Search results (23 results)
-
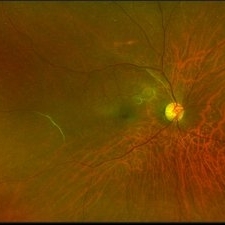 Vascular Sheathing
Vascular Sheathing
Dec 19 2019 by Lauren Schuler
Ultra-wide field pseudocolor fundus photograph of a 68-year-old female with vascular sheathing affecting her right eye. This was noted on initial exam on 1/15/16, at patient's first appointment. This remains unchanged and patient is asymptomatic at this time.
Photographer: Lauren Schuler
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: fundus photograph, ghost vessels, pseudocolor, vascular sheathing of retina
-
Branch Arterial Occlusion
Apr 12 2018 by Marco D'Angelo
Branch artery occlusion with collateral circulation (arterio-arterial vascular anastomosis) around the residual perfused branch. Left eye, 76-years-old male patient, normal visual acuity (20/20).
Photographer: Dr. Marco D'Angelo, S.Chiara Hospital, Trento, Italy
Imaging device: Topcon TRC-NW 6S
Condition/keywords: arteriovenous anastomosis, collateral retinal vessel, ghost vessels
-
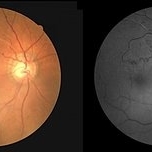 BRVO
BRVO
Sep 26 2018 by Andrea Arriola-Lopez, MD MSc
Color fundus and red free photographs OD. Ghost vessels and shunts are shown.
Photographer: Lourdes Guambo MD
Condition/keywords: branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO), ghost vessels, occlusion of retinal vein, shunts vessels
-
 Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OD - Color
Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OD - Color
Jun 28 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
70-year-old woman, seen for initial eye exam, with endstage PDR and H/O prior Focal/ PRP OU , somewhere else.
Imaging device: Optos - California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, focal laser, ghost vessels, optic atrophy, pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
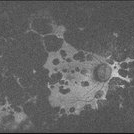 Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OD - FAF
Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OD - FAF
Jun 28 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
70-year-old woman, seen for initial eye exam, with endstage PDR and H/O prior Focal/ PRP OU , somewhere else.
Imaging device: Optos - California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, focal laser, ghost vessels, optic atrophy, pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
 Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OS - Color
Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OS - Color
Jun 28 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
70-year-old woman, seen for initial eye exam, with endstage PDR and H/O prior Focal/ PRP OU , somewhere else.
Imaging device: Optos - California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, focal laser, ghost vessels, optic atrophy, pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
 Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OS - FAF
Extensive/ Heavy Focal/ PRP OS - FAF
Jun 28 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
70-year-old woman, seen for initial eye exam, with endstage PDR and H/O prior Focal/ PRP OU , somewhere else.
Imaging device: Optos - California
Condition/keywords: chorioretinal scar, ghost vessels, laser scarring, optic atrophy, pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), retinal scar
-
 Ghost Retinal Vessel
Ghost Retinal Vessel
Aug 28 2017 by Bastián Schmidt Arias
Fundus photograph.
Photographer: TM. Bastian Schmidt
Imaging device: TRC-50DX - Topcon
Condition/keywords: fundus photograph, ghost vessels, retina
-
Ghost Retinal Vessel
Aug 28 2017 by Bastián Schmidt Arias
Fluorescein angiograma of ghost retinal vessel.
Photographer: TM. Bastian Schmidt
Imaging device: TRC-50DX - Topcon
Condition/keywords: ghost vessels, retina
-
Ghost Retinal Vessel
Aug 28 2017 by Bastián Schmidt Arias
Fluorescein angiograma of ghost retinal vessel.
Photographer: TM. Bastian Schmidt
Imaging device: TRC-50DX - Topcon
Condition/keywords: ghost vessels
-
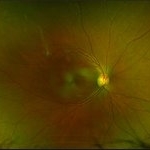 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel tractional vs combined tractional/rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with large neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (Not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached Ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control, etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, neovascularization elsewhere (NVE), tractional retinal detachment
-
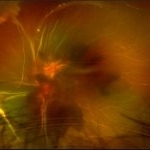 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel tractional vs combined tractional/rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with large neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (Not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached Ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischaemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachment
-
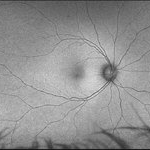 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel tractional vs combined tractional/rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with large neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (Not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control, etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachment
-
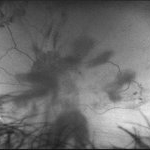 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with large Neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (Not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached Ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control, etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischaemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachment
-
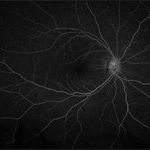 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with large neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (Not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached Ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control, etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischaemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachment
-
 Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Tractional vs Combined Tractional/Rhegmatogenous Retinal Detachment with Active Neovascularization OS
Jun 1 2018 by Hosam Attia, MD
47-year-old African American, with history of diabetes mellitus of unknown duration and control, was referred for initial evaluation for conjunctival laceration in his left eye, following accidental finger nail injury, 6 days prior to presentation. - On exam, his vision was 20/50 OD and Bare HM/ LP OS. - Fundus color photos OD: No significant pathology, aside from attenuated vasculature OS: Chronic, Mac-Off, almost closed funnel tractional vs combined tractional/rhegmatogenous retinal detachment with large neovascularization (NVE) superiorly, detached ghost vessels, mild fresh vitreous hemorrhage, sub-retinal bands and inferior white vitreous debris from old hemorrhage (not shown) - FA OD: No significant pathology aside from possible mild capillary non-perfusion in the extreme periphery, attenuated vasculature and possible tiny microaneurysms, nasally. OS: Extensive, wide spread capillary non- perfusion (correlate w/ detached Ghost vessels on color photos), and leakage from the NVE. - B/L Carotid Duplex was recommended due to the striking asymmetry in pathology with unknown medical history, diabetes duration and control, etc (even in absence of any signs suggestive of possible ocular ischemic syndrome OD)
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: combined retinal detachment, tractional retinal detachment
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows punctate hyperfluorescence and inferior RD. Ghost vessels are seen superior to the RD. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and RD.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows massive leak under inferior RD suggestive of severe choroidal inflammation and hyperpermability. Ghost vessels are seen superior to the RD. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and RD.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows massive leak under inferior RD suggestive of severe choroidal inflammation and hyperpermability. Ghost vessels are seen superior to the RD. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and RD.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows punctate hyperfluorescence, ghost vessels and disc hyperfluorescence. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows inferior RD with underlying choroidal hyperfluorescence and ghost vessels. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and RD.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows punctate hyperfluorescence and shadow/ ghost vessels. Disc hyperfluorescence is also seen. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and optic nerve head inflammation.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis
-
Uveitis With Exudative Retinal Detachment
May 3 2014 by Mallika Goyal, MD
Fluorescein angiogram of an elderly patient with bilateral posterior uveitis shows punctate hyperfluorescence and shadow/ ghost vessels. Disc hyperfluorescence is also seen. He responded well to oral steroids with complete resolution of the uveitis and optic nerve head inflammation.
Photographer: Mallika Goyal, MD, Apollo Health City, Jubilee Hills, Hyderabad, India
Condition/keywords: exudative retinal detachment, uveitis

 Loading…
Loading…