-
 By McGill University Health Centre
By McGill University Health Centre
The MUHC-McGill University
Co-author(s): Sabrina Bergeron, P. Zoroquiain, E. Esposito, S. Corredor Casas, P. Logan, A. N. Odashiro, Miguel N. Burnier, Paulina García de Alba Graue, McGill University Health Center-McGill University Ocular Pathology & Translational Research Laboratory - Uploaded on May 18, 2020.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on May 19, 2020.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Retinoblastoma
- Condition/keywords
- retinoblastoma
- Description
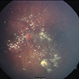
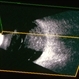
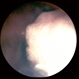
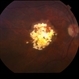
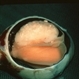
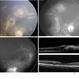
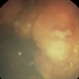
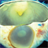
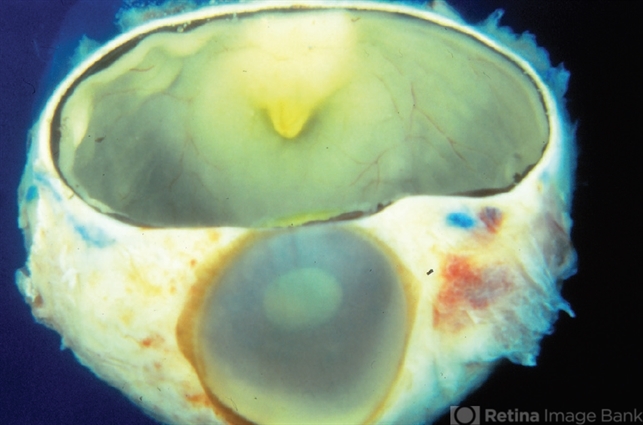
- Retinoblastoma is the most frequent intraocular tumor in children. It usually affects patients younger than 2 years. Leukocoria is the major clinical sign. The tumor arises in the sensory retina, and can be endophytic, exophytic, or diffuse. The molecular signature is the inactivation of both copies of the retinoblastoma gene on chromosome 13. In this enucleation specimen, the eye is sectioned to show the posterior pole and above the optic nerve, revealing an endophytic tumor; the rest of the retina is diffusely infiltrated. Note the retinal vessels overlying the area of the tumor.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.