-
 By McGill University Health Centre
By McGill University Health Centre
The MUHC-McGill University
Co-author(s): Sabrina Bergeron, P. Zoroquiain, E. Esposito, S. Corredor Casas, P. Logan, A. N. Odashiro, Miguel N. Burnier, Paulina García de Alba Graue, McGill University Health Center-McGill University Ocular Pathology & Translational Research Laboratory - Uploaded on May 18, 2020.
- Last modified by Caroline Bozell on May 19, 2020.
- Rating
- Appears in
- Leiomyoma
- Condition/keywords
- leiomyoma, tumor, enucleation
- Description
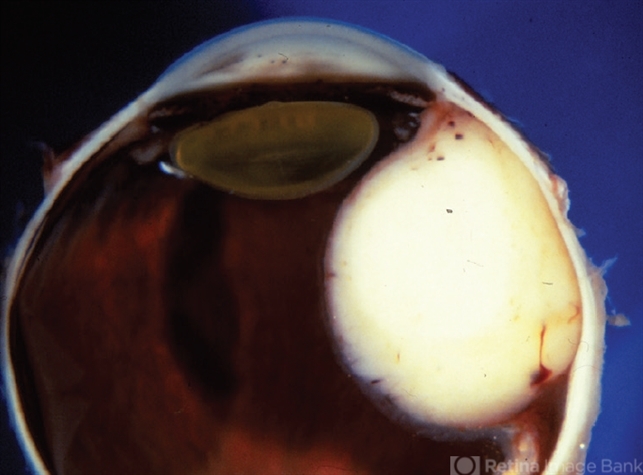
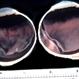
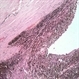
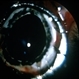
- Leiomyoma is a benign, smooth muscle tumor. Ninety percent of cases occur in women. The differential diagnosis includes amelanotic melanoma and nerve sheath tumors. This transversal pupil–optic nerve (PO) section of an enucleation specimen shows a nodular, well-delineated, whitish tumor in the ciliary body. The cut surface shows small foci of hemorrhage without necrosis. The retina partially covers the inner surface of the tumor, and the sclera is not infiltrated. Note the slightly displaced (subluxated) cataractous lens and the choroidal detachment artifact in the right inferior corner.

 Initializing download.
Initializing download.
---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)



---thumb.jpg/image-square;max$79,0.ImageHandler)