Search results (111 results)
-
 Chorioretinal Coloboma
Chorioretinal Coloboma
Oct 6 2025 by Seif Allah Anwar
Fundus photograph of the patient left eye showing large, well-demarcated, excavated chorioretinal coloboma involving the inferior fundus, extending from the optic disc to the periphery. The lesion appears white due to bare sclera visibility, with absence of overlying choroid and retina. Retinal vessels course over the colobomatous area inferiorly.
Photographer: Dr. Seif Anwar, FRCSEd
Imaging device: Centervue Eidon
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal coloboma
-
Amelanotic Melanoma
Sep 19 2025 by Aditya S Kelkar, MS, FRCS, FASRS,FRCOphth
Widefield fundus photograph of a 37 year old showing a large, dome-shaped, intraocular mass involving the temporal retina. The lesion appears elevated and lacks surface pigmentation. Overlying retinal vessels are displaced and draped across the tumor surface, with surrounding retinal elevation noted. The appearance is suggestive of amelanotic variant of choroidal melanoma.
Photographer: Dr. Muskan Mangal
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: choroidal melanoma, intraocular tumor
-
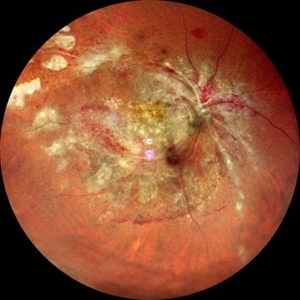 CMV Retinitis: Turning Retina into Abstract Art Since Immunosuppression
CMV Retinitis: Turning Retina into Abstract Art Since Immunosuppression
Aug 4 2025 by rohan jain
We report a case of 34 years old HIV positive male who presented with Diminution of vision in OD since 1 month .Examination of OD showed hazy media due to vitritis, diffuse yellowish-whitish retinal necrosis and retinal hemorrhages around the disc and attenuated retinal vessels.
Photographer: Dr. ROHAN JAIN
Imaging device: mirante
Condition/keywords: CMV chorioretinitis, CMV retinitis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
-
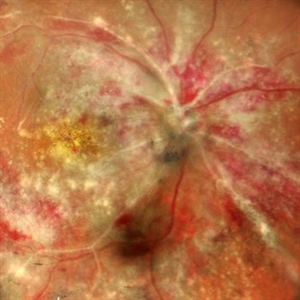 CMV Retinitis: Turning Retina into Abstract Art Since Immunosuppression
CMV Retinitis: Turning Retina into Abstract Art Since Immunosuppression
Aug 4 2025 by rohan jain
We report a case of 34 years old HIV positive male who presented with Diminution of vision in OD since 1 month. Examination of OD showed hazy media due to vitritis, diffuse yellowish-whitish retinal necrosis and retinal hemorrhages around the disc and attenuated retinal vessels.
Photographer: Dr. ROHAN JAIN
Imaging device: mirante
Condition/keywords: CMV chorioretinitis, CMV retinitis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), Cytomegalovirus Retinitis
-
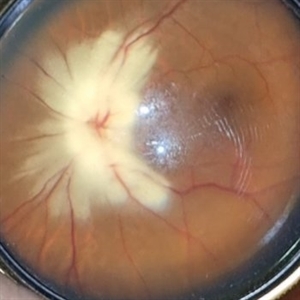 Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Myelinated Nerve Fibers
Apr 18 2025 by DR Rohit Gupta
The **myelinated nerve fibers of the optic disc** (also known as **medullated nerve fibers**) are retinal nerve fibers that retain their myelin sheath as they pass through the optic nerve head. Normally, retinal nerve fibers are unmyelinated to allow for light transparency, but in some cases, myelination extends anteriorly into the retina, appearing as a striking white, feathery patch on the optic disc or peripapillary retina. ### **Key Features:** 1. **Appearance:** - Dense, white, striated patches with feathery edges. - Typically located at the superior or inferior pole of the optic disc. - May obscure retinal vessels underneath. 2. **Clinical Significance:** - Usually **benign** and asymptomatic. - **Congenital** (present at birth or early childhood). - Rarely associated with **visual field defects** (e.g., scotomas corresponding to the area of myelination). - Occasionally linked with **high myopia** or **amblyopia** if extensive. 3. **Pathophysiology:** - Failure of oligodendrocytes or Schwann cells to stop myelination at the lamina cribrosa. - Normally, myelination stops at the optic nerve head, but in this condition, it extends into the retina. 4. **Diagnosis:** - **Fundoscopy:** Classic white, feathery appearance. - **Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT):** Shows thickened retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL). - **Visual Field Testing:** May detect defects if large. 5. **Differential Diagnosis:** - Optic disc edema - Cotton wool spots - Retinoblastoma (rarely, but must be ruled out in children) 6. **Management:** - No treatment required if asymptomatic. - Monitor for amblyopia in children. - Rare cases with significant visual impairment may need further evaluation. ### **Fun Fact:** Myelinated nerve fibers are seen in **~0.5-1%** of the population and are usually an incidental finding.
