Search results (1584 results)
-
 Choroidal Detachment Secondary to Pan Retinal Photocoagulation Right Eye
Choroidal Detachment Secondary to Pan Retinal Photocoagulation Right Eye
Oct 14 2025 by NIDHI PANWAR, MD FRCS Glasgow FNB FICO
Serous choroidal detachment noted temporally after two sittings of pan retinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy right eye, which resolved in 1 week of observation and topical steroid drops.
Photographer: NIDHI PANWAR, NMC ROYAL HOSPITAL, SHARJAH
Imaging device: optos
Condition/keywords: choroidal detachment, laser photocoagulation, pan retinal photocoagulation, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
 Choroidal Detachment Secondary to Pan Retinal Photocoagulation Left Eye
Choroidal Detachment Secondary to Pan Retinal Photocoagulation Left Eye
Oct 14 2025 by NIDHI PANWAR, MD FRCS Glasgow FNB FICO
Serous choroidal detachment noted temporally after two sittings of pan retinal photocoagulation in proliferative diabetic retinopathy left eye, which resolved in 1 week of observation and topical steroid drops.
Photographer: NIDHI PANWAR, NMC ROYAL HOSPITAL, SHARJAH
Imaging device: OPTOS
Condition/keywords: choroidal detachment, laser photocoagulation, pan retinal photocoagulation, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
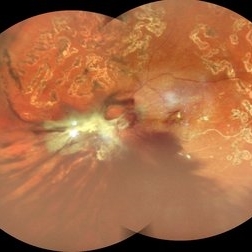 Table Top Tractional Retinal Detachment With Vitreous Hemorrhage in a Case of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Table Top Tractional Retinal Detachment With Vitreous Hemorrhage in a Case of Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Sep 12 2025 by Akansha Sharma
Color fundus photograph of a 56 year old male with table top tractional retinal detachment with vitreous hemorrhage in a case of proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: DR. AKANSHA SHARMA
Condition/keywords: pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), PDR, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), PRP, TABLE TOP TRD, tractional retinal detachment, TRD, VH, vitreous hemorrhage
-
 Optic Disc Neovascularization
Optic Disc Neovascularization
Sep 9 2025 by Seif Allah Anwar
A case of high risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy with large disc neovascularization.
Photographer: Dr Seif Anwar
Imaging device: Topcon
Condition/keywords: optic disc neovascularization
-
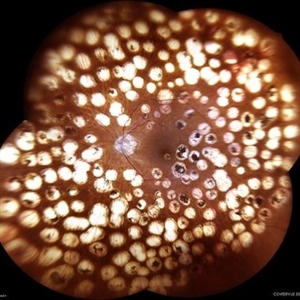 Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Aug 19 2025 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
Female patient, 74 years old, with a history of severe photocoagulated diabetic retinopathy in both eyes.
Photographer: JEFFERSON ROCHA DE SOUSA - Retinal Department at Lens Oftalmologia, Sao Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: EIDON fundus camera with a 110° field of view, confocal scanning technology. Widefield co-op with 6 images.
Condition/keywords: background diabetic retinopathy (BDR), Diabetic Retinopathy
-
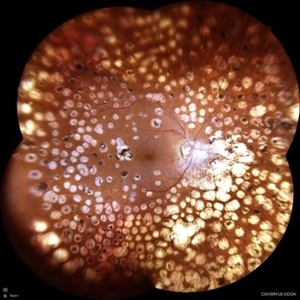 Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Aug 19 2025 by JEFFERSON R SOUSA, Tecg.º (Biomedical Systems Technology)
Female patient, 74 years old, with a history of severe photocoagulated diabetic retinopathy in both eyes.
Photographer: JEFFERSON ROCHA DE SOUSA - Retinal Department at Lens Oftalmologia, Sao Paulo-Brazil
Imaging device: EIDON fundus camera with a 110° field of view, confocal scanning technology. Widefield co-op with 4 images.
