-
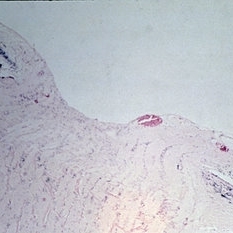 Slide 11-1
Slide 11-1
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
The normal optic disk and optic nerve. Horizontal section of optic disk (X 16}. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 6583.)
Condition/keywords: optic disc, optic nerve
-
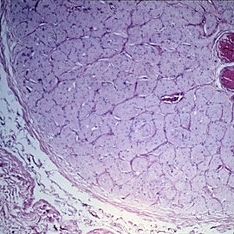 Slide 11-2
Slide 11-2
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
The normal optic disk and optic nerve. Cross-section ( x 16). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 6608.)
Condition/keywords: optic disc, optic nerve
-
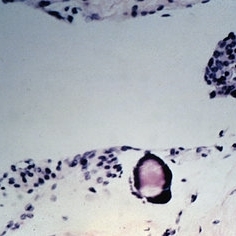 Slide 11-3
Slide 11-3
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Corpora aranacea. A laminated body found among hyperplastic arachnoidal cells in a normal optic nerve sheath (xllO). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3661).
Condition/keywords: corpora aranacea, optic nerve
-
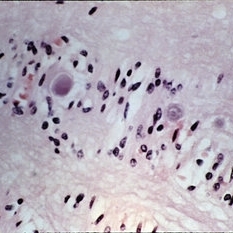 Slide 11-4
Slide 11-4
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Corpora amylacea (xllO). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3878.)
Condition/keywords: corpora amylacea
-
 Slide 11-5
Slide 11-5
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
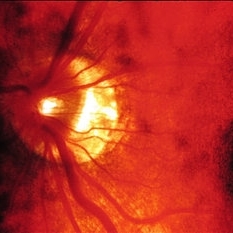
The optic disk in myopia. Clinical appearance. Note exposure of the sclera and choroid in the temporal crescent.
Condition/keywords: myopia, optic disc
-
 Slide 11-6
Slide 11-6
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
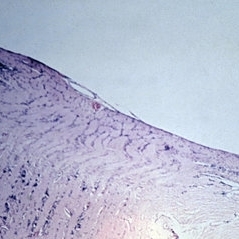
The optic disk in myopia. Horizontal section of optic disk ( x 16). The temporal crescent is to the right (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5109.)
Condition/keywords: myopia, optic disc
-
 Slide 11-7
Slide 11-7
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
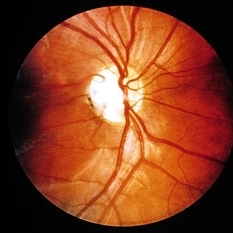
Optic nerve pit. This defect may lead to macular edema. (Courtesy of H. G. Scheie, M.D.}
Condition/keywords: optic nerve pit
-
 Slide 11-8
Slide 11-8
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
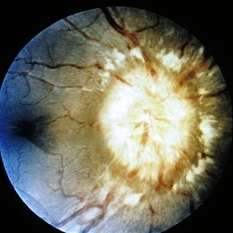
Papilledema. Clinical characteristics include blurred margins, elevation, concentric folds of retina, and congested vessels. Hemorrhages and cotton wool exudates are commonly seen.
Condition/keywords: papilledema
-
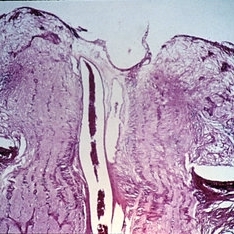 Slide 11-9
Slide 11-9
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Papilledema. Section through the center of the disk shows swelling of the nerve fibers and lateral displacement of the sensory retina ( x16). (Thomas Jefferson University, No. 71-0897.)
Condition/keywords: papilledema
-
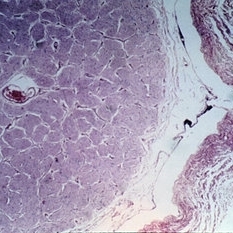 Slide 11-10
Slide 11-10
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Papilledema. Enlargement of the nerve sheath (X 16).
