Search results (431 results)
-
 Franceschetti's Sign
Franceschetti's Sign
Jun 5 2025 by César Adrián Gómez Valdivia, MD
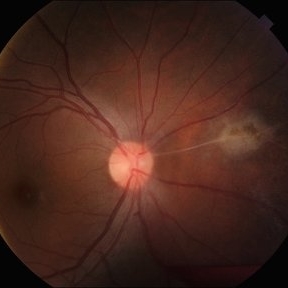
Franceschetti's sign found in a 22 year-old female patient diagnosed with ocular toxoplasmosis. These bands typically link an old scar to the optic disc, indicative of previous inflammation. Findings were unilateral.
Photographer: @eyemissu2
Imaging device: TOPCON TRC-50DX
Condition/keywords: chorio, Franceschetti's Sign, toxoplasmosis
-
 Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer
May 20 2025 by Ignacio Leonardo Pueyo Bestue, MD
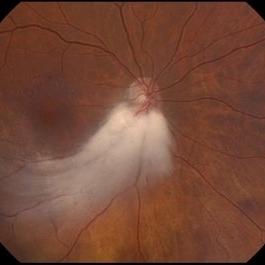
Fundus photo of an 80-year-old woman with myelinated RNFL, 20/20 vision, and mild hyperopia
Photographer: Pueyo-Bestue, I.L., MD, Universite Libre de Bruxelles, Ophthalmology Department
Condition/keywords: myelinated nerve fiber layer
-
 VKH Pseudotumor – Chronic Subretinal Fibrosis
VKH Pseudotumor – Chronic Subretinal Fibrosis
May 11 2025 by Felipe Murati
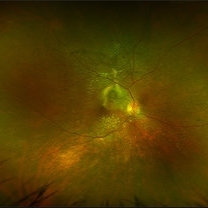
Ultra-widefield fundus image from a 36-year-old woman with chronic VKH syndrome showing a pseudotumor-like subretinal fibrotic lesion in the right eye. The lesion developed after multiple relapses and remained stable over a 1-year follow-up with immunosuppressive treatment including prednisone, mycophenolate mofetil, and adalimumab. No active choroiditis or exudative detachment was observed. Multimodal imaging was essential for disease monitoring.
Photographer: Felipe A. Murati, MD, University of Arizona
Imaging device: Optos California ultra-widefield retinal imaging system, single-capture, color fundus modality.
Condition/keywords: adalimumab, chronic inflammation, granulomatous uveitis, OCT, Optos ultra-widefield imaging, pseudotumor, subretinal fibrosis, VKH, Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada
-
 Retinocoroiditis Inactiva Por Toxoplasmosis
Retinocoroiditis Inactiva Por Toxoplasmosis
Apr 28 2025 by Paulina Araujo
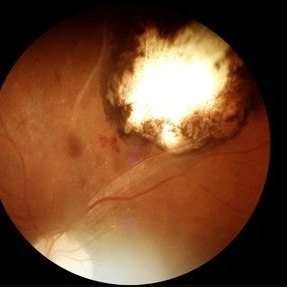
Fundus photography demonstrates a 2-disc-diameter chorioretinal scar in the superior temporal arcade, consistent with inactive toxoplasmic retinochoroiditis. The lesion exhibits pigmented borders and central atrophy, with adjacent splinter hemorrhages and vascular sheathing. No vitreous inflammation or active satellite lesions are present.
Photographer: Paulina D.Araujo Martínez, Asociación para Evitar la Ceguera en México I.A.P., Hospital Dr Luis Sánchez Bulnes.
