-
 By Dhaivat Shah
By Dhaivat Shah
Sankara Nethralaya
Co-author(s): Dr Achal Singhal, Dr Mradula Gangwar - Uploaded on Feb 24, 2023.
- Last modified by Joshua Friedman on Feb 27, 2023.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Imaging marvels
- Condition/keywords
- OCTA, RAP lesion, feeder vessel
- Photographer
- Choithram Netralaya, Indore
- Imaging device
- Optical coherence tomography system
- Description
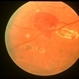
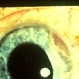
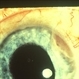
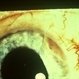
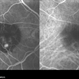
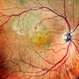
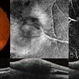
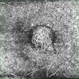
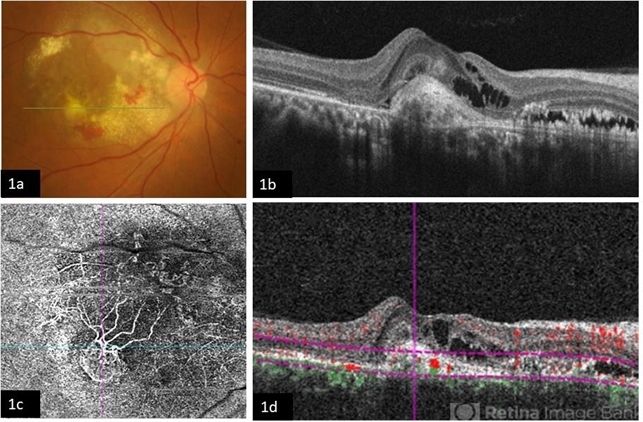
- A 58-year-old male patient, a chronic smoker, came to our OPD with complaints of a diminution of vision in the right eye (BCVA: 2/60). On examination, the following findings were observed in the patient. On fundus examination (Image 1a) - Large areas of exudation with multiple superficial and deep hemorrhages at the macula were noted. On SD-OCT imaging (Image 1b) - Multiple intraretinal spaces were seen along with shallow subretinal fluid and hyperreflective dots (indicative of phagocytosed photoreceptors). On the foveal area- a hyperreflective membrane was noted which seemed to dip down and establish a retino-choroidal anastomosis. On OCT-A imaging (Image 1c) - In the ORCC complex, the neovascularization frown, correlating with the membrane complex on the fundus and structural OCT, was visible which was noted to be supplied by small feeder vessels coming from the superior aspect of the fovea. On OCT-A blood flow analysis imaging (Image 1d) - The blood flow analysis showed increased blood flow signals at the level of the membrane (indicative of increased color signal). Based on the findings of the above investigations and clinical examination, the patient was diagnosed with a Case of CNVM Type 3, also described as RAP, and was managed by Anti VEGF injections. This condition usually requires more injections as compared to Type 1 and 2 CNVMs, and the visual prognosis is guarded. Hence, it's very important to counsel the patient before initiating the treatment that the treatment would be long-term and the aim would be preservation of existing vision.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)