-
 By Marcelo Zas, MD PhD
By Marcelo Zas, MD PhD
Hospital de Clinicas-University of Buenos Aires
Co-author(s): Mariano Cotic MD, Julieta Fourcade MD, Marcos Mendaro MD, Maria Carolina Pozzoni MD, Adriana Nieva MD, Luciano Scorsetti MD, Daniela Contartese MD, Sofia Ghigliotti - Uploaded on Jun 24, 2025.
- Last modified by Joshua Friedman on Jun 25, 2025.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Miscellaneous
- Condition/keywords
- RETINAL VASOPROLIFERATIVE TUMOR
- Photographer
- Marcelo Zas MD PhD
- Description
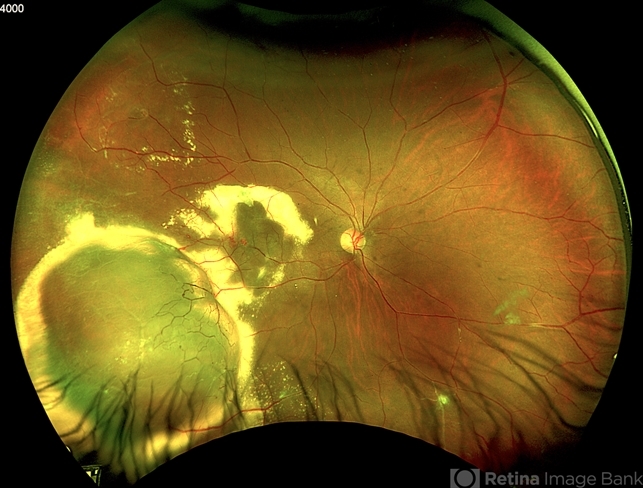
- We present a case of a 33-year-old male patient, who presented with decreased visual acuity in his right eye with 20/80, presenting a primary retinal vasoproliferative tumor in the lower temporal quadrant. The tumor is associated with serous retinal detachment, hard exudation, neovascularization and telangiectasias. Lipid exudates extend toward the macula, indicating macular involvement, which may contribute to decreased visual acuity. Oi was normal with 20/20 of BCVA. The patient was treated initially with IV anti-VEGF therapy and cryotherapy.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)

---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)