Photographer: Dr Rohit gupta
Imaging device: Samsung S21
Condition/keywords: Medulated Nerve fibre, Medullated Nerve fibres, myelinated nerve fibers, Myelinated Nerve Fibres, optic disc drusen
-
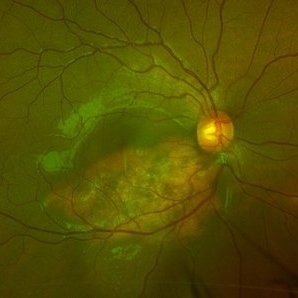 Choroidal Osteoma
Choroidal Osteoma
Apr 17 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
Scanning laser ophthalmoscopy reveals a well-circumscribed, yellowish-white choroidal osteoma overlying the macular region and extending into the inferior temporal vascular arcade. Retinal vessels course normally over the tumor surface, with no evidence of subretinal fluid or hemorrhage. The surrounding retina shows preserved architecture without secondary degenerative changes.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: choroidal osteoma, macular choroidal osteoma
-
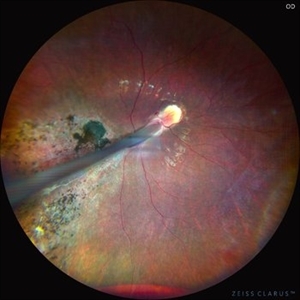 Comets in the Eye (Retinopathy of Prematurity)
Comets in the Eye (Retinopathy of Prematurity)
Apr 8 2025 by KANWALJEET HARJOT MADAN, M.S. (Ophthalmology); FAICO (Vitreous - Retina)
This is the fundus picture of right eye (RE) of a 4 years female child presented with outward deviation of right eye. Her parents also complained of diminution of vision in both eyes. On examination, her best corrected vision in RE was hand movements close to face and was 20/80 in LE. Posterior segment exam revealed presence of macular scar in RE and presence of dry retinal fold with dragging of retinal vessels. LE fundus revealed presence of nasal drag of optic disc. Parents gave history of untreated ROP as an infant. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) is a Vaso proliferative disorder of Retina occurring in premature infants. Advances in neonatal care and ROP treatment has led these babies to live longer with this disease.
Photographer: Dr. Kanwaljeet Harjot Madan, Thind Eye Hospital, Jalandhar City (Punjab) INDIA.
Imaging device: Zeiss Fundus Camera
Condition/keywords: Retinopathy of Prematurity, Vaso proliferative disorder
-
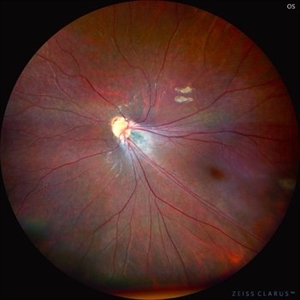 Comets in the Eye (Retinopathy of Prematurity)
Comets in the Eye (Retinopathy of Prematurity)
Apr 8 2025 by KANWALJEET HARJOT MADAN, M.S. (Ophthalmology); FAICO (Vitreous - Retina)
This is the fundus picture of right eye (RE) of a 4 years female child presented with outward deviation of right eye. Her parents also complained of diminution of vision in both eyes. On examination, her best corrected vision in RE was hand movements close to face and was 20/80 in LE. Posterior segment exam revealed presence of macular scar in RE and presence of dry retinal fold with dragging of retinal vessels. LE fundus revealed presence of nasal drag of optic disc. Parents gave history of untreated ROP as an infant. Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) is a Vaso proliferative disorder of Retina occurring in premature infants. Advances in neonatal care and ROP treatment has led these babies to live longer with this disease.