Condition/keywords: papilledema
-
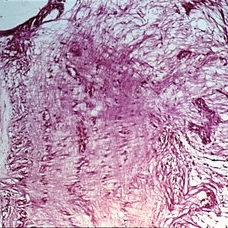 Slide 11-11
Slide 11-11
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Papilledema. Forward bowing of fine glial fibers in front of the lamina (xllO). (Thomas Jefferson University, No. 71-0897.)
Condition/keywords: papilledema
-
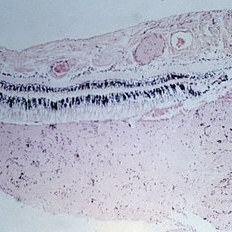 Slide 11-12
Slide 11-12
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Myelin artifact ( x16). Myelin has been squeezed from nerve into retinal vessels and subretinal space, and may be confused with papilledema. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5031.)
Condition/keywords: myelin
-
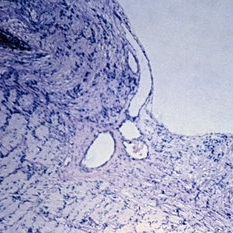 Slide 11-13
Slide 11-13
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Papilledema in a patient with severe hypertension. Edema is less severe than in other forms of choked disk. Low-power view of disk ( x 16).
Condition/keywords: papilledema
-
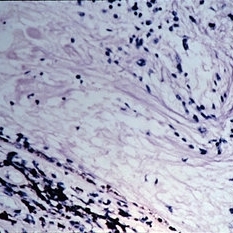 Slide 11-14
Slide 11-14
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
High-power view of same disk to show cytoid bodies (small nerve fiber swellings) adjacent to disk ( x110). (Courtesy of Henry Ring, M.D., Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, No. E399-66.)
Condition/keywords: cystoid
-
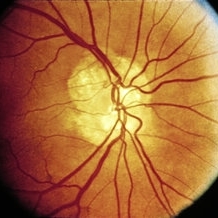 Slide 11-15
Slide 11-15
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Drusen of optic nerve. Clinical appearance. Drusen may be confused with papilledema. (Courtesy of H. G. Scheie, M.D.)
Condition/keywords: drusen, optic nerve
-
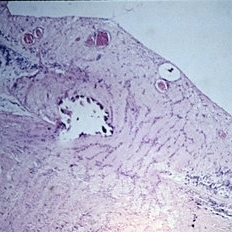 Slide 11-16
Slide 11-16
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Drusen of optic nerve. Hyaline bodies are usually in front of the lamina cribrosa ( x 16). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5092.)
Condition/keywords: drusen, optic nerve
-
 Slide 11-17
Slide 11-17
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
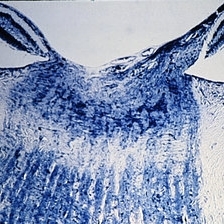
Optic neuritis in demyelinizing diseases. Horizontal section of optic nerve showing loss of myelin behind the lamina in a case of Schilder's disease (Kluver Barerra stain x16). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3031.)
Condition/keywords: optic neuritis, Schilder's disease
-
 Slide 11-18
Slide 11-18
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
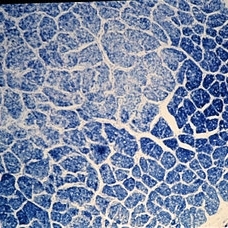
Cross-section of nerve further posteriorly to show atrophy in the central portion of the nerve (Kluver-Barerra stain x 16}. Similar atrophy might be seen in multiple sclerosis. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3031.)
Condition/keywords: nerve
-
 Slide 11-19
Slide 11-19
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
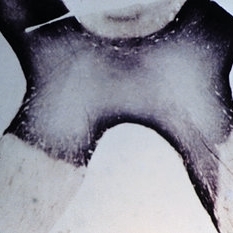
Optic chiasm in neuromyelitis optica (Devic's disease). Note the complete transverse atrophy. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 47-2.)
Condition/keywords: Devic's disease, neuromyelitis optica, optic chiasm
-
 Slide 11-20
Slide 11-20
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
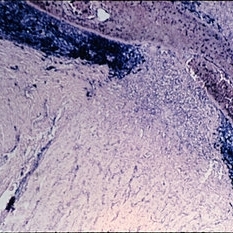
Optic neuritis secondary to endophthalmitis ( x 16). Note the heavy infiltrate of inflammatory cells in the choroid and retina, extending into the optic nerve. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5710.)
