Search results (14 results)
-
 IOFA-ROP
IOFA-ROP
Dec 21 2023 by Nassim Alejandro Abreu Arbaje, MD
Frame grab of a 2 months old baby with advance ROP. The patient had intraoperative angiography done during the vitrectomy to correctly evidence all the ischemic retinal tissue.
Photographer: Nassim Abreu, Hospital Dr. Elías Santana
Imaging device: NGenuity 3D system
Condition/keywords: intraoperative fluorescein angiography, IOFA, rop retinal detachment
-
 Spent-force
Spent-force
Jun 27 2023 by Maneesh M Bapaye, MD, MBA
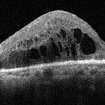
Composite OCT image of left eye of a 53 years old male diabetic patient with recuuent spongy diabetic macular edema. Structural image depicts presence of ozurdex temporal to fovea. B-Scan image shows localized action of ozurdex in retinal tissue underlying it while cystoid changes are seen nasal to foveal center
Photographer: Maneesh Bapaye MD
Condition/keywords: diabetic macular edema, Ozurdex implant
-
 Choroid hemangioma
Choroid hemangioma
Sep 7 2022 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
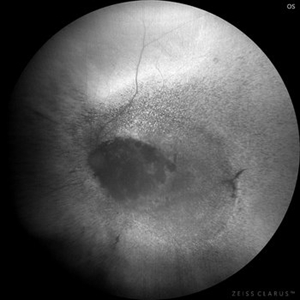
Patient 54 years old, Female, progressive loss of vision. In the multimodal evaluation of the retina showed important retinal alterations. A discreet opacity of the media impairs the quality of the images. In the Autofluorescent Background Image with a green filter, because it reaches a depth in the retinal tissue, it is able to show changes that affect the retinal pigment epithelium, it was better in this case than with the green filter. WF retinography shows an elevated, slightly reddish lesion, probable serous retinal detachment, mobilization of pigments and phantom vessels.
Photographer: JEFFERSON ROCHA DE SOUSA - Retinal Department at Instituto Dr. Suel Abujamra Sao Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: Clarus 700 - Zeiss 135 degree images. Multimodal Evaluation
Condition/keywords: elevated retinal lesion, hemangioma, melanoma, serous retinal detachment
-
 Choroid hemangioma
Choroid hemangioma
Sep 7 2022 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
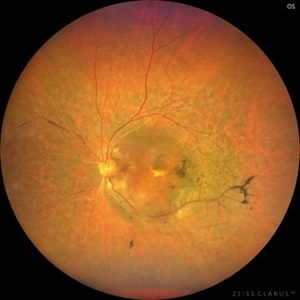
Patient 54 years old, Female, progressive loss of vision. In the multimodal evaluation of the retina showed important retinal alterations. A discreet opacity of the media impairs the quality of the images. In the Autofluorescent Background Image with a green filter, because it reaches a depth in the retinal tissue, it is able to show changes that affect the retinal pigment epithelium, it was better in this case than with the green filter. WF retinography shows an elevated, slightly reddish lesion, probable serous retinal detachment, mobilization of pigments and phantom vessels.
Photographer: JEFFERSON ROCHA DE SOUSA - Retinal Department at Instituto Dr. Suel Abujamra Sao Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: Clarus 700 - Zeiss 135 degree images. Multimodal Evaluation
Condition/keywords: elevated retinal lesion, hemangioma, melanoma, serous retinal detachment
-
 Congenital Toxoplasmosis Macular Scarring
Congenital Toxoplasmosis Macular Scarring
Nov 6 2021 by Emmanouil Gavalas, MD
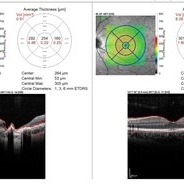
Right eye OCT image showing atrophy and loss of foveal neuroretinal tissue and RPE.
Photographer: Emmanouil Gavalas MD, Ophthalmos Reseach and Educational Institute,Nicosia,Cyprus
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis OCT
Condition/keywords: congenital toxoplasmosis, macular scar, ocular toxoplasmosis
-
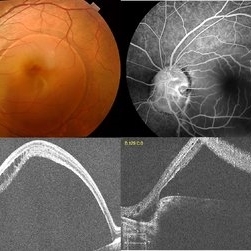 Optic Disc Pit with Coloboma (Hybrid Anomaly)
Optic Disc Pit with Coloboma (Hybrid Anomaly)
Jun 10 2021 by Janani Sreenivasan
Optic disc pit is a rare anomaly of the optic nerve head that can be associated with maculopathy leading to progressive visual deterioration. It belongs to the spectrum of congenital cavitary anomalies of the optic disc which encompasses extrapapillary cavitation, optic disc coloboma, and morning glory. Very rarely, optic disc pits are seen in combination with optic disc colobomas. Histopathologically, disc pit is defined as herniation of dysplastic retinal tissue into an excavation, rich in collagen, which can stretch into the subarachnoid space via a defect in the lamina cribrosa. Interestingly, this structural abnormality leading to a non-physiological communication between the intraocular and extraocular spaces is a common feature among all the congenital cavitary disc anomalies. Optic disc pit maculopathy is characterized by intraretinal and subretinal fluid at the area of macula. The origin of the retinal fluid remains unclear. Possible sources include the vitreous cavity, the subarachnoid space and the orbital space surrounding the dura. It has been estimated that approximately 25% to 75% of patients will develop serous detachment and/or retinoschisis of the central macula at some stage of their life. On fundus examination, ODPs typically appear as single grayish, round or oval depressions at the optic disc. Most commonly, they are detected at the inferotemporal segment of the disc, but may also be observed elsewhere, including the central area.The coexisting macular detachment can be related to lamellar or full-thickness macular holes, cystoid changes, retinal pigment epithelium atrophy and eventually to irreversible loss of vision,especially in longstanding cases. Herewith, we present a 32-years-old male patient presenting with an unusual combination of optic disc pit with maculopathy and optic disc coloboma (hybrid anomaly) in the same eye with corrected visual acuity of 3/60.