Photographer: Dr. Kanwaljeet Harjot Madan, Thind Eye Hospital, Jalandhar City (Punjab) INDIA.
Imaging device: Zeiss Fundus Camera
Condition/keywords: Retinopathy of Prematurity
-
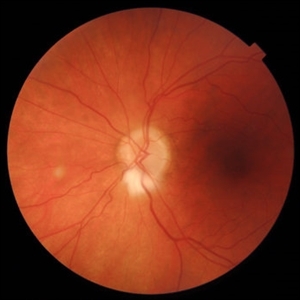 Persistent Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fibers
Persistent Myelinated Retinal Nerve Fibers
Apr 7 2025 by Juan J. Prados-Carmona
This fundus photograph shows a well-defined, whitish, feathery lesion radiating from the optic disc, consistent with myelinated retinal nerve fibers. The lesion follows the distribution of the retinal nerve fiber layer and appears superficial, partially obscuring the underlying retinal vessels. The optic disc itself is slightly blurred but without signs of true disc edema or hyperemia. The rest of the retina appears unremarkable, with normal vessel caliber and no evidence of hemorrhages, exudates, or signs of hypertensive or diabetic retinopathy. The findings are compatible with a benign congenital anomaly—persistent myelinated retinal nerve fibers.
Photographer: Juan J. Prados-Carmona
Condition/keywords: Persistent myelinated retinal nerve fibers, persistent myelination
-
 Retinal Arteriolar Variation
Retinal Arteriolar Variation
Oct 31 2024 by AVIK DEY SARKAR, MS, FVRS, FAICO(VR)
A 43-year-old hypertensive patient, diagnosed with Non-Ischemic Central retinal vein Occlusion in OS, presented with a striking anatomical variation in retinal vasculature. The inferior first-order retinal arteriole after initiating from the optic disc bifurcates, before reaching the fovea, and the superior branch after crossing the midline forms the superior arcade afterwards and produces dichotomous branching as usual. This defies basic anatomical considerations for retinal vasculature as they never cross the midline, also known as the watershed line for retinal vessels.1,2 References: 1. May CA, Rutkowski P. The Horizontal Raphe of the Human Retina and its Watershed Zones. Vision. 2019; 3(4):60. 2. May CA, Rutkowski P. Hypothesis: watershed zones in the human eye are a key for understanding glaucomatous retinal damage. Med Hypotheses. 2017;109:1-5.
Photographer: Dr. Avik Dey Sarkar, MBBS, MS, FVRS, FAICO, Consultant, Department of Vitreoretinal Services, Aravind Eye Hospital, Madurai, India
Imaging device: Wide angled Fundus imaging with Clarus 300
Condition/keywords: background diabetic retinopathy (BDR), Diabetic Retinopathy, retina, vascular anomaly
-
 End Point of Macular Telangiectasia (Mac Tel) Type 2
End Point of Macular Telangiectasia (Mac Tel) Type 2
Oct 31 2024 by Julián Villarreal, MD
60 year old female with an end-stage proliferative macular telangiectasia type 2 with right-angle retinal vessels, manifested as blunted arterioles and venules that connect the superficial and deeper retinal plexus, chorioretinal anastomosis with a fibrovascular scar and a typical retinal pigment hyperplasia , fellow eye showed a focal discontinuity in the ellipsoid zone with a loss of the outer and a disorganization of the inner retinal layers, not involving the foveal center and a non exudative neovascularization
Photographer: Julián Villarreal MD
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: Mac Tel type 2, macular telangiectasia type 2
-
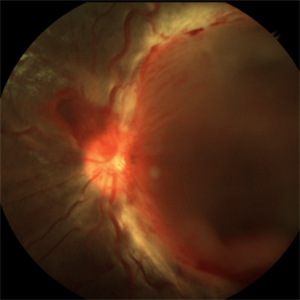 Sea Fan Neovascular Frond in Rare Case of Fanconi Anemia
Sea Fan Neovascular Frond in Rare Case of Fanconi Anemia
May 18 2024 by Amol yuvraj ganvir
A 15-year-old female patient brought by her parents with defective vision in left eye for 15 days. The patient had a known case of Fanconi Anemia. Left eye tortuous vessels and new retinal vessels along the major temporal arcade, with intraretinal and subretinal hemorrhage covering the macula.
