Search results (11 results)
-
Eye of the Hurricane
Apr 9 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
Ultrasound biomicroscopy of a post-operative eye (status post trabeculectomy and phacoemulsification) reveals a patent ostium on the right side, along with an intraocular lens in position. A hyphema is observed displaying small convection currents, creating a circular motion pattern due to the temperature gradient between the iris and cornea. Notably, the blood flow can be seen circulating toward the trabeculectomy site.
Condition/keywords: hyphema, trabeculectomy
-
 Eye of the Hurricane
Eye of the Hurricane
Apr 8 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
Ultrasound biomicroscopy of a post-operative eye (status post trabeculectomy and phacoemulsification) reveals a patent ostium on the right side, along with an intraocular lens in position. A hyphema is observed displaying small convection currents, creating a circular motion pattern due to the temperature gradient between the iris and cornea. Notably, the blood flow can be seen circulating toward the trabeculectomy site.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: Hyphema, trabeculectomy
-
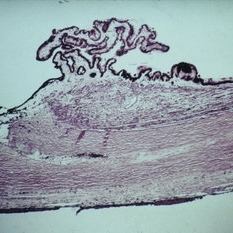 Slide 7-114
Slide 7-114
Feb 25 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Trabeculectomy. A small defect is present in the area of the trabecular meshwork and is continuous with a linear tract in the sclera.
Condition/keywords: sclera, trabecular meshwork, trabeculectomy
-
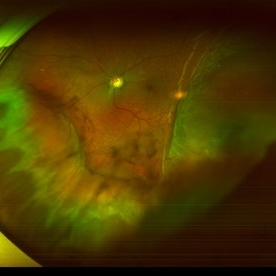 Suprachoroidal Hemorrhage
Suprachoroidal Hemorrhage
Sep 2 2020 by Rinal Pandit
Fundus photograph of left eye of a 56-year-old female with primary angle closure glaucoma showing massive hemorrhagic choroidal detachment that developed following trabeculectomy surgery. Suprachoroidal hemorrhage is defined as the accumulation of blood within the potential space between the choroid and sclera, with the source of the blood being the long or short posterior ciliary artery. Delayed suprachoroidal hemorrhage (DSHC) remains one of the most dreaded and sight threatening complications of glaucoma filtration surgery. The risk factors include old age, hypertension, high myopia, arteriosclerosis, chronically elevated IOP, sudden hypotony, trauma, aphakia/pseudophakia, prior vitrectomy, history of 5 FU injections and anti-platelet agents. The incidence of postoperative SCH after trabeculectomy varies between 0.6%- 1.4%. DSCH after surgery varies considerably in severity but is generally characterized by the sudden onset of severe pain, decreased vision, and a shallow anterior chamber usually associated with raised intraocular pressure. B-scan ultrasonography can help to distinguish serous from hemorrhagic choroidals.Suprachoroidal hemorrhages appear as dome-shaped elevations of the retina with increased echo densities that are often heterogeneous and within the suprachoroidal space. Choroidal effusions appear as dome-shaped elevations with hypoechoic suprachoroidal space. The first step in the management is the timely diagnosis. Medical management includes oral and topical antiglaucoma drugs to lower IOP, oral and topical steroids to control inflammation and topical cycloplegics and oral analgesics to tackle pain. Serial ultrasound B scans of the affected eye should be performed in order to monitor progression of the SCH and help determine apposition, height, and liquefaction of the SCH. Indications of surgical drainage include non resolution with medical management,concurrent retinal detachment, central retinal apposition (kissing choroidals) and incarceration of vitreous in the wound site. The ideal time of drainage is between 7-14 days depending upon clot lysis. The prognosis of both intraoperative and postoperative SCH is poor. An overwhelming majority of patients do not achieve pre-hemorrhage visual acuity and most do not recover to a visual acuity of 20/200 or better. The major determinants of good or bad visual outcomes of SCH’s are preoperative visual acuity and retinal detachment at the time of hemorrhage, respectively.
