-
 Vitreomacular Traction
Vitreomacular Traction
Mar 13 2013 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a montage of three separately-captured Spectralis SD-OCT images.
Photographer: Lauren Welch, CPT
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis 3_mode.
Condition/keywords: optical coherence tomography (OCT), vitreomacular traction (VMT)
-
 Geographic Atrophy
Geographic Atrophy
Mar 27 2013 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a combined FAF/SD-OCT in EDI mode of a patient with geographic atrophy and foveal sparing.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS. Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Eye Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: enhanced depth imaging, foveal sparing, fundus autofluorescence (FAF), geographic atrophy, optical coherence tomography (OCT)
-
Stargardts Disease in Fundus Autofluorescence
Sep 12 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Fundus autofluorescence of a patient with Stargardts disease. Note the central area of hypo-autofluorescence indicating atrophy surrounded by smaller areas of hyper-autofluorescence. Note also the much smaller, and in greater number, pinpoints of hyper-autofluorescence extending from the vascular arcades into the mid-periphery.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), Stargardt disease
-
 Sickle Cell Retinopathy
Sickle Cell Retinopathy
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Fluorescein angiogram image of an individual with sickle cell retinopathy using an Optos P200MA ultra-wide field imaging device.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Imaging device: Optos P200MA
Condition/keywords: Optos, sea fan, sickle cell retinopathy, ultra-wide field imaging
-
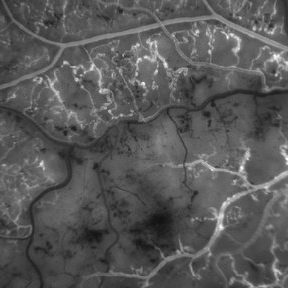 Branch Retinal Vein Occulsion
Branch Retinal Vein Occulsion
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a high-magnification fluorescein angiogram image of an area distal to the point of a branch retinal vein occlusion.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Condition/keywords: branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO), high magnification, ischemia
-
 Epiretinal Membrane
Epiretinal Membrane
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Epiretinal membrane imaged using a high magnification retinal fundus camera and red free illumination.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke Universtiy Hospital
Condition/keywords: epiretinal membrane (ERM), high magnification, monochromatism, red-free
-
 Macular Hole, Autofluorescence
Macular Hole, Autofluorescence
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Fundus autofluorescence (FAF) of a macular hole captured using a Heidelberg Spectralis.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Cneter Labs, Duke Universty Hospital
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), macular hole
-
 Macular Hole
Macular Hole
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Condition/keywords: macular hole
-
 Stargardts Disease in FAF
Stargardts Disease in FAF
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a scanning laser ophthalmoscopic FAF image of a patient with Stargardts Disease captured with a Heidelberg Spectralis imaging unit. Note, besides the obvious hyper-autofluorescent areas centrally, the much smaller, and in greater number, pinpoints of hyper-autofluorescence extending from the vascular arcades into the mid-periphery.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke Universtiy Hospital
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: fundus autofluorescence (FAF), Stargardt disease
-
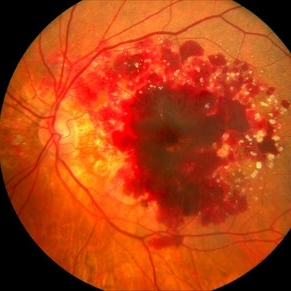 Age-related Macular Degeneration
Age-related Macular Degeneration
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke Universtiy Hospital
Imaging device: Zeiss FF450
Condition/keywords: age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
-
 Sticklers Syndrome
Sticklers Syndrome
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Imaging device: Zeiss FF450
Condition/keywords: Stickler Syndrome
-
 Melanocytoma
Melanocytoma
Sep 14 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Imaging device: Zeiss FF450
Condition/keywords: melanocytoma
-
 Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Sep 17 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of a macular hole.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: macular hole, myelinated nerve fibers
-
 Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Sep 17 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of myelinated nerve fibers
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: myelinated nerve fibers
-