Photographer: Dr. Amol Ganvir
Condition/keywords: Fanconi Anemia, sea fan
-
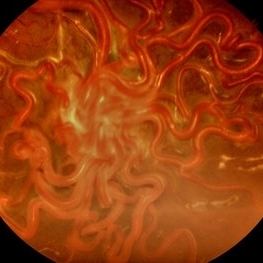 Wyburn-Mason Syndrome (Racemose Angioma)
Wyburn-Mason Syndrome (Racemose Angioma)
Mar 23 2024 by Pushkar Mahale
Fundus photograph of a 10 year old child presenting with no perception of light in right eye. Fundus examination revealed dilated and tortuous retinal vessels suggestive of Racemose Hemangioma.
Photographer: Dr Pushkar Mahale
Condition/keywords: racemose hemangioma, Wyburn -Mason Syndrome
-
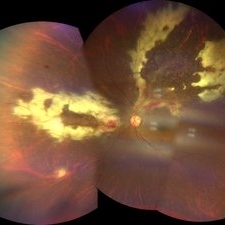 CMV Retinitis
CMV Retinitis
Feb 17 2024 by Eloy Mata-Cortes, MD
Fundus photograph of left eye showing Cytomegalovirus retinitis of a 40-year-old male with positive HIV history. He presented with CD4 cell count of 50 cells/mm3 and decreased vision of left eye. In the photograph we can see the three typical patterns in this retinitis: a hemorrhagic appearance in superior temporal arcade and between nasal arcades, granular pattern in superior temporal retina, and a “frosted branch” angiitis surrounding the retinal vessels in nasal and superior retina.
Photographer: Eloy Mata-Cortes, Instituto Mexicano de Oftalmologia, Queretaro, Mexico
Imaging device: Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: CMV retinitis, cytomegalovirus (CMV), frosted branch angiitis, Frosted Branch Angitis
-
 Morning Glory Disc Anomaly
Morning Glory Disc Anomaly
Feb 12 2024 by NIDHI PANWAR, MD FRCS Glasgow FNB FICO
Fundus photograph of 43 year old male, hypertensive on medication, came for routine check up, and has been diagnosed to have poor vision left eye since childhood, denies any history of trauma. Vision left eye 6/18, Anterior segment normal, Fundus left eye shows excavated ,funnel-shaped optic nerve head, with central tuft of glial tissue obscuring the cup . The retinal vessels were seen emanating from the edge of disc in radial manner. In addition, the sectoral nasal retina shows localized area of hyperpigmented bony spicules like lesions. However, no history of nyctalopia or any other neurological disorder could be obtained.
Photographer: Nidhi Panwar, NMC Royal hospital, Sharjah , UAE
Imaging device: OPTOMAP
Condition/keywords: Morning Glory Anomaly, optic disc excavation
-
 PPCRA
PPCRA
Jan 31 2024 by Pallavi Goel
A 14-year-old male, presented to our clinic for a regular ophthalmic examination. Both Eyes Best Corrected Visual Acuity was 6/6, N6. The Indirect Ophthalmoscopic examination revealed an incidental finding in both eyes with patches of chorioretinal atrophy and pigment clumps along the veins consistent with pigmented paravenous chorioretinal atrophy (PPCRA) with early attenuation of retinal vessels, normal discs, and macula. ERG was normal. The patient was counseled and explained the nature of his condition. He was asked to be in yearly follow-up.
Photographer: Pallavi Goel, Dr. Shroff's Charity eye hospital,Delhi
Condition/keywords: ERG
-
Morning Glory Disc
Sep 21 2023 by Ben Serar
Fundus photograph showing funnel shaped optic disc with radiating retinal vessels in a case of Morning glory syndrome.
Condition/keywords: Morning Glory Syndrome
-
Tortuous Retinal Vessels
Sep 14 2023 by Ben Serar
Fundus photograph of the LE showing tortuous retinal vessels.
Condition/keywords: Tortuous Retinal Vessels
-
Tortuous Retinal Vessels
Sep 12 2023 by Ben Serar
Fundus photograph of RE showing tortuous retinal arteries and veins.