Condition/keywords: optic neuritis
-
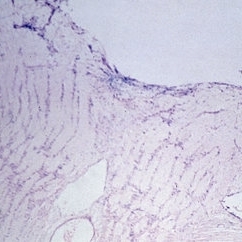 Slide 11-21
Slide 11-21
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Optic neuritis in a patient with measles endophthalmitis ( x 16). Note the swelling of the optic disk identical to that in papilledema, but inflammatory cells are the key to the diagnosis. (Thomas Jefferson University, No. 68-3043.)
Condition/keywords: endophthalmitis, optic neuritis
-
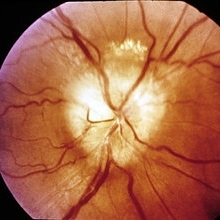 Slide 11-22
Slide 11-22
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Ischemic optic neuropathy. Sudden onset of segmental edema of the upper pole of the disk and adjacent retina accompanied by an inferior altitudinal field defect.
Condition/keywords: ischemic optic neuropathy
-
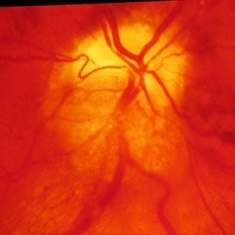 Slide 11-23
Slide 11-23
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Ischemic optic neuropathy. In the same eye, 3 years later, the patient developed edema of the lower pole of the disk, together with a superior altitudinal field defect.
Condition/keywords: ischemic optic neuropathy
-
 Slide 11-24
Slide 11-24
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Atherosclerosis of a posterior ciliary artery in a patient with clinical signs of ischemic optic neuropathy (Verhoeff-Van Gieson stain xllO). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5368.)
Condition/keywords: atherosclerosis, ciliary
-
 Slide 11-25
Slide 11-25
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Segment of temporal artery in a patient with temporal arteritis. Inflammatory infiltrate and thickening of all layers (x 101).
Condition/keywords: temporal arteritis
-
 Slide 11-26
Slide 11-26
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Verhoeff-Van Gieson stain of same segment to show rupture of elastic intima ( x40). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3571.)
Condition/keywords: elastic intima, rupture, temporal arteritis
-
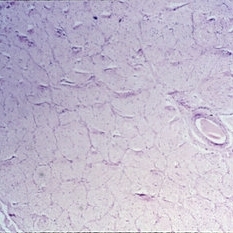 Slide 11-27
Slide 11-27
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Optic atrophy. A normal optic nerve ( x 16). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 2333.)
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy, optic nerve
-
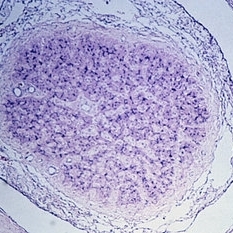 Slide 11-28
Slide 11-28
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Optic atrophy taken at the same magnification to show marked shrink age. Note that the optic sheath appears to be enlarged. The nerve is almost completely replaced by connective tissue. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3917.)
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy
-
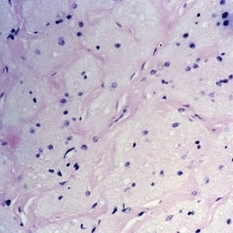 Slide 11-29
Slide 11-29
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Optic atrophy. Early atrophy is accompanied by thickening of the pial septa ( x 110). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 5838.)
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy
-
 Slide 11-30
Slide 11-30
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Primary or descending optic atrophy. Horizontal section of the optic disk ( x 16). Note the increase in thickness of the pial septa in the nerve, the loss of ganglion cell and nerve fiber layers in the adjacent retina, and the loss of the optic cup.
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy, pial septa
-
 Slide 11-31
Slide 11-31
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Primary or descending optic atrophy. Higher-power longitudinal section of the optic disk showing loss of nerve fibers (Bodian stain x40). (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 3580.)
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy
-
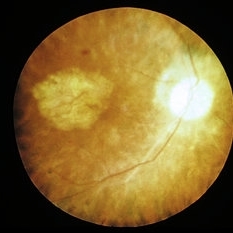 Slide 11-32
Slide 11-32
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Ascending optic atrophy. Clinical appearance of optic atrophy associated with retinitis pigmentosa. The arterioles are nearly obliterated due to profound retinal atrophy.