Condition/keywords: background diabetic retinopathy (BDR), Diabetic Retinopathy
-
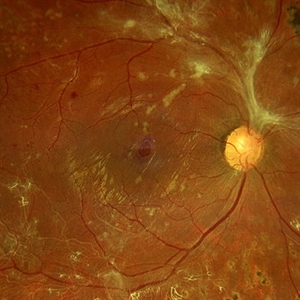 Macular Hole Due to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Macular Hole Due to Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Aug 13 2025 by Ricardo Leitão Guerra
A macular hole formation after anti-VEGF injection prior to vitrectomy for tractional retinal detachment in a patient presenting proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: Ricardo Leitão Guerra
Imaging device: ZEISS CLARUS 700
Condition/keywords: macular hole, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
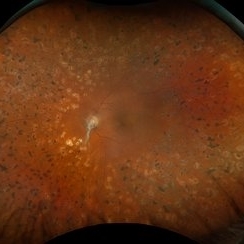 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Aug 11 2025 by Marin Shehata
Fundus photograph of a 63 year-old male with diabetic retinopathy has been treated with PRP.
Photographer: Marin Shehata, Retina Consultants of Carolina
Imaging device: Optos California
Condition/keywords: proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), PRP
-
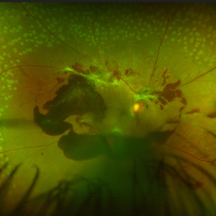 Unstable PDR s/p Laser
Unstable PDR s/p Laser
Aug 4 2025 by Anjana Mirajkar, MS Ophthalmology
Fundus photograph of a 60 year old male with an unstable PDR showing traction at the posterior pole with sub hyaloid hemorrhage. Peripheral PRP marks can be seen.
Photographer: Dr. Anjana Mirajkar- HV Desai eye hospital ,Pune
Imaging device: Optos
Condition/keywords: pan-retinal photocoagulation (PRP), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), subhyaloid hemorrhage, tractional retinal detachment
-
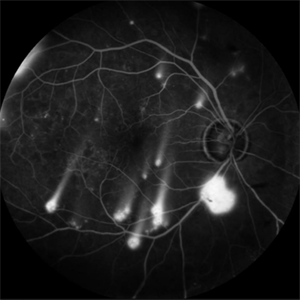 Shooting Stars
Shooting Stars
Jul 9 2025 by Majda Hadziahmetovic, MD
Fluorescein angiography image demonstrating multiple areas of neovascularization in a middle-aged male patient with long-standing diabetes.
Condition/keywords: proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
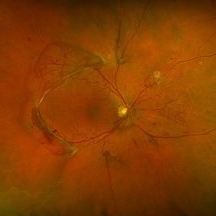 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Jul 9 2025 by Jeffrey Barker
57 year old male presents with Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Tractional Retina detachment.
Photographer: Jeffrey P. Barker, B.S. Retina Vitreous Surgeons of CNY
Condition/keywords: Diabetes, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), Traction retinal detachment
-
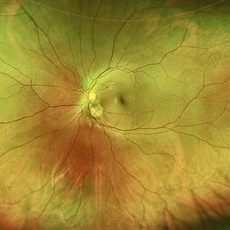 Pseudoduplication of the Optic Disc
Pseudoduplication of the Optic Disc
Jul 9 2025 by Hrishikesh Naik, MS
A peripapillary colobomatous pseudo-duplication of the optic disc as seen in an asymptomatic 23 year old female with myopia referred for routine retinal periphery screening. Rest retinal exam was normal. Duplication of the optic disc can be classified as either true duplication or pseudoduplication, both of which are rare clinical conditions. Pseudodoubling of the optic disc is commonly caused by optic disc or peripapillary colobomas, characterized by a circumscribed, disc-like lesion with radiating vessels but only one normal optic nerve. A few cases have involved pathological myopia, moderate myopia, proliferative diabetic retinopathy and CHARGE syndrome. The lesion is often found inferior to the normal optic disc. The patient was advised regular follow ups.
Photographer: Hrishikesh Naik
Imaging device: Optos Daytona
Condition/keywords: Coloboma, Pseudoduplication of optic disc
-
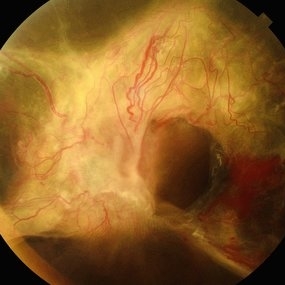 Annular Tractional Retinal Detachment
Annular Tractional Retinal Detachment
Jul 5 2025 by César Adrián Gómez Valdivia, MD
Fundus photograph of an 66 YO female patient diagnosed with advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: @eyemissu2
Imaging device: TOPCON TRC-50DX
Condition/keywords: tractional retinal detachment
-
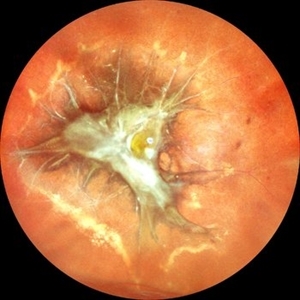 Traction in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Traction in Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Jun 9 2025 by Malvika Singh
Fundus photograph of a 44 year old with uncontrolled diabetes showing fibrovascular proliferation and traction with details of disc and macula obscured with sclerosed vessels in the periphery.
