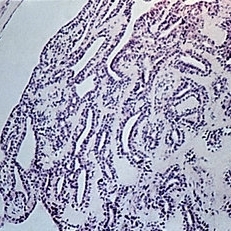 Slide 5-30
Slide 5-30
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Two-layered sweat gland ducts in a tubular hidradenoma.
Condition/keywords: sweat gland ducts, tubular hidradenoma
-
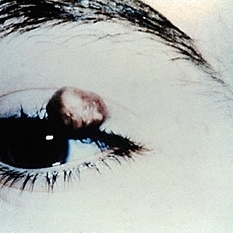 Slide 5-31
Slide 5-31
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Pilomatrixoma of the lid. (Courtesy of Schiele Brewer, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: lids, tumor
-
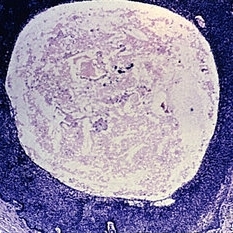 Slide 5-33
Slide 5-33
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Cystic basal cell carcinoma arising in the skin of the lid, which was incorrectly diagnosed clinically.
Condition/keywords: basal cell, lids
-
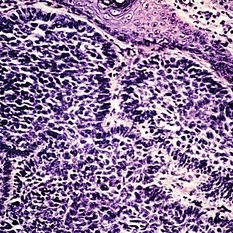 Slide 5-34
Slide 5-34
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Large nuclei of an ulceronodular basal cell carcinoma can be compared with the adjacent normal epithelial cell nuclei. Note the peripheral palisading of the nuclei around the edge of the tumor lobules.
Condition/keywords: basal cell carcinoma of eyelid, epithelial, nuclei
-
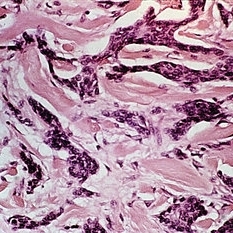 Slide 5-35
Slide 5-35
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Cords of infiltrating basal cells in the dense, fibrous stroma of a morphea type basal cell carcinoma.
Condition/keywords: basal cell, basal cell carcinoma of eyelid, fibrous stroma
-
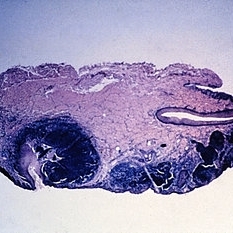 Slide 5-36
Slide 5-36
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Basal cell carcinoma originating from five separate sites in the surface epithelium over the lacrimal punctum and canaliculus.
Condition/keywords: basal cell, canaliculus, epithelium, lacrimal punctum
-
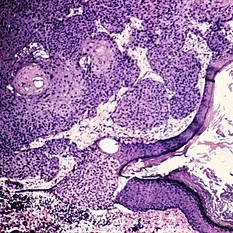 Slide 5-37
Slide 5-37
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Edge of squamous cell carcinoma of the skin showing sudden change from normal epithelium to infiltrating islands of large, malignant squamous cells.
Condition/keywords: epithelium, squamous cells
-
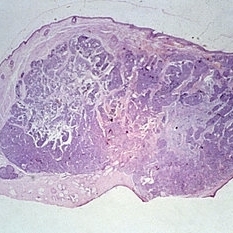 Slide 5-38
Slide 5-38
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Cross-section of lid showing sebaceous carcinoma occupying the tarsal and middle compartments.
Condition/keywords: lids, tarsus
-
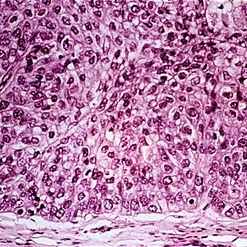 Slide 5-39
Slide 5-39
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Lobule of with central foamy cells best seen in upper left.
Condition/keywords: lobule
-
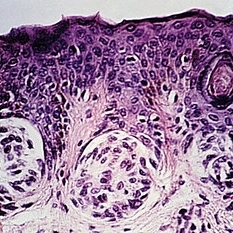 Slide 5-40
Slide 5-40
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Three nests of nevus cells at the tips of epithelial rete pegs, forming a "junctional" nevus.
Condition/keywords: epithelial, nevus
-
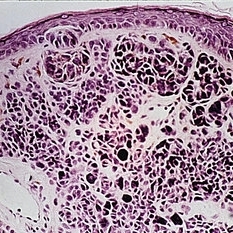 Slide 5-41
Slide 5-41
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
One nest of junctional nevus cells at the base of the epidermis and larger nodules of nevus cells in the dermis make this a "compound" nevus.
Condition/keywords: epidermis, junctional nevus
-
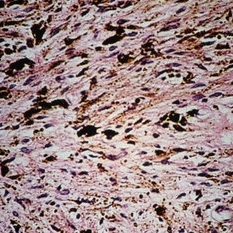 Slide 5-42
Slide 5-42
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Inconspicuous spindle nevus cells and pigment in dense collagen of the dermis constitute a "blue" nevus.
Condition/keywords: collagen, nevus, pigment
-
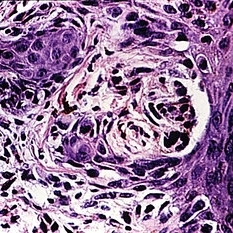 Slide 5-43
Slide 5-43
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Nest of atypical melanocytes resembling a junctional nevus at the edge of a superficial spreading melanoma in a 70-year-old female. Note the inflammatory cells in the dermis.
Condition/keywords: junctional nevus, melanocytes, melanoma

A project from the American Society of Retina Specialists