Search results (4 results)
-
 Extensive Macular Atrophy with Pseudodrusen (EMAP)
Extensive Macular Atrophy with Pseudodrusen (EMAP)
Jul 2 2023 by Heitor Nogueira
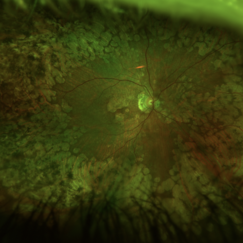
Fundus photograph of an 56-year-old woman with a macular atrophy caused by EMAP. We can also observe the presence of Paving stones grouped throughout the middle and extreme periphery.
Photographer: Heitor Nogueira, Instituto Penido Burnier, Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil.
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: macular atrophy, paving stone degeneration
-
 Extensive Macular Atrophy with Pseudodrusen (EMAP)
Extensive Macular Atrophy with Pseudodrusen (EMAP)
Jul 2 2023 by Heitor Nogueira
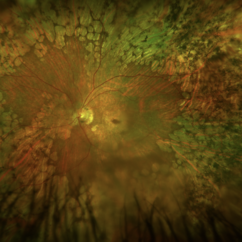
Fundus photograph of an 56-year-old woman with a macular atrophy caused by EMAP. We can also observe the presence of Paving stones grouped throughout the middle and extreme periphery.
Photographer: Heitor Nogueira, Instituto Penido Burnier, Campinas, São Paulo, Brazil.
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: macular atrophy, paving stone degeneration
-
 High Myopia with Cobblestone Degeneration
High Myopia with Cobblestone Degeneration
Nov 5 2019 by Nichole Lewis
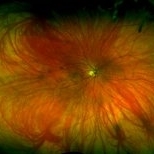
50-year-old female with high myopia, diffuse myopic thinning and cobblestone degeneration.
Photographer: Nichole Lewis
Imaging device: Optos
Condition/keywords: high myopia, myopia, paving stone degeneration
-
 Pseudo Retinal Break
Pseudo Retinal Break
Nov 9 2012 by Norman Byer
This 23-year-old man presented with a fresh retinal detachment in a highly myopic eye and this very unusual retinal appearance. You can see two reddish areas with fairly distinct borders which at first make us think of retinal breaks. However, the left area has two tiny vessels visible in it, and the right area shows visible translucent retinal tissue extending across it. This patient has extensive areas of paving stone degeneration. Usually, such lesions present a barrier to a detaching retina and areas of paving stone usually remain attached. However, in this photograph we can see two paving stone lesions, and the detachment has extended right through them peeling them off from the underlying pigment epithelium. The two reddish areas, therefore, represent the very thin retina which previously constituted part of two paving stone lesions. The yellow atrophic areas which are visible deep to the detached retina represent the deeper parts of the same two original paving stone lesions.
Condition/keywords: myopic eye, pigment epithelium, reddish lesion, yellow atrophic area

 Loading…
Loading…