Imaging device: OPTOS,Ultra wide field retinal imaging system
Condition/keywords: suprachoroidal hemorrhage, trabeculectomy, ultra-wide field imaging
-
 Bleb-related Endophthalmitis Slide 1
Bleb-related Endophthalmitis Slide 1
Oct 22 2012 by Ronald C. Gentile, MD
Patient with a history of glaucoma status post trabeculectomy 3 years prior presented with pain, redness, and loss of vision in the left eye. A limbal infected bleb can be seen superior temporal adjacent to the iridectomy.
Photographer: The New York Eye & Ear Infirmary Department of Medical Imaging
Condition/keywords: Bleb-related endophthalmitis
-
 Choroidal Detachment
Choroidal Detachment
Oct 1 2021 by Marcelo Zas, MD PhD
Right eye from a 65-year-old patient with a choroidal detachment post trabeculectomy.
Photographer: Zas Marcelo MD, PhD
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: choroidal detachment, post-trabeculectomy
-
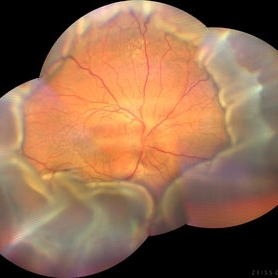 Choroidal Detachment
Choroidal Detachment
Aug 14 2024 by STEFANY DAVILA
Montage of fundus photography of an elderly male with choroidal detachment 360 degrees after trabeculectomy surgery.
Photographer: Stefany Dávila Avila, Instituto Mexicano de Oftalmología, Querétaro
Imaging device: Zeiss Clarus 700
Condition/keywords: Choroidal, detachment
-
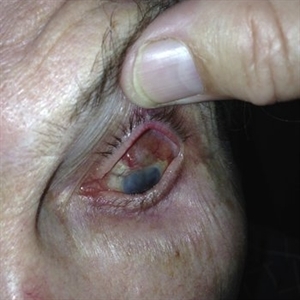 Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis
Jul 12 2014 by Philip J. Polkinghorne, MD
A 75-year-old man who presented with reduced vision and pain 6 years following mitomycin assisted trabeculectomy.
Photographer: Philip Polkinghorne
Condition/keywords: endophthalmitis, post-trabeculectomy
-
Glaucoma
Feb 8 2018 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
Male patient, 61-years-old in follow-up of glaucoma has several years. She performed trabeculectomy surgery with a tube implant.
Photographer: JEFFERSON R SOUSA - Study Center and Ophthalmological Research Dr. Andre M V Gomes, Dr. Suel Abujamra Institute São Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: Fundus camera Acquisition of the image in the Camera background Topcon TRC-50 Dx - IA, field photo of 50 Degrees. Composition manual adjustment.
Condition/keywords: glaucoma
-
 Ocular Hypotony Due to Leaking Bleb
Ocular Hypotony Due to Leaking Bleb
Apr 1 2019 by Anfisa Ayalon, MD
81-year-old male who had trabeculectomy in his right eye 4 years ago, presented to the emergency room with complains of decreased vision in that eye for two months. Slit-lamp examination showed cystic bleb with leakage, intraocular pressure was 0 MMHg. Fundus examination showed hypotony maculopathy, peripheral choroidal detachments, multiple chorioretinal folds with subretinal fluid.
Photographer: Anfisa Ayalon, MD., Meir Medical Center, Kfar Saba, Israel.
Imaging device: California, Optos 200 DTX
Condition/keywords: choroidal detachment, hypotonous retinopathy, hypotony maculopathy
-
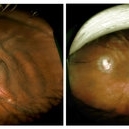 Scleral Infolding Due to Hypotony
Scleral Infolding Due to Hypotony
Feb 17 2015 by Danielle Strauss, MD FASRS
Wide field imaging of the left eye in a patient with scleral infolding due to hypotony from ruptured trabeculectomy. Left side image shows the eye prior to revision of the trabeculectomy and pars plana vitrectomy. Right side shows post-op image of the eye.
Photographer: Robert Masini, New York Eye and Ear Infirmary of Mount Sinai
Condition/keywords: hypotony

 Loading…
Loading…