Search results (309 results)
-
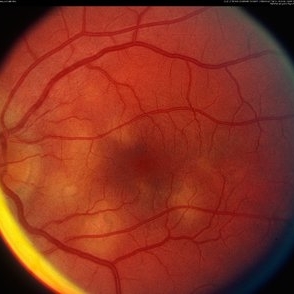 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment
Mar 4 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
Multiple posterior placoid subretinal lesions in the left eye #2.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Jan 4 2019 by Cláudia Farinha
Composite image of both eyes of a 27-year-old male with APMPPE. In the fundus photograph, multiple yellowish placoid lesions are observed in the posterior pole in both eyes. The ICGA revealed more lesions than those observed in fundoscopy, and these were hypofluorescent through the angiogram as expected. The en face OCTA segmented at the level of the choriocapillaris revealed areas of ischemia in close correspondence with the hypofluorescent lesions (image superimposed in ICGA ). The OCT b-scan with superimposed flow shows disruption and hyperreflectivity of the external retinal layers in the affected areas and again the absence of flow in the choriocapillaris underneath. A systemic study was carried out to exclude other inflammatory and infectious causes of placoid retinochoroidopathy. The clinical picture resolved after approximately one month from the onset, without recurrence.
Photographer: Pedro Melo, Ophthalmology Department, Centro Hospitalar e Universitário de Coimbra, Coimbra Portugal
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
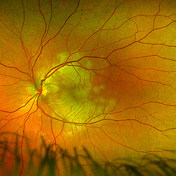 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Optos color fundus photograph of a 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). Imaging of her left eye shows multiple bilateral creamy yellow-white placoid lesions at the level of RPE and choroid throughout the posterior pole.
Photographer: Ashley Metzger, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Imaging
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), bacilliary layer detachment, Optos, uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
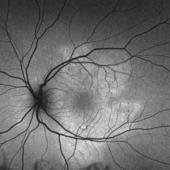 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Optos fundus autofluorescence photograph of a 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). Imaging of her left eye shows hypoautofluorescent areas corresponding to multiple bilateral placoid lesions at the level of RPE and choroid throughout the posterior pole.
Photographer: Ashley Metzger, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Autoflurescence Imaging
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), autofluorescence imaging, bacilliary layer detachment, Optos, OPTOS CALIFORNIA, uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
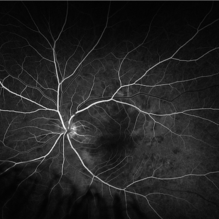 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Fluorescein angiogram of a 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). Early blockage with late hyperfluorescent leakage can be seen on fluorescein angiography of the left eye.
Photographer: Ashley Metzger, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), bacilliary layer detachment, FA, FA early phase, fluorescein angiogram (FA), Optos, uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
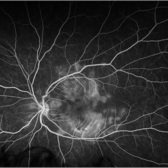 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
Fluorescein angiogram of a 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). Early blockage with late hyperfluorescent leakage can be seen on fluorescein angiography of the left eye.
Photographer: Ashley Metzger, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: Optos Ultra-Widefield Fluorescein Angiography
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), bacilliary layer detachment, FA, FA late phase, FA late phase leakage, fluorescein angiogram (FA), Optos, uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
A 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). OCT of the left macula shows bacillary layer detachment.
Photographer: Kim Seay, Elman Retina Group
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), bacilliary layer detachment, OCT, Uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
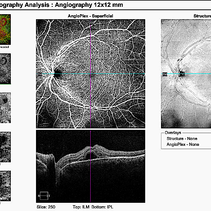 Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 20 2024 by Soobien Lee
12x12mm OCT Angiography of a 20-year-old caucasian female with viral prodrome and vision loss OS>OD secondary to Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy (APPME). Imaging shows multifocal flow voids.
