-
 Senile Retinoschisis
Senile Retinoschisis
Jul 27 2021 by Dhaivat Shah
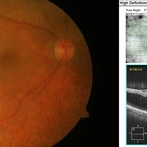
Senile retinoschisis is an acquired, idiopathic, degenerative condition of the neurosensory layer of the retina. It is characterized by separation at the outer plexiform layer or less commonly at the neurosensory layer of the retina. A 71-year-old male underwent cataract surgery in the right eye 1 week before his presentation to retina clinic. His chief complaint was minimal visual improvement after the surgery. His visual acuity in the right eye was 5/60 before cataract surgery and 6/60 after the surgery and no improvement with pinhole. On fundus examination of the right eye, an immobile, transparent subtle bullous elevation of the retina with minimal pigmentary changes was noted at the macula. The absence of a retinal tear , corrugations and demarcation lines differentiate it from rhegmatogenous retinal detachment. Optical Coherence Tomography is a confirmatory tool to diagnose senile retinoschisis. The OCT of this patient showed epiretinal membrane and coalescence of microcystic degenerations with splitting of the outer plexiform layer from rest of the outer retinal layers. Guarded visual prognosis was explained.
Photographer: Choithram Netralaya
Condition/keywords: optical coherence tomography (OCT), retinoschisis

A project from the American Society of Retina Specialists