Photographer: Dr Janani Sreenivasan
Imaging device: Zeiss Cirrus HD-OCT
Condition/keywords: coloboma of optic disc, hybrid anomaly, macular detachment, optic disc, optic disc pit
-
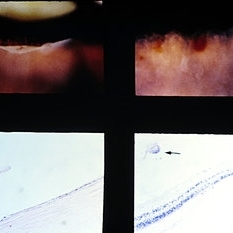 Slide 8-19
Slide 8-19
Mar 4 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Traumatic retinal dialysis in a 15-year-old male who died 2 weeks following a motorcycle accident. Upper left shows dialysis of the retina at the ora serrata. Upper right shows hemorrhage In the retina of the fellow eye. Sections through dialysis (lower views) show the detached vitreous base with a small tag of adherent retinal tissue (arrow). (E.P. No. 32955)
Condition/keywords: hemorrhage, ora serrata, retinal dialysis
-
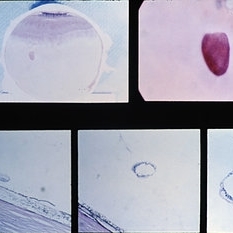 Slide 8-6
Slide 8-6
Mar 4 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Gross and microscopic appearance of a retinal hole. Vitreous tractim has resulted in the hole and detachment of the operculum. Upper right shows the plug of retinal tissue (arrow) attached to the posterior aspect of the detached vitreous. Lower left shows the rounded posterior margin of the retinal hole and the small area of associated retinal detachment. Lower middle and right views are of sections through the detached retinal operculum. (E.P. No. 35238)
Condition/keywords: operculum, retinal hole, retinal tissue
-
 OCT of Papillomacular Fold in Posterior Microphthalmos
OCT of Papillomacular Fold in Posterior Microphthalmos
Jul 30 2014 by Jordan L. Heffez, MD
OCT from a healthy 47-year-old gentleman with BCVA 20/50 OU and no known past ocular history. Note the lack of epiretinal tissue as a cause of retina malformation.
Condition/keywords: macular fold
-
 Choroideremia
Choroideremia
Jan 26 2013 by Ratimir Lazic, MD, PhD
FAG image of a 66-year-old male. Diffuse chorioretinal atrophy is present. Large choroidal vessels can be seen. "Hyperflorescent" areas represent normal chorioretinal tissue.
Photographer: Marko Lukic, MD
Imaging device: Zeis Visucam Lite 2
Condition/keywords: choroideremia, fundus photograph
-
 Choroideremia
Choroideremia
Jan 26 2013 by Ratimir Lazic, MD, PhD
Color fundus photography of a 66-year-old male. Diffuse chorioretinal atrophy is seen. “Patches” or retinal tissue can be seen, some of it in macular area. Visual acuity on that eye is 0,15.
Photographer: Marko Lukic, MD
Imaging device: Zeis Visucam Lite 2
Condition/keywords: choroideremia, large choroidal vessels
-
 Endoscopy: Infusion Cannula Positions
Endoscopy: Infusion Cannula Positions
Dec 11 2012 by Yale L. Fisher, MD
Infusion cannula positions can be visualized with the endoscope, especially useful when microscopic views are limited or impossible as in this short movie. Here, the infusion cannula had been placed in a standard fashion but endoscopic imaging reveals partial engagement of peripheral retinal tissue. Manipulation of the tip under endoscopic viewing eliminates the undesired engagement and reveals the proper infusion position with no obstruction.
Condition/keywords: endoscopy, infusion cannula positions, video
-
 Laser Photocoagulation
Laser Photocoagulation
Nov 9 2012 by Norman Byer
This shows the same lesion 11 days following laser photocoagulation. Still more new hemorrhages can now be seen, and the retinal tissue in the center of the lesion is being visibly pulled forward. If you look carefully, you can see the sharp lower edge of a developing tractional horseshoe tear.
Condition/keywords: laser photocoagulation, retinal tissue, vitreous traction
-
 Pseudo Retinal Break
Pseudo Retinal Break
Nov 9 2012 by Norman Byer
This 23-year-old man presented with a fresh retinal detachment in a highly myopic eye and this very unusual retinal appearance. You can see two reddish areas with fairly distinct borders which at first make us think of retinal breaks. However, the left area has two tiny vessels visible in it, and the right area shows visible translucent retinal tissue extending across it. This patient has extensive areas of paving stone degeneration. Usually, such lesions present a barrier to a detaching retina and areas of paving stone usually remain attached. However, in this photograph we can see two paving stone lesions, and the detachment has extended right through them peeling them off from the underlying pigment epithelium. The two reddish areas, therefore, represent the very thin retina which previously constituted part of two paving stone lesions. The yellow atrophic areas which are visible deep to the detached retina represent the deeper parts of the same two original paving stone lesions.
Condition/keywords: myopic eye, pigment epithelium, reddish lesion, yellow atrophic area

 Loading…
Loading…