-
 By McGill University Health Centre
By McGill University Health Centre
The MUHC-McGill University
Co-author(s): Sabrina Bergeron, P. Zoroquiain, E. Esposito, S. Corredor Casas, P. Logan, A. N. Odashiro, Miguel N. Burnier, Paulina García de Alba Graue, McGill University Health Center-McGill University Ocular Pathology & Translational Research Laboratory - Uploaded on May 18, 2020.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on May 19, 2020.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Adenocarcinoma
- Condition/keywords
- metastatic adenocarcinoma, breast cancer, tumor, foci of necrosis
- Description
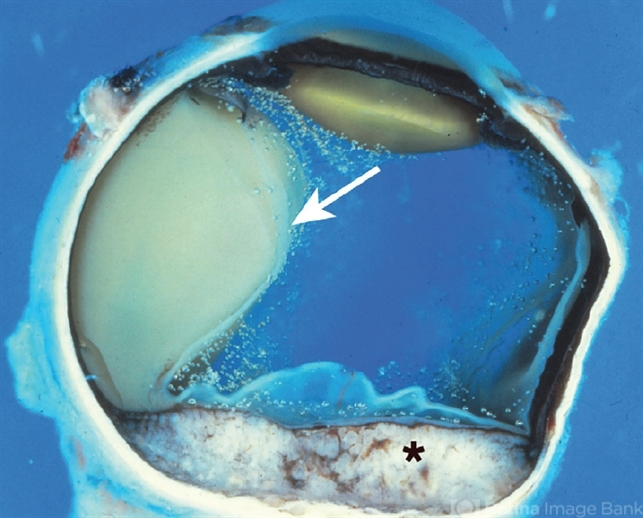
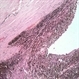
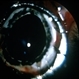
- Metastatic disease is the most frequent intraocular malignant tumor. In women, the most common origin is breast cancer. In men, the most common origin is lung cancer. This pupil–optic nerve section shows a whitish tumor with several foci of necrosis (*) occupying the posterior aspect of the choroid. Note the pigment epithelium over the inner surface of the tumor. A serous retinal detachment is present (arrow) with a retinal detachment artifact overlying the tumor and normal choroid. Note the air bubble artifacts in the vitreous cavity. Another artifact, the compression of the eyeball, is present on the right side.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)



---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)