-
 By Arwa Azmeh, MD, PhD
By Arwa Azmeh, MD, PhD
Damascus University, Faculty of medicine - Uploaded on May 16, 2014.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on May 16, 2014.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Miscellaneous
- Condition/keywords
- macular infarction, subconjunctival gentamicin
- Imaging device
-
Fundus camera
OCT - Description
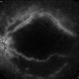
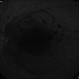
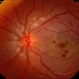
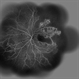
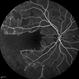
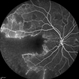
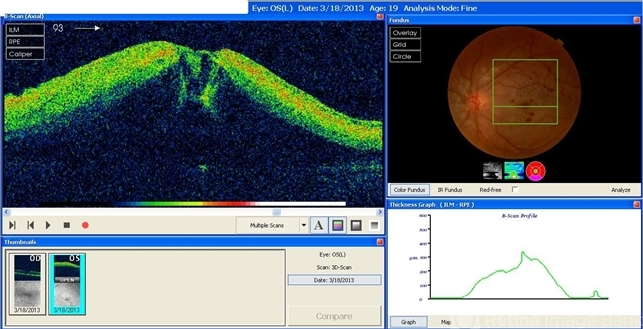
- A 20-year-old male suffered from diplopia since age one. He was diagnosed to have acquired fourth nerve palsy in his left eye. VA at time of diagnosis was 20/20 in OU and fundus exam was WNL in OU. His history reaveled no other complaints. 3 days ago he underwent left superior oblique tucking for relief of his diplopia.The surgery was uneventful and at the end of surgery subconjunctival gentamicin was injected. Immediately following surgery his VA in OS decreased from 20/20 to complete loss of central vision and sensation of HM from the periphery. He was referred to us 3 days after surgery. At time of referral fundus exam of his left eye revealed macular infarction with cherry red spot appearance with few retinal hemorrhages , mild optic disc edema and CWS surrounding optic disc. Peripheral retina had normal color and appearance. The vitreous was clear. Anterior segment was quiet. IOP was WNL. Macular OCT was consistent with macular infarction. FA revealed delay in central retinal artery filling as fluorescein started to appear in the arteries at the level of the optic disc at 28 sec, and in the retinal veins at 38 sec. Macular area remained to be non-perfused throughout the whole FA. In late phases staining of blood vessels walls was noticed. The "wipe out" of large vessels and capillaries persisted in the central area. OCT through foveal area showed diffuse thickening of the retina with severe elevation in the fovea, reduced backscattering from the outer layers of the retina and enhanced reflectivity from the inner retina, due to ischemia. Complete blood count and cardiovascular study were WNL. The final diagnosis was macular infarction secondary to subconjunctival gentamicin injection.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)