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy, retinitis pigmentosa
-
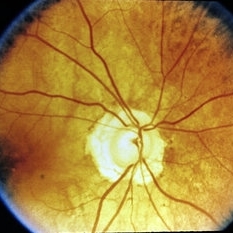 Slide 11-33
Slide 11-33
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Glaucoma cupping. Clinical picture shows a peripapillary halo, a nasal shift of vessels, and a complete cup extending to the margin of the disk.
Condition/keywords: glaucoma, peripapillary halo
-
 Slide 11-34
Slide 11-34
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Glaucoma cup ( x16). Histopathology shows a posterior bowing of the lamina cribrosa, an excavation of disk margins, a loss of nerve fiber layers, and optic atrophy. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 6596.)
Condition/keywords: glaucoma, lamina cribrosa
-
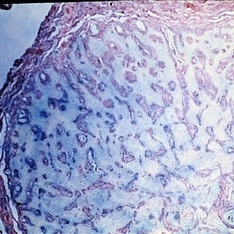 Slide 11-35
Slide 11-35
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Schnabel's cavernous optic atrophy. Large spaces within the nerve are filled with acid mucopolysaccharide (Aician blue stain x40).
Condition/keywords: acid mucopolysaccharide, optic atrophy
-
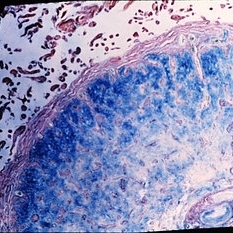 Slide 11-36
Slide 11-36
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Schnabel's cavernous optic atrophy. After treatment with hyaluronidase, the mucopolysaccharide stain is negative.
Condition/keywords: optic atrophy
-
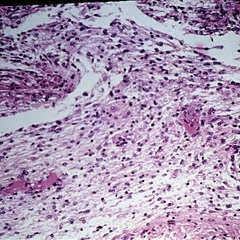 Slide 11-37
Slide 11-37
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Glioma of the optic nerve in a child with neurofibromatosis (x16). (scheie Eye Institute, No. 78-110.)
Condition/keywords: glioma, optic nerve
-
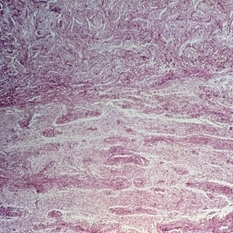 Slide 11-38
Slide 11-38
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Glioma of the optic nerve showing a meningeal reaction ( x 16). This is a frequent source of confusion with meningioma. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 78-110.)
Condition/keywords: glioma, optic nerve
-
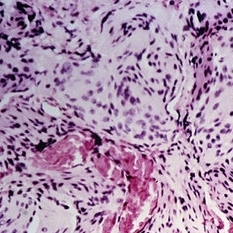 Slide 11-39
Slide 11-39
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Meningioma of the optic nerve sheath ( x40). The tumor is slow-growing but may extend posteriorly to involve the intracranial meningeal layers. It is more aggressive in children than in adults. (Scheie Eye Institute, No. 77-745.)
Condition/keywords: meningioma, optic nerve
-
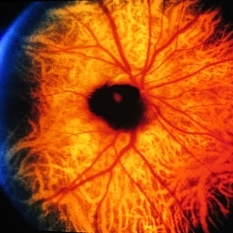 Slide 11-40
Slide 11-40
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Clinical appearance of a melanocytoma of the optic disk. This tumor is more common in blacks and in persons with congenital melanosis. It should not be confused with malignant melanoma.
Condition/keywords: melanocytoma, optic disc
-
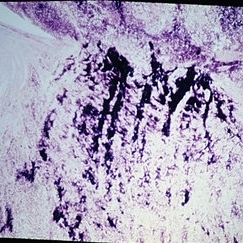 Slide 11-41
Slide 11-41
Feb 26 2019 by Lancaster Course in Ophthalmology
Retinoblastoma invading the optic nerve. The extension indicates a poor prognosis.
Condition/keywords: optic nerve, retinoblastoma

A project from the American Society of Retina Specialists