Photographer: Dr Malvika Singh, Retina Foundation, Ahmedabad, India
Imaging device: Mirante SLO/OCT
Condition/keywords: proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), TRACTION
-
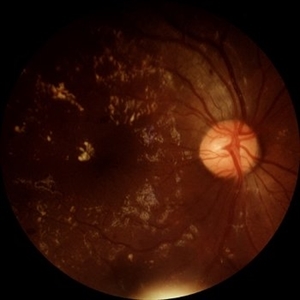 Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic Retinopathy
Jun 4 2025 by Paulina Araujo
The 55-degree central fundus photograph of the right eye demonstrates numerous hard exudates, dot intraretinal hemorrhages, and microaneurysms.
Photographer: Paulina D.Araujo Martínez, Asociación para Evitar la Ceguera en México I.A.P., Hospital Dr Luis Sánchez Bulnes.
Condition/keywords: diabetic retinopathy
-
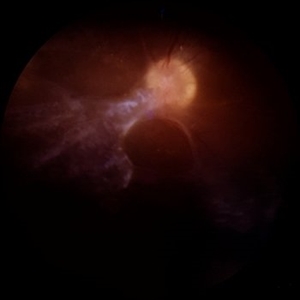 Tractional Retinal Detachment
Tractional Retinal Detachment
Jun 4 2025 by Paulina Araujo
The 55-degree central fundus photograph of the right eye reveals a thickened and opacified hyaloid exerting traction on the optic disc and posterior pole of the retina, along with hard exudates and microaneurysms consistent with advanced proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: Paulina D.Araujo Martínez, Asociación para Evitar la Ceguera en México I.A.P., Hospital Dr Luis Sánchez Bulnes.
Condition/keywords: tractional retinal detachment
-
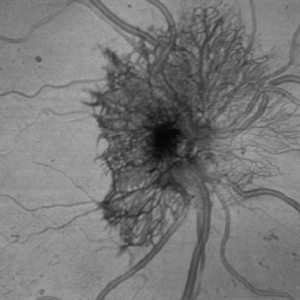 Neovascularization of the Disc
Neovascularization of the Disc
Jun 3 2025 by Scott D Walter, MD, MSc, FASRS
Near-infrared (NIR) en face OCT image showing neovascularization of the disc (NVD) in a patient with type II diabetes mellitus, complicated by proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR).
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: Diabetes, Heidelburg Spectralis, microaneurysms, Neovascularisation at the Disc (NVD), NEOVASCULARISATION OF DISC, OCT EN FACE, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
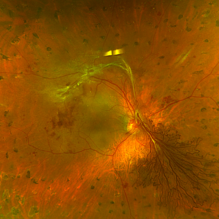 The Dread of the Crimson Red
The Dread of the Crimson Red
Jun 2 2025 by Thirumalesh Mochi Basavaraj, MD
Fundus photograph of a 64 year man post laser depicting a regressed NVD in the superior aspect and a Persistent Neo vascularization in the inferior aspect
Photographer: Vivek
Condition/keywords: Neovascularisation at the Disc (NVD), proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
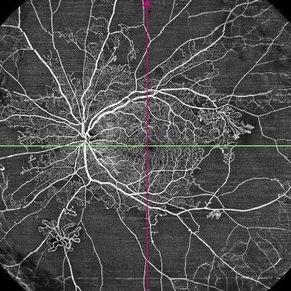 Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
May 29 2025 by KANWALJEET HARJOT MADAN, M.S. (Ophthalmology); FAICO (Vitreous - Retina)
This is widefield optic coherence tomography angiography (WF-OCTA) picture of LE of a diabetic patient. This patient had Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and depicts large areas of capillary non perfusion with neovascularization elsewhere.