Condition/keywords: tortuous vessels
-
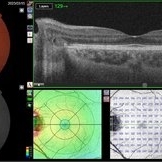 Situs-Inversus-Left-eye
Situs-Inversus-Left-eye
Mar 29 2023 by Nizamuddin HM Shaik, MD, FRCS
Situs inversus of the optic disc is a rare, usually bilateral, congenital embryological abnormality associated with high myopia, optic disc coloboma or tilted optic disc. Our patient, 24 years old lady without these conditions presented with bilateral situs inversus. Her BCVA OD 0.4 and OS 0.5. It is characterized by emergence of the retinal vessels in an anomalous direction with dysversion of the optic disc.
Photographer: Mahmoud A Abdelmaguid
Condition/keywords: Nasalization of temporal retinal vessels
-
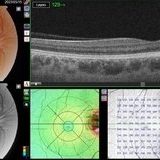 Situs-Inversus-OD
Situs-Inversus-OD
Mar 29 2023 by Nizamuddin HM Shaik, MD, FRCS
Situs inversus of the optic disc is a rare, usually bilateral, congenital embryological abnormality associated with high myopia, optic disc coloboma or tilted optic disc. Our patient, 24 years old lady without these conditions presented with bilateral situs inversus. Her BCVA OD 0.4 and OS 0.5. It is characterized by emergence of the retinal vessels in an anomalous direction with dysversion of the optic disc.
Photographer: Mahmoud A Abdelmaguid
Condition/keywords: Nasalization of temporal vessels
-
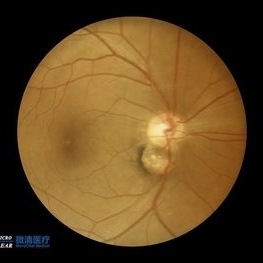 Double disc sign
Double disc sign
Oct 13 2022 by Vaibhavi Noticewala, M S Ophthalmology, FVRS
Double disc sign Doubling of the optic disc is rare and can manifest as true or pseudo doubling. Duke-Elder describes duplication of the optic disc as a rare anomaly wherein two discs, each provided with retinal vessels are seen in an otherwise normal eye. Rare cases of true duplication of optic discs with separation of optic nerve into two or more strands have been reported, based either on incidental necropsy findings, demonstration of two optic foramina in the same orbit on x ray, or angioscotomas as indirect evidence of the existence of double optic nerves. Pseudo doubling of the optic discs caused by lesions such as optic disc coloboma, peripapillary chorioretinal coloboma, or inflammatory foci are more common. Our case had Ipsilateral isolated ectatic peripapillary chorioretinal coloboma simulating double optic discs.
Photographer: Priyal Mistry
Condition/keywords: Pseudoduplication of optic disc
-
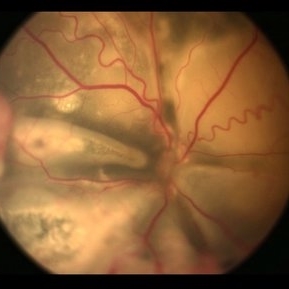 Stage 3 Coats' Disease
Stage 3 Coats' Disease
Aug 7 2022 by Muhammad Amer Awan, MD, FRCSEd, FRCOphth, FRCS Glasgow, FACS, FASRS
Fundus photography of a 6 months old baby boy who presented with unilateral leucoria. There was right exudate retinal detachment with extensive hard exudates and tortuous retinal vessels. Diagnosis of Coats' disease was made that was externally drained and intravitreal rhanibizumab was given.
Photographer: Muhammad Amer Awan, Shifa Taamer e Millat University
Condition/keywords: Coats' disease, exudative retinal detachment, exudative retinopathy, unilateral exudative retinal detachment
-
Racemose Hemangioma
Apr 7 2022 by Sengul Ozdek, MD, FEBO, FASRS
This is a fundus picture of a case with Racemose hemangioma. It is a rare sporadic congenital arteriovenous malformation, with unilateral involvement. It is characterized by a dilated, tortuous, tangled network of retinal vessels, mostly emerging from the optic disc and extending towards periphery, with no distinction between arterioles and venules.
Photographer: Refiye Basdogan
Imaging device: Canon
Condition/keywords: congenital arteriovenous malformation, Racemose hemangioma
-
 Tortuous Retinal Vessels
Tortuous Retinal Vessels
Apr 29 2021 by Giselle DeOliveira
Infared photograph of 30-year-old male with tortuous retinal vessels .
Photographer: Giselle DeOliveira
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: tortuous vessels

 Loading…
Loading…