 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Sep 17 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of a patient with PDR and NVD.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: blot hemorrhages, neovascularization of the disc (NVD)
-
 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Sep 17 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of a patient with PDR and NVD.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: neovascularization of the disc (NVD)
-
 Macular Hole
Macular Hole
Sep 18 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of a macular hole.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: macular hole
-
 Kearns-Sayre Syndrome
Kearns-Sayre Syndrome
Sep 18 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal fundus photograph of a Kearns-Sayre Syndrome patient.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center
Imaging device: Canon 60UV
Condition/keywords: bilateral pigmentary retinopathy, cardiac conduction abnormalities, chronic progressive ophthalmoplegia, heart-block, Kearns-Sayre Syndrome, ptosis
-
 Lamellar Macular Hole
Lamellar Macular Hole
Sep 18 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Imaging device: Zeiss Cirrus
Condition/keywords: lamellar macular hole
-
 Choroidal Detachment, In Stereo
Choroidal Detachment, In Stereo
Sep 25 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Zeiss FF3C
Condition/keywords: choroidal detachment, stereo pair
-
 Choroideremia
Choroideremia
Sep 27 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a 60 degree fluorescein angiogram image of choroideremia.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Canon 60UV
Condition/keywords: choroideremia
-
 Asteroid Hyalosis, In Stereo
Asteroid Hyalosis, In Stereo
Sep 28 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Asteriod hyalosis, stereo.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Zeiss FF3C
Condition/keywords: asteroid hyalosis, stereo pair
-
 Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization, In Stereo
Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization, In Stereo
Sep 28 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Subfoveal Choroidal Neovascularization.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Zeiss FF4
Condition/keywords: pigment epithelial detachment (PED), stereo pair, subfoveal choroidal neovascularization
-
 Horseshoe Tear, In Stereo
Horseshoe Tear, In Stereo
Sep 28 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Horse shoe tear, stereo.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Zeiss FF3C
Condition/keywords: stereo pair
-
 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy, In Stereo
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy, In Stereo
Sep 28 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Proliferative diabetic retinopathy, PDR, Stereo.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Imaging device: Zeiss FF4
Condition/keywords: stereo pair
-
 Sickle Cell Retinopathy
Sickle Cell Retinopathy
Sep 28 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Peripheral non-perfusion in sickle cell retinopathy.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Imaging device: Zeiss FF3C
Condition/keywords: non-perfusion, sickle cell retinopathy
-
 Coloboma, In Stereo
Coloboma, In Stereo
Oct 1 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a stereo retinal fundus photograph of a coloboma, with the optic nerve centered, using a Zeiss FF3C retinal fundus camera.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Labs, Duke University Hospital, Duke Eye Center, Durham, NC
Condition/keywords: coloboma, fundus photograph, stereo pair
-
 Retinal Detachment, in Stereo
Retinal Detachment, in Stereo
Oct 4 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Retinal detachment showing bare RPE, in stereo.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS, Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital, Durham, NC
Condition/keywords: stereo pair
-
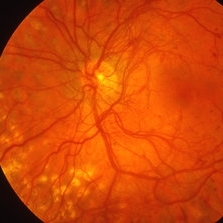 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with NVD
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with NVD
Oct 4 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Condition/keywords: neovascularization of the disc (NVD), retinal neovascularization
-
 Neuroretinitis
Neuroretinitis
Oct 4 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Condition/keywords: neuroretinitis
-
 Retinal Tack
Retinal Tack
Oct 11 2012 by Michael P. Kelly, FOPS
This is a retinal fundus photograph I took in 1987 while working with Howard Schatz, MD and H. Richard McDonald, MD, when retinal tacks were used to repair giant retinal tears. I purposely underexposed the retina because the retinal tack is so highly relective.
Photographer: Michael P. Kelly, FOPS Director, Duke Eye Center Labs, Duke University Hospital
Condition/keywords: retinal tacks, retinal tear

A project from the American Society of Retina Specialists