Photographer: Dr. Kanwaljeet Harjot Madan, Thind Eye Hospital, Jalandhar City (Punjab) INDIA.
Imaging device: Widefield Optic Coherence Tomography Angiography (WF-OCTA).
Condition/keywords: OCTA, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), ultra-wide field imaging
-
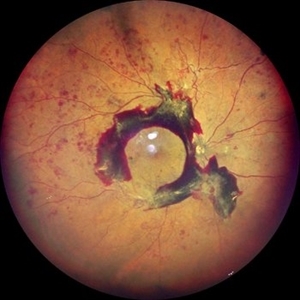 High Risk Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with Sub-hyaloid Hemorrhage
High Risk Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy with Sub-hyaloid Hemorrhage
May 13 2025 by Anupama Kiran Kumar
This image shows a case of high risk proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The retina is unlasered with a taut posterior hyaloid and a sub-hyaloid hemorrhage at the macula and along the arcades ,sparing the fovea.
Photographer: Mr Pratap
Imaging device: Mirante SLO/OCT (Nidek Co., Gamagori, Japan)
Condition/keywords: Diabetes, Diabetic Retinopathy, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR), subhyaloid hemorrhage
-
Posterior Hyphema
Apr 29 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This kinetic B-mode ultrasound scan (inferior transverse view) reveals combined vitreous and subhyaloid hemorrhage, accompanied by a mobile posterior hyphema level. The dynamic evaluation shows dependent blood shifting with positional changes, confirming fresh hemorrhage without organization.
Condition/keywords: diabetic retinopathy
-
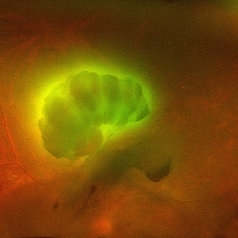 Aurora Borealis in Retina
Aurora Borealis in Retina
Apr 25 2025 by Poornachandra B, MS, FVRS
Fundus picture of 54 year old male with proliferative diabetic retinopathy with fluorescent blood clot in vitreous cavity.
Photographer: Mr Dhikshith
Imaging device: Optos daytona
Condition/keywords: blood, proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR)
-
Vitreous Waltz vs Retinal Rigidity
Apr 18 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
B-mode dynamic ultrasound of an eye with vitreous hemorrhage shows hyaloid traction inducing retinal detachment in diabetic retinopathy. The video clearly delineates all anatomical compartments: vitreous, subhyaloid, and subretinal spaces. Characteristic movement patterns are observed - the vitreous demonstrates smooth, wide excursions while the detached retina shows shorter, stiffer motions -confirming tractional pathology.
Condition/keywords: diabetic retinopathy, retinal detachment
-
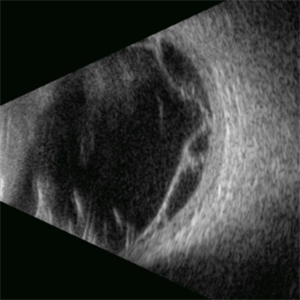 Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy
Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy
Apr 17 2025 by Gustavo Uriel Fonseca Aguirre
This B-mode transverse ultrasound scan depicts a post-vitrectomy eye with recurrent retinal detachment in a patient with diabetic retinopathy history. The image reveals fresh vitreous cavity hemorrhage and subretinal bleeding, along with subretinal proliferative bands (PVR strands). These findings indicate complicated tractional re-detachment with active hemorrhagic components.
Photographer: Gustavo U. Fonseca Aguirre, Hospital Conde de Valenciana, Ciudad de México
Condition/keywords: proliferative vitreoretinopathy (PVR)
-
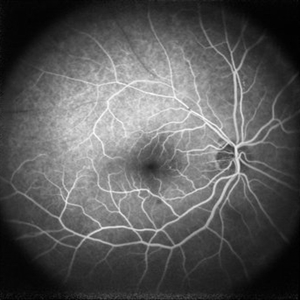 Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion
Apr 10 2025 by Rinat Sutiushev
Fluorescein angiography of a 77-year-old woman with ischemic occlusion of the superior temporal branch of the central retinal vein with non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
Photographer: Rinat Sutiushev, Ophthalmological center “Vision”, Saint Petersburg
Imaging device: Heidelberg Spectralis
Condition/keywords: branch retinal vein occlusion (BRVO), nonproliferative diabetic retinopathy

 Loading…
Loading…