Condition/keywords: toxoplasmosis chorioretinitis
-
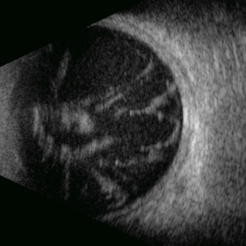 Vitreous Bands
Vitreous Bands
Apr 28 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This B-mode transversal ultrasound scan shows condensed vitreous bands with anterior traction toward the cornea, accompanied by vitreous cellularity, in a patient with corneal perforation secondary to bacterial keratitis. The findings indicate severe intraocular inflammation with potential vitreous involvement.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: keratitis, vitreous bands
-
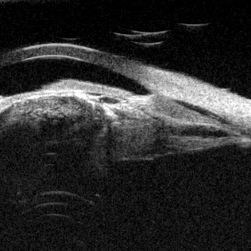 Cyclic Membrane
Cyclic Membrane
Apr 23 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This UBM scan reveals pars planitis with characteristic findings: an inflammatory pupillary membrane, a cataractous lens, and cyclitic membrane causing ciliary body detachment and traction. The lens demonstrates spherical deformation due to zonular laxity from ciliary body traction.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: cyclic membrane, pars planitis
-
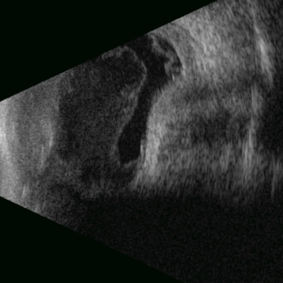 Posterior Nodular Scleritis
Posterior Nodular Scleritis
Apr 23 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This B-mode ultrasound scan demonstrates a posterior scleral nodule accompanied by vitritis, serous retinal detachment, and annular choroidal detachment. The nodule appears as a localized hypoechoic scleral thickening, while the serous retinal detachment shows a smooth convex configuration. The choroidal detachment presents with the characteristic ring-shaped elevation, suggesting significant intraocular inflammation or hypotony.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: posterior nodular scleritis, posterior scleritis
-
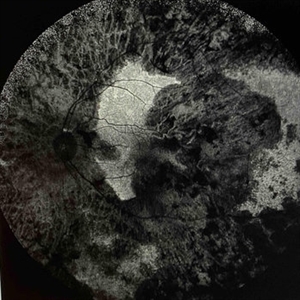 Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring With Partial Macular Sparing
Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring With Partial Macular Sparing
Apr 22 2025 by Maxwell J Wingelaar, MD
Fundus autofluorescence of extensive chorioretinal scarring in the left eye.
Photographer: Killian Roberts
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis AF
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal atrophy, chorioretinal inflammations
-
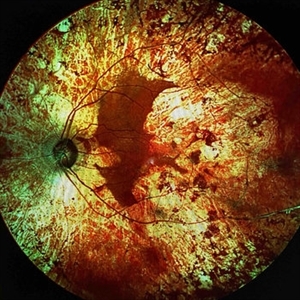 Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring with Partial Macular Sparring
Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring with Partial Macular Sparring
Apr 22 2025 by Maxwell J Wingelaar, MD
A multicolor photo showing chorioretinal scarring with partial macular sparing in the left eye.
Photographer: Killian Roberts
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis Multicolor Photo
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal atrophy, chorioretinal inflammations
-
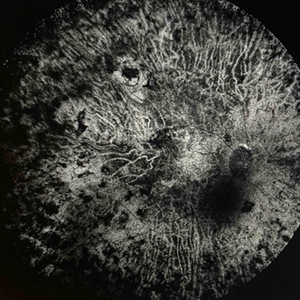 Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring in the Right Eye
Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring in the Right Eye
Apr 22 2025 by Maxwell J Wingelaar, MD
Fundus autofluorescence of Extensive chorioretinal scarring in the right eye.
Photographer: Killian Roberts
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis AF
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal atrophy, chorioretinal inflammations
-
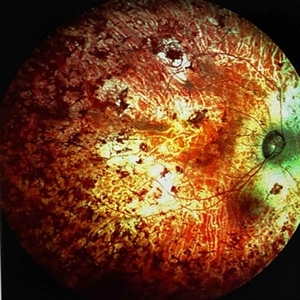 Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring in the Right Eye
Extensive Chorioretinal Scarring in the Right Eye
Apr 22 2025 by Maxwell J Wingelaar, MD
A multicolor photo showing chorioretinal scarring with macular involvement in the right eye
Photographer: Killian Roberts
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis Multicolor Photo
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal atrophy, chorioretinal inflammations
-
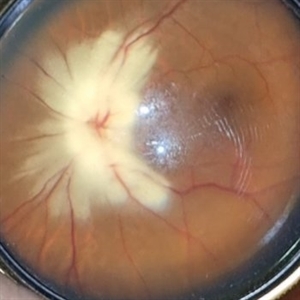 Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Apr 18 2025 by DR Rohit Gupta
The **myelinated nerve fibers of the optic disc** (also known as **medullated nerve fibers**) are retinal nerve fibers that retain their myelin sheath as they pass through the optic nerve head. Normally, retinal nerve fibers are unmyelinated to allow for light transparency, but in some cases, myelination extends anteriorly into the retina, appearing as a striking white, feathery patch on the optic disc or peripapillary retina. ### **Key Features:** 1. **Appearance:** - Dense, white, striated patches with feathery edges. - Typically located at the superior or inferior pole of the optic disc. - May obscure retinal vessels underneath. 2. **Clinical Significance:** - Usually **benign** and asymptomatic. - **Congenital** (present at birth or early childhood). - Rarely associated with **visual field defects** (e.g., scotomas corresponding to the area of myelination). - Occasionally linked with **high myopia** or **amblyopia** if extensive. 3. **Pathophysiology:** - Failure of oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells to stop myelination at the lamina cribrosa. - Normally, myelination stops at the optic nerve head, but in this condition, it extends into the retina. 4. **Diagnosis:** - **Fundoscopy:** Classic white, feathery appearance. - **Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT):** Shows thickened retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). - **Visual Field Testing:** May detect defects if large. 5. **Differential Diagnosis:** - Optic disc edema - Cotton wool spots - Retinoblastoma (rarely, but must be ruled out in children) 6. **Management:** - No treatment required if asymptomatic. - Monitor for amblyopia in children. - Rare cases with significant visual impairment may need further evaluation. ### **Fun Fact:** Myelinated nerve fibers are seen in **~0.5-1%** of the population and are usually an incidental finding.
Photographer: Dr Rohit gupta
Imaging device: Samsung S21
Condition/keywords: Medulated Nerve fibre, Medullated Nerve fibres, myelinated nerve fibers, Myelinated Nerve Fibres, optic disc drusen
-
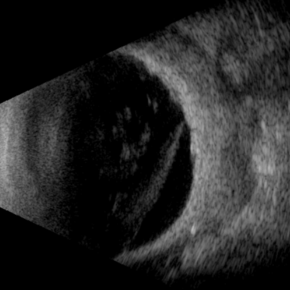 Necrotizing Scleritis USG
Necrotizing Scleritis USG
Apr 17 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This B-mode transverse ultrasound scan reveals necrotizing scleritis with inferior perilimbal uveal tissue prolapse, demonstrating scleral thinning and irregular uveal protrusion. Vitreous cellularity and partial vitreous detachment are also observed, indicating associated intraocular inflammation. These findings collectively characterize this severe inflammatory condition.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: necrotizing scleritis
-
Endophthalmitis
Apr 9 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
B-mode ultrasound video of a vitrectomized eye reveals characteristic vitreous cavity membranes secondary to endophthalmitis. The real-time imaging demonstrates these inflammatory membranes exhibit semi-rigid dynamics, displaying viscoelastic behavior with limited displacement during ocular movements while maintaining structural integrity. This restricted mobility pattern, showing both resistance to kinetic forces and slow recoil, represents a pathognomonic feature of advanced fibrotic organization in endophthalmitis.
Condition/keywords: endophthalmitis
-
 New Choroidal Melanoma
New Choroidal Melanoma
Jan 3 2025 by Virginia Gebhart
22 year old male referred for 2nd opinion on large choroidal mass with subretinal fluid. Clinical exam and ultrasound consistent with choroidal melanoma. CT scan of orbits showed possible inflammation involving orbital fat. Pt has been on oral prednisone for 1 week, inflammation has not responded. Referred to Emory for 2nd opinion on treatment
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: melanoma
-
 Snowbank in Intermediate Uveitis
Snowbank in Intermediate Uveitis
Dec 12 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
25 year old female with intermediate uveitis. Improved inflammation after 40mg prednisone taper. Pt has multiple autoimmune diseases, will order MRI to r/o demyelinating disease.
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: intermediate uveitis, snowballs, snowbank, uveitis
-
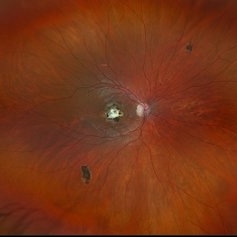 Inactive Chorioretinal Scars
Inactive Chorioretinal Scars
Dec 11 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
30 year old female with chorioretinal and macula scars. Appears post-infectious, most likely toxoplasmic. No active inflammatory changes or choroidal neovascularization. Will continue to monitor. Central vision limited by macula scar, BCVA 20/100
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, inactive toxoplasmosis
-
 Retinal Telangiectasis
Retinal Telangiectasis
Nov 13 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
42 year old female with telangiectatic vessels and vascular sheathing. FA showed mild leakage with areas of peripheral non-perfusion. Pt is asymptomatic without inflammation in the vitreous. No history of systemic inflammatory disease. Will observe.
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: retinal telangiectasia, telangiectatic vessels, vascular sheathing of retina
-
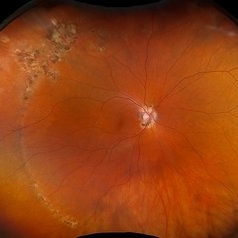 POHS/Schlaegel Lines
POHS/Schlaegel Lines
Sep 19 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
46 year old female with h/o Histoplasmosis. Multiple punched out chorioretinal scars with Schlaegel lines. No evidence of CNV or active inflammation. VA 20/20
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, histoplasmosis, presumed ocular histoplasmosis syndrome (POHS)
-
 Uveal Effusion Syndrome
Uveal Effusion Syndrome
Sep 19 2024 by Virginia Gebhart
61 year old female with idiopathic uveal effusion syndrome. 360 degrees of choroidal thickening, especially anterior with exudative fluid inferior. Mild vitritis present. Unable to gain venous access for FA, ultrasound and UBM performed which confirm choroidal and ciliary body thickening. Pt sent for inflammatory work up including MRI of brain and orbits. Treatment pending results.
Photographer: Virginia Gebhart, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: idiopathic uveal effusion syndrome, uveal effusion
-
 Atypical Tubercular Occlusive Peripheral Retinal Vasculitis
Atypical Tubercular Occlusive Peripheral Retinal Vasculitis
Jun 21 2024 by Tejaswita Verma
Follow up right eye fundus photograph of a 27 year old male with vision 6/12 , diagnosed with systemic tuberculosis(mediastinal lymphadenopathy on chest CT) on oral steroids, and started on ATT .We can see a parafoveal sub-ILM hemorrhage with vascular sheathing and hemorrhages in inferior and temporal quadrants . The patient was advised anti-VEGF intravitreal injection, later sectoral laser after resolution of inflammation
Photographer: DR. TEJASWITA VERMA
Imaging device: MIRANTE
Condition/keywords: obliterative peripheral vasculitis, ocular tuberculosis
-
 FFA in Atypical Tubercular Peripheral Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis
FFA in Atypical Tubercular Peripheral Occlusive Retinal Vasculitis
Jun 21 2024 by Tejaswita Verma
Right eye FFA montage of a 27 year male with peripheral occlusive tubercular vasculitis, showing CNP areas inferiorly and temporally, leakages and blocked fluorescence due to hemorrhages. The patient was advised intravitreal anti-VEGF injection and later sectoral laser once inflammation subsides.
Photographer: DR. TEJASWITA VERMA
Imaging device: MIRANTE
Condition/keywords: obliterative peripheral vasculitis, ocular tuberculosis
-
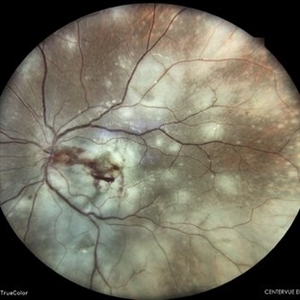 Multifocal Chorioretinitis
Multifocal Chorioretinitis
Apr 9 2024 by Akansha Sharma
Color fundus photograph of a 34 year old male patient with multifocal chorioretinitis with subretinal bleed.
Photographer: Dr. Akansha Sharma, Bharati Eye Hospital
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal inflammations, chorioretinitis, subretinal hemorrhage
-
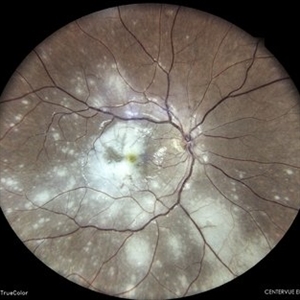 Multifocal Chorioretinitis
Multifocal Chorioretinitis
Apr 9 2024 by Akansha Sharma
Color fundus photograph of a 34 year old male patient with multifocal chorioretinitis.
Photographer: Dr. Akansha Sharma, Bharati Eye Hospital
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal inflammations, chorioretinitis
-
 Familial Dominant Drusen
Familial Dominant Drusen
Mar 28 2024 by Houda Brarou
Familial Dominant Drusen is a genetically inherited retinal dystrophy and thought to represent an early-onset variant of age related macular degeneration. The gene responsible is EFEMP1 and inherited in autosomal dominant manner with variable expressivity. It is represented with multiple radially elongated small drusen in early stages and in later stages they become larger and more confluent. Geographic atrophy occurs in advanced stages.
Photographer: Houda Braou , Mohammed V military hospital of Rabat
Imaging device: TOPCON DRI OCT Triton Plus
Condition/keywords: FAMILIAL DOMINANT DRUSEN

 Loading…
Loading…