Photographer: Kim Seay, Elman Retina Group
Imaging device: 12x12mm OCT-Angiography
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), bacillary layer detachment, OCT, OCT Angiography, Uveitis, white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE, red free imaging: right eye #1.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE. F/A .Late hyperfluorescence and staining of the lesions apparent #3.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE fundus photographs. Right Eye multiple placoid yellowish subretinal lesions #1.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE, fundus photographs. Left eye: Multiple placoid subretinal yellow - white lesions #2.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy Late Stage Scar Formation
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy Late Stage Scar Formation
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE late stage scar formation. Right Eye Multiple scar formations occurs in some of the patients #1
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), late stage, white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Late Stage
Acute Posterior Multifocal Placoid Pigment Late Stage
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE late stage scar formation.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), late stage, white dot syndrome
-
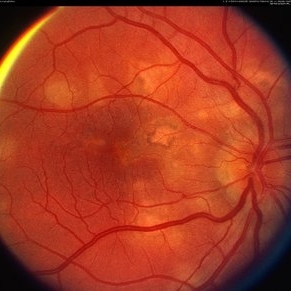 Acute Posterior Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Acute Posterior Placoid Pigment Epitheliopathy
Mar 4 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE; right eye; transition from acute stage to residual scar formation in some of the lesions. #1
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
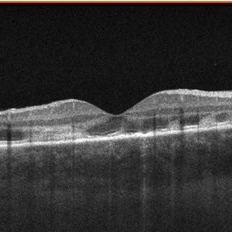 APMPE
APMPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
One week later, same slice as initial scan.
Imaging device: cirrus
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
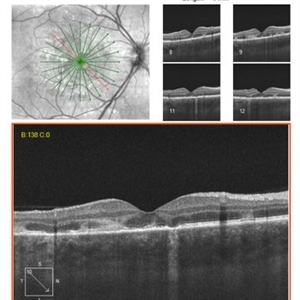 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
One week later, same slice as initial scan.
Imaging device: cirrus
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
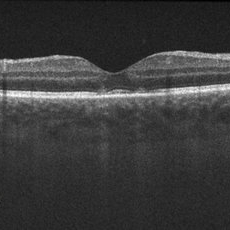 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
Initial scan
Imaging device: cirrus
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
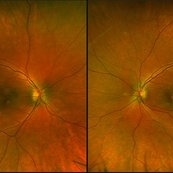 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
Initial pics.
Imaging device: optos
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
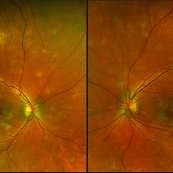 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
About a week later
Imaging device: optos
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
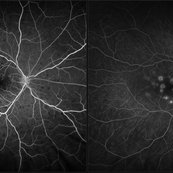 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
Mid and late FA - initial presentation
Imaging device: optos
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
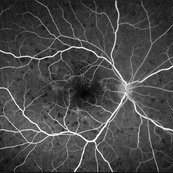 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
30 sec - initial visit.
Imaging device: optos
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
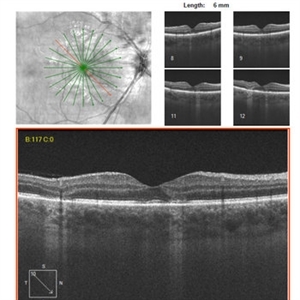 APMPPE
APMPPE
Dec 14 2017 by John S. King, MD
Initial scan.
Imaging device: cirrus
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) APMPPE Late Stage Scar Formation
APMPPE Late Stage Scar Formation
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE late stage, multiple scar formation, left eye #2.
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), late stage, white dot syndrome
-
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$300,300.ImageHandler) APMPPE Late Stage Scar Formation
APMPPE Late Stage Scar Formation
Feb 27 2013 by Henry J. Kaplan, MD
APMPPE late stage scar formation. F/A hypofluorescence in the lesions area is due to masking effect of pigments . #1
Condition/keywords: acute posterior multifocal placoid pigment epitheliopathy (APMPPE), late stage, white dot syndrome

 